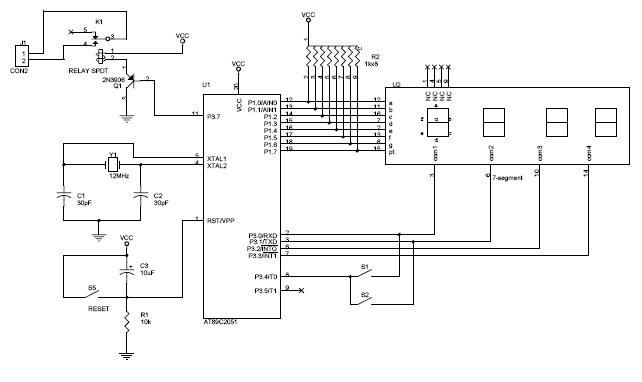
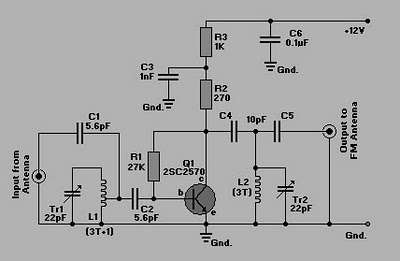
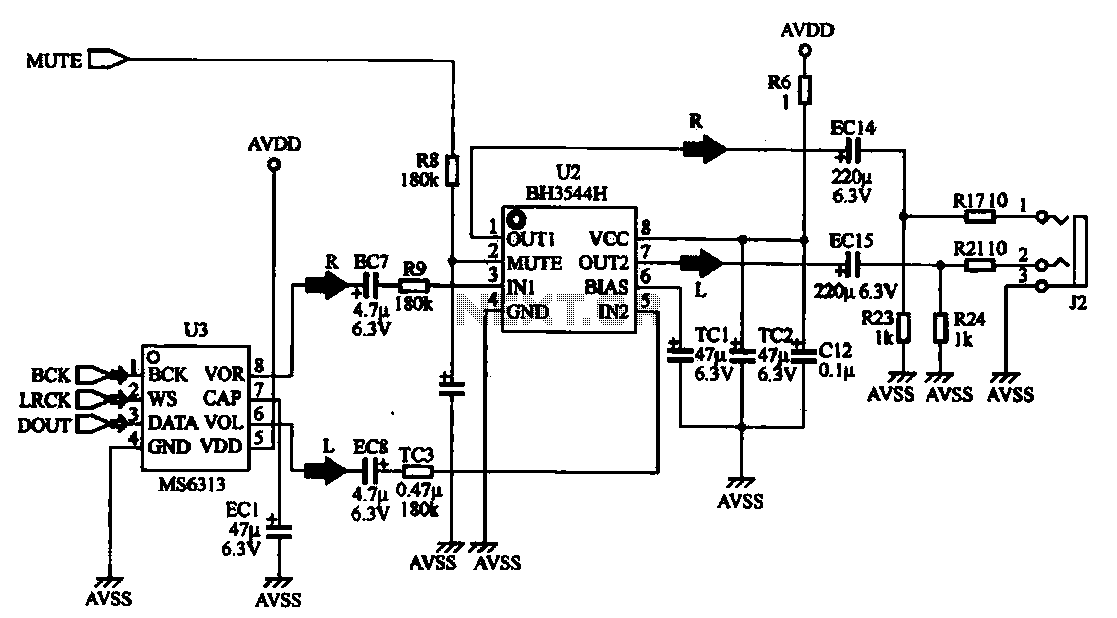
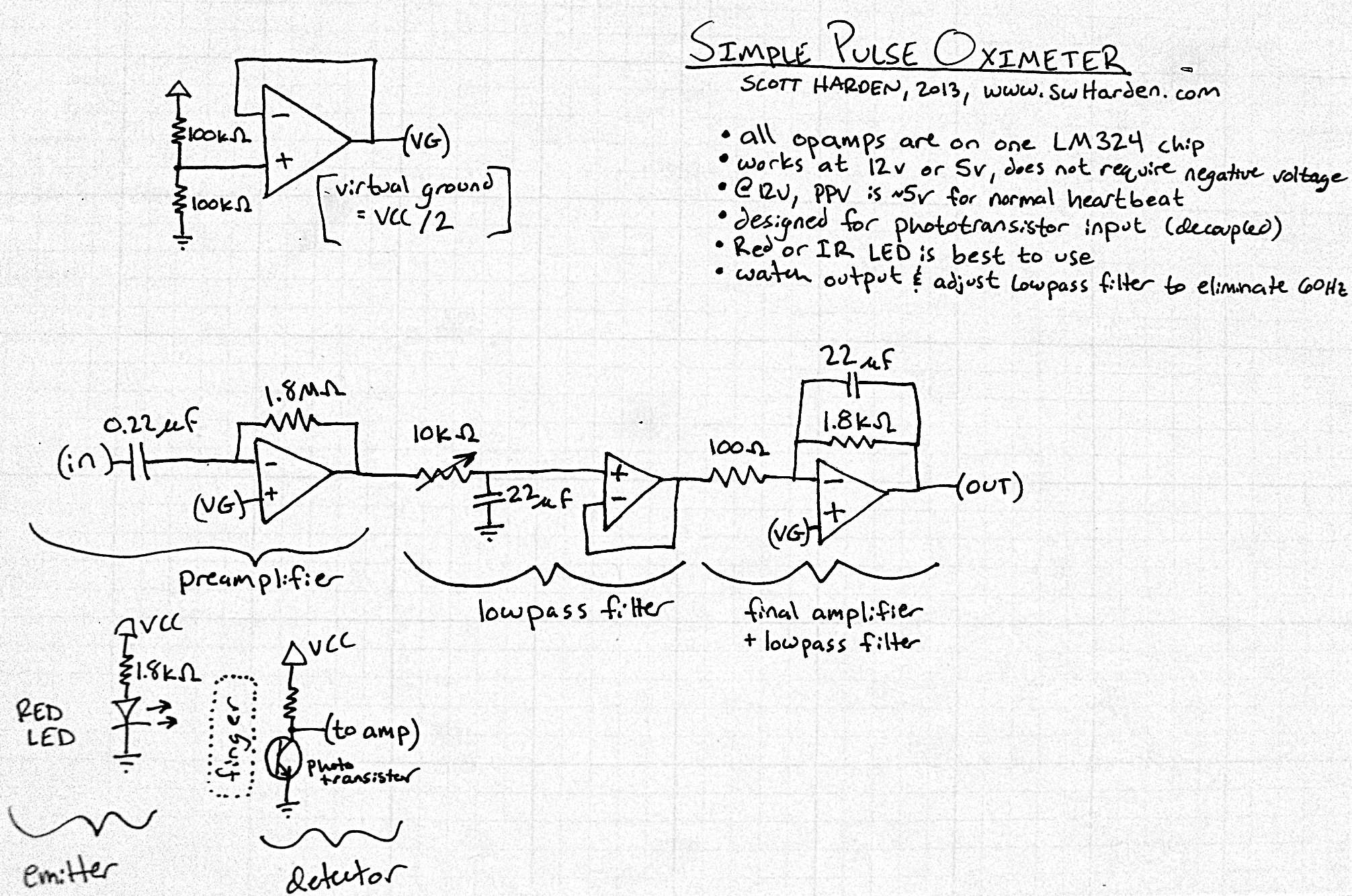
Usb Power Socket With Indicator circuit
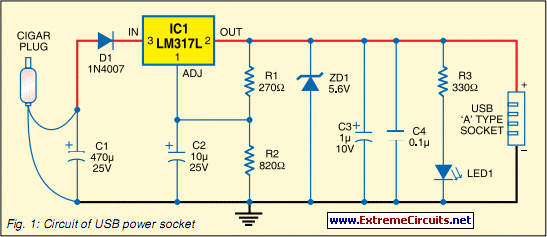
Today, nearly all computers are equipped with logic blocks designed to implement a USB port. In practice, a USB port can deliver over 100 mA of continuous current at 5V to the peripherals connected to the bus. This capability allows a USB port to power small electronic gadgets that operate on 5V DC without any issues. Many modern handheld devices, such as portable reading lamps, utilize the USB port's functionality to recharge their built-in battery packs through internal circuitry.
The USB port serves as a critical interface in modern electronic systems, enabling both data transfer and power supply to various peripherals. The standard USB specifications dictate that the port can provide a nominal voltage of 5V, which is essential for powering devices such as sensors, microcontrollers, and other low-power electronics. The ability to deliver more than 100 mA ensures compatibility with a wide range of devices, allowing for efficient operation without the need for additional power sources.
In terms of circuit design, the USB port typically incorporates a series of logic blocks that manage the communication protocols and power delivery. These logic blocks may include a USB controller, which handles data transfer and device recognition, as well as power management circuits that regulate the output voltage and current. The internal circuitry of devices like portable reading lamps is designed to convert the USB power input into a suitable form for charging their battery packs, often employing voltage regulators and charging ICs to ensure safe and effective charging.
Furthermore, the versatility of USB ports extends beyond simple power delivery; they are also capable of supporting various data communication standards, allowing for the integration of diverse peripherals. This dual functionality makes USB ports a favored choice in the design of consumer electronics, where space and power efficiency are paramount. As technology continues to advance, the role of USB ports in powering and connecting devices is expected to grow, further enhancing the capabilities of modern electronics.Today, almost all computers contain logic blocks for implementing a USB port. A USB port, in practice, is capable of delivering more than 100 mA of continuous current at 5V to the peripherals that are connected to the bus. So a USB port can be used, without any trouble, for powering 5V DC operated tiny electronic gadgets. Nowadays, many handheld devices (for instance, portable reading lamps) utilise this facility of the USB port to recharge their built-in battery pack with the help of an internal circuitry..
🔗 External reference
The USB port serves as a critical interface in modern electronic systems, enabling both data transfer and power supply to various peripherals. The standard USB specifications dictate that the port can provide a nominal voltage of 5V, which is essential for powering devices such as sensors, microcontrollers, and other low-power electronics. The ability to deliver more than 100 mA ensures compatibility with a wide range of devices, allowing for efficient operation without the need for additional power sources.
In terms of circuit design, the USB port typically incorporates a series of logic blocks that manage the communication protocols and power delivery. These logic blocks may include a USB controller, which handles data transfer and device recognition, as well as power management circuits that regulate the output voltage and current. The internal circuitry of devices like portable reading lamps is designed to convert the USB power input into a suitable form for charging their battery packs, often employing voltage regulators and charging ICs to ensure safe and effective charging.
Furthermore, the versatility of USB ports extends beyond simple power delivery; they are also capable of supporting various data communication standards, allowing for the integration of diverse peripherals. This dual functionality makes USB ports a favored choice in the design of consumer electronics, where space and power efficiency are paramount. As technology continues to advance, the role of USB ports in powering and connecting devices is expected to grow, further enhancing the capabilities of modern electronics.Today, almost all computers contain logic blocks for implementing a USB port. A USB port, in practice, is capable of delivering more than 100 mA of continuous current at 5V to the peripherals that are connected to the bus. So a USB port can be used, without any trouble, for powering 5V DC operated tiny electronic gadgets. Nowadays, many handheld devices (for instance, portable reading lamps) utilise this facility of the USB port to recharge their built-in battery pack with the help of an internal circuitry..
🔗 External reference