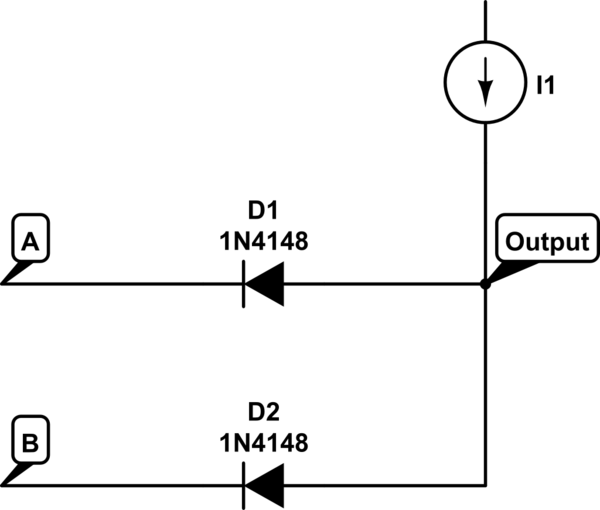
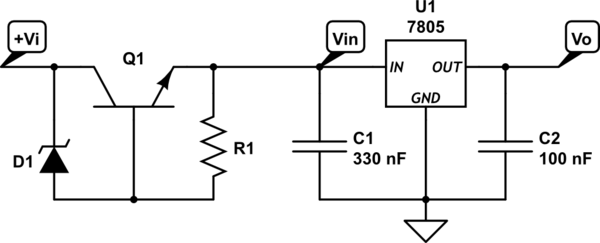
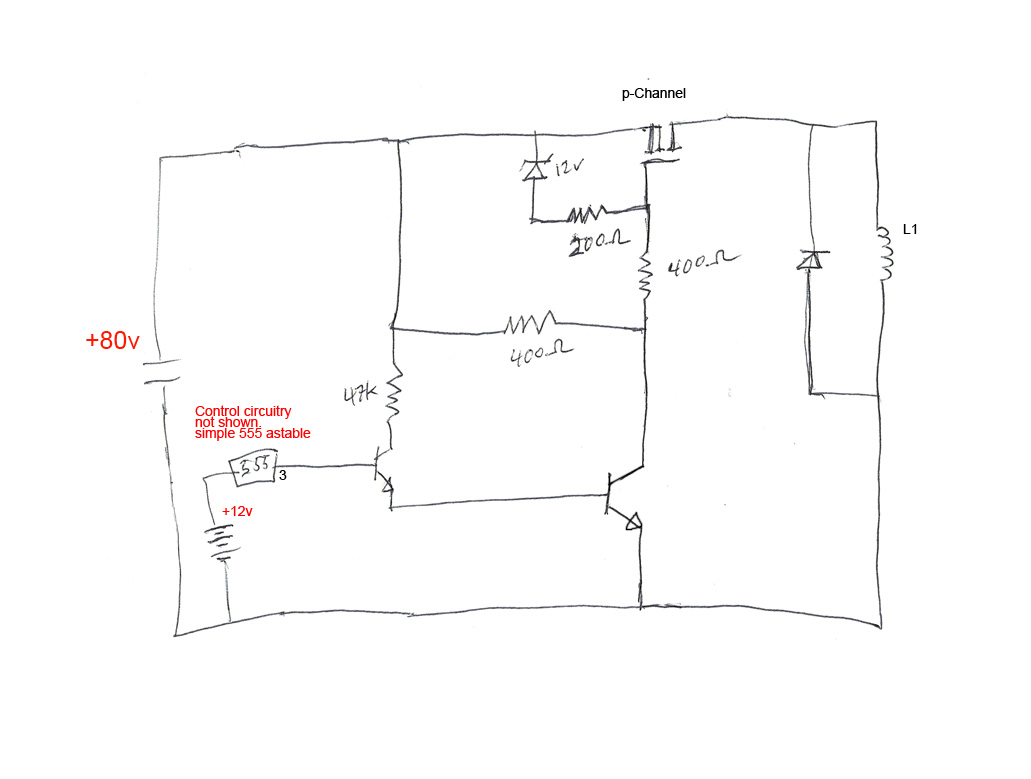
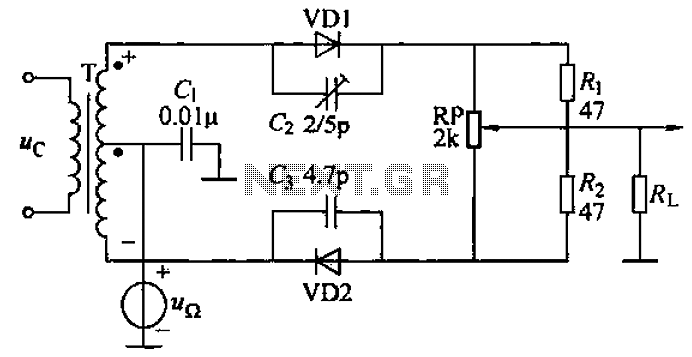
Variable zener diode
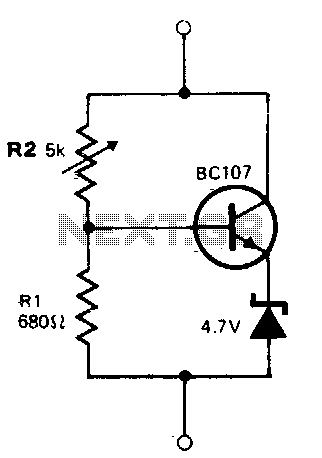
The circuit operates similarly to a zener diode across a wide range of voltages. The current flowing through the voltage divider formed by resistors R1 and R2 is significantly greater than the base current of the transistor, approximately 8 mA. The stabilizing voltage can be adjusted between 5 V and 45 V by modifying the resistance value of R2. The total current consumed by the circuit varies from 15 mA to 50 mA, which is influenced by the maximum power dissipation capability of the zener diode. For a zener diode rated at 250 mW, this maximum current is around 50 mA.
The described circuit functions as a voltage regulator, utilizing a zener diode to maintain a stable output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. The configuration includes a voltage divider made up of resistors R1 and R2, which sets the base voltage for the transistor. The transistor acts as a switch or amplifier, enabling or controlling the flow of current based on the voltage across the zener diode.
The adjustable stabilizing voltage, achieved by altering the resistance of R2, allows for flexibility in applications requiring different voltage levels. The current through the voltage divider is designed to be significantly higher than the base current of the transistor to ensure reliable operation and quick response to changes in load. This design consideration minimizes the risk of the transistor entering saturation, which could lead to voltage fluctuations.
The total current drawn by the circuit is a critical parameter, as it must remain within the safe operating limits of the components involved, particularly the zener diode. The maximum dissipation rating of the zener diode dictates the upper limit of the current, ensuring that the device does not overheat and fail. In this instance, with a 250 mW zener diode, the circuit is designed to operate effectively up to the specified current threshold of 50 mA.
In summary, this circuit provides a robust solution for applications requiring a stable voltage supply across a range of conditions, with adjustable output and careful consideration of component ratings to ensure reliable performance.The circuit behaves like a zener diode over a large range of voltages. The current passing through the voltage divider R1-R2 is substantially larger than the transistor base current and is in the region of 8 mA. The stabilizing voltage is adjustable over the range 5-45 V by changing the value of R2. The total current drawn by the circuit is variable over the range 15 mA to 50 mA This value is determined by the maximum dissipation of the zener diode. In the case of a 250 mW device, this is of the order of 50 mA.
The described circuit functions as a voltage regulator, utilizing a zener diode to maintain a stable output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. The configuration includes a voltage divider made up of resistors R1 and R2, which sets the base voltage for the transistor. The transistor acts as a switch or amplifier, enabling or controlling the flow of current based on the voltage across the zener diode.
The adjustable stabilizing voltage, achieved by altering the resistance of R2, allows for flexibility in applications requiring different voltage levels. The current through the voltage divider is designed to be significantly higher than the base current of the transistor to ensure reliable operation and quick response to changes in load. This design consideration minimizes the risk of the transistor entering saturation, which could lead to voltage fluctuations.
The total current drawn by the circuit is a critical parameter, as it must remain within the safe operating limits of the components involved, particularly the zener diode. The maximum dissipation rating of the zener diode dictates the upper limit of the current, ensuring that the device does not overheat and fail. In this instance, with a 250 mW zener diode, the circuit is designed to operate effectively up to the specified current threshold of 50 mA.
In summary, this circuit provides a robust solution for applications requiring a stable voltage supply across a range of conditions, with adjustable output and careful consideration of component ratings to ensure reliable performance.The circuit behaves like a zener diode over a large range of voltages. The current passing through the voltage divider R1-R2 is substantially larger than the transistor base current and is in the region of 8 mA. The stabilizing voltage is adjustable over the range 5-45 V by changing the value of R2. The total current drawn by the circuit is variable over the range 15 mA to 50 mA This value is determined by the maximum dissipation of the zener diode. In the case of a 250 mW device, this is of the order of 50 mA.