Light-emitting diode rectifier circuit
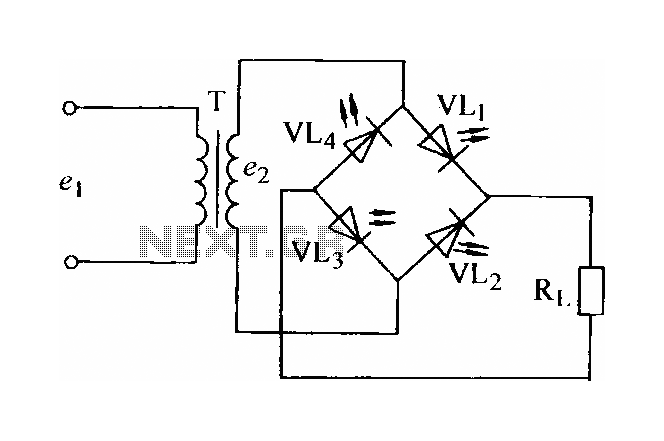
In certain applications, the current from a non-rectified voltage power supply circuit is insufficient. A light-emitting diode (LED) rectifier circuit can be employed to address this issue, serving as a power indicator. It is important to ensure that the forward current of the LED does not exceed its maximum rating.
The proposed circuit utilizes a half-wave rectifier configuration, which is a simple yet effective method for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). In this arrangement, an LED is connected in series with a diode, which allows current to flow in only one direction. The diode conducts during the positive half-cycle of the AC waveform, enabling the LED to illuminate. However, during the negative half-cycle, the diode blocks the current, preventing the LED from lighting up.
To design this circuit, a transformer may be included to step down the AC voltage to a suitable level for the LED. The diode should be selected based on its peak inverse voltage (PIV) rating, which must exceed the maximum voltage of the AC supply to prevent breakdown. The LED's forward voltage drop and forward current specifications must also be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
A resistor may be added in series with the LED to limit the forward current, thus protecting the LED from overcurrent conditions. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm's Law, taking into account the supply voltage, the forward voltage of the LED, and the desired forward current.
This half-wave rectifier circuit can be effectively used in low-power applications where a simple and compact solution is required for indicating power status through an LED. Careful selection of components and adherence to specifications will ensure reliable operation and visual indication of power availability.In some of the requirements and the current is not rectified voltage power supply circuit is not high, can be used to form a light emitting diode rectifier circuit, and power indicator cater to. Be careful not to exceed the maximum light-emitting diode forward current. Half-wave rectifier:
The proposed circuit utilizes a half-wave rectifier configuration, which is a simple yet effective method for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). In this arrangement, an LED is connected in series with a diode, which allows current to flow in only one direction. The diode conducts during the positive half-cycle of the AC waveform, enabling the LED to illuminate. However, during the negative half-cycle, the diode blocks the current, preventing the LED from lighting up.
To design this circuit, a transformer may be included to step down the AC voltage to a suitable level for the LED. The diode should be selected based on its peak inverse voltage (PIV) rating, which must exceed the maximum voltage of the AC supply to prevent breakdown. The LED's forward voltage drop and forward current specifications must also be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
A resistor may be added in series with the LED to limit the forward current, thus protecting the LED from overcurrent conditions. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm's Law, taking into account the supply voltage, the forward voltage of the LED, and the desired forward current.
This half-wave rectifier circuit can be effectively used in low-power applications where a simple and compact solution is required for indicating power status through an LED. Careful selection of components and adherence to specifications will ensure reliable operation and visual indication of power availability.In some of the requirements and the current is not rectified voltage power supply circuit is not high, can be used to form a light emitting diode rectifier circuit, and power indicator cater to. Be careful not to exceed the maximum light-emitting diode forward current. Half-wave rectifier: