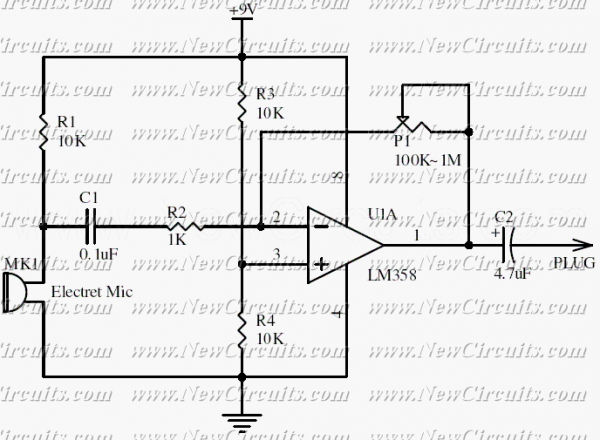
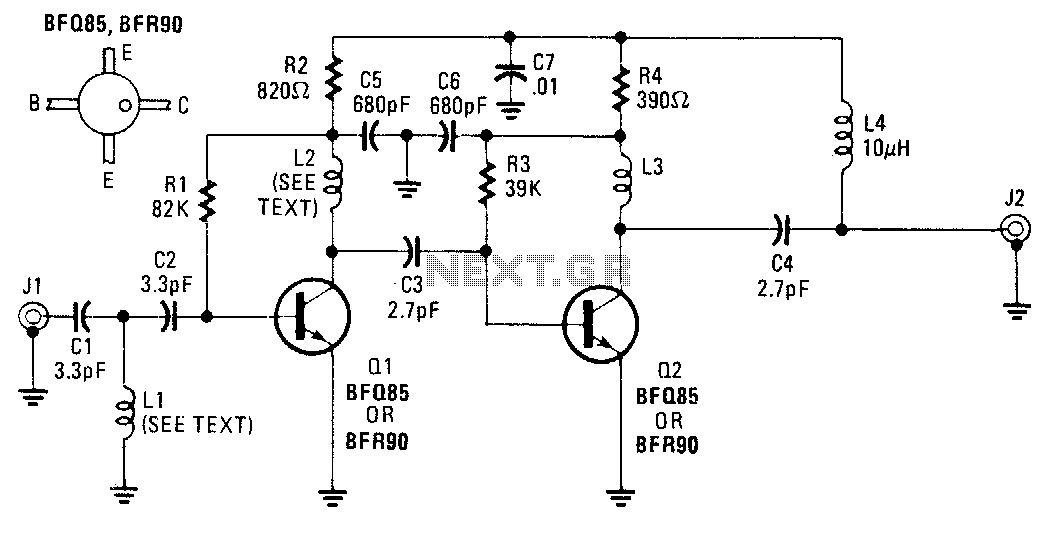
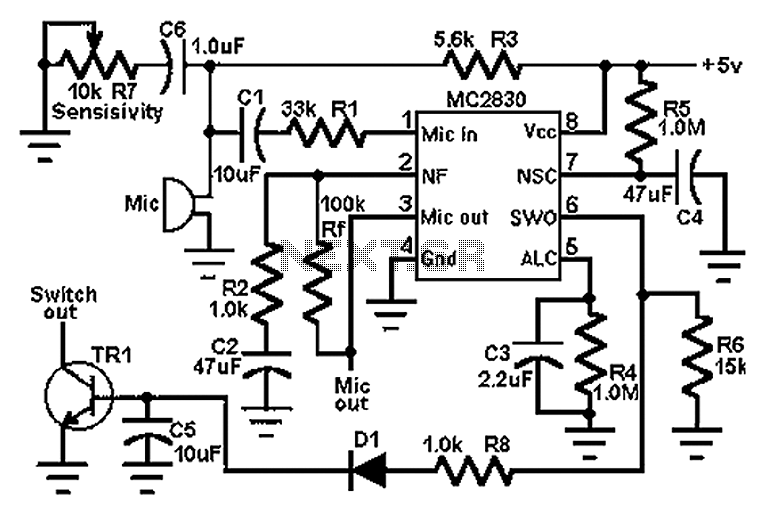
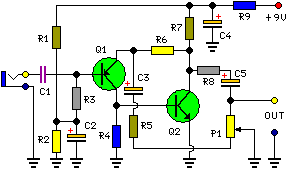
Vanda F-9500A preamplifier b
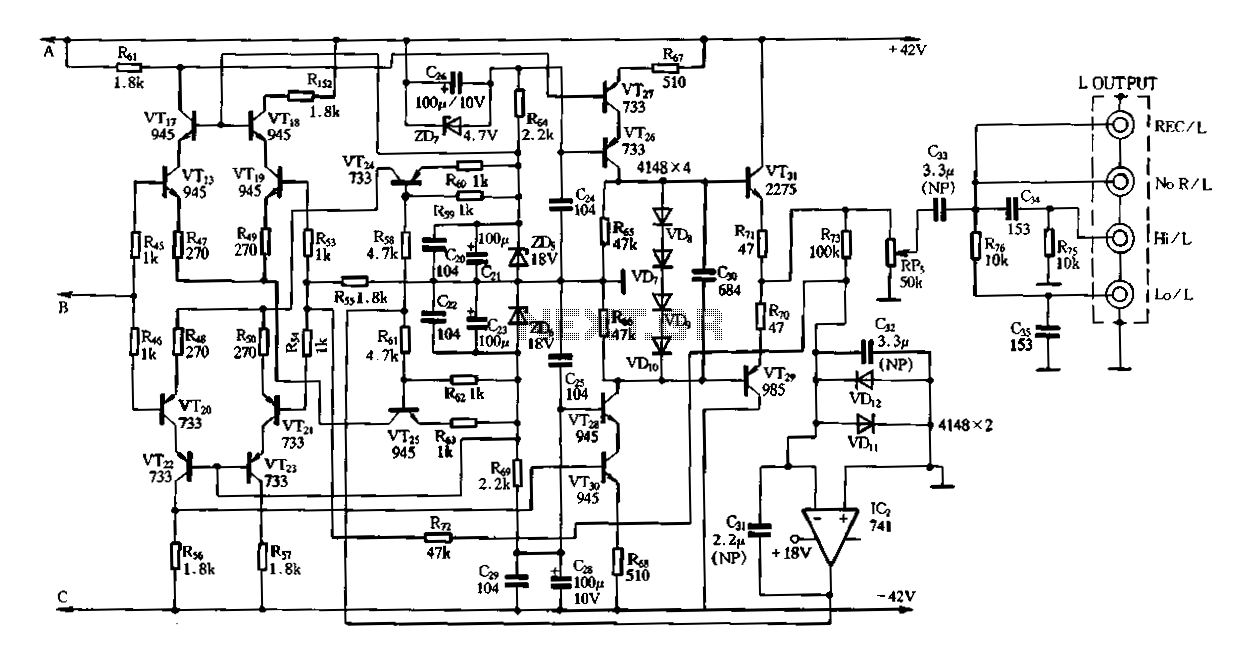
Figure 3-2 (b) represents the second half of the circuit, where transistors VT17 to VT31 are configured as power amplifiers and pre-amplifiers. This section is structurally identical to the operational integrated circuit IC2 and includes zero servos. The circuit is designed with a series insertion between the amplifier and the attenuated tone control circuit, along with a two-bit access control switch. This switch allows for the control of the tone circuit, which can either be engaged or disengaged. The configuration includes an additional stage amplifier that connects to the final amplifier's volume potentiometer through the tone circuit. It features a resistor-capacitor (RC) network that provides recording interfaces, which connect to a common amplifier circuit, offering high-pass and low-pass filtering with four output options.
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-2 (b) integrates a complex arrangement of power and pre-amplifiers utilizing transistors VT17 through VT31. Each transistor serves a specific role in amplifying the audio signal, ensuring that the output maintains fidelity and clarity. The design mirrors that of operational integrated circuit IC2, emphasizing a consistent approach to signal processing within the system.
The series insertion of the tone control circuit allows for precise adjustments to the audio output. The two-bit access control switch provides flexibility, enabling the user to toggle the tone control functionality on or off. This feature is crucial for applications where audio characteristics need to be tailored to specific requirements or environments.
The additional stage amplifier is linked to the final amplifier's volume potentiometer, ensuring that the audio levels can be finely tuned. The integration of an RC network facilitates the recording interface, which is essential for connecting to external devices or additional processing units. The common amplifier circuit supports both high-pass and low-pass filters, allowing for a versatile range of output configurations. The four output options provide adaptability for various audio systems, making this circuit highly functional in both professional and consumer audio applications.
Overall, the design exemplifies a sophisticated approach to audio amplification and control, ensuring high-quality sound reproduction through careful engineering of each component within the circuit.Figure 3-2 (b) is the second half of the circuit, VT17 ~ VT31 group into power amplifiers, pre-amplifiers, and it is a structure composed of exactly the same oIC2 its zero serv o circuit. Before and after class is inserted in series between the amplifier and attenuated tone control circuit, and a two-bit access control switch, it can control the tone Zouren circuit or not formed around through-o-stage amplifier in the final amplifier volume potentiometer via tone circuit Rong) 5 and RC network consisting of a recording o interfaces, common (connected amplifier circuit), high-pass, low-pass four outputs
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-2 (b) integrates a complex arrangement of power and pre-amplifiers utilizing transistors VT17 through VT31. Each transistor serves a specific role in amplifying the audio signal, ensuring that the output maintains fidelity and clarity. The design mirrors that of operational integrated circuit IC2, emphasizing a consistent approach to signal processing within the system.
The series insertion of the tone control circuit allows for precise adjustments to the audio output. The two-bit access control switch provides flexibility, enabling the user to toggle the tone control functionality on or off. This feature is crucial for applications where audio characteristics need to be tailored to specific requirements or environments.
The additional stage amplifier is linked to the final amplifier's volume potentiometer, ensuring that the audio levels can be finely tuned. The integration of an RC network facilitates the recording interface, which is essential for connecting to external devices or additional processing units. The common amplifier circuit supports both high-pass and low-pass filters, allowing for a versatile range of output configurations. The four output options provide adaptability for various audio systems, making this circuit highly functional in both professional and consumer audio applications.
Overall, the design exemplifies a sophisticated approach to audio amplification and control, ensuring high-quality sound reproduction through careful engineering of each component within the circuit.Figure 3-2 (b) is the second half of the circuit, VT17 ~ VT31 group into power amplifiers, pre-amplifiers, and it is a structure composed of exactly the same oIC2 its zero serv o circuit. Before and after class is inserted in series between the amplifier and attenuated tone control circuit, and a two-bit access control switch, it can control the tone Zouren circuit or not formed around through-o-stage amplifier in the final amplifier volume potentiometer via tone circuit Rong) 5 and RC network consisting of a recording o interfaces, common (connected amplifier circuit), high-pass, low-pass four outputs