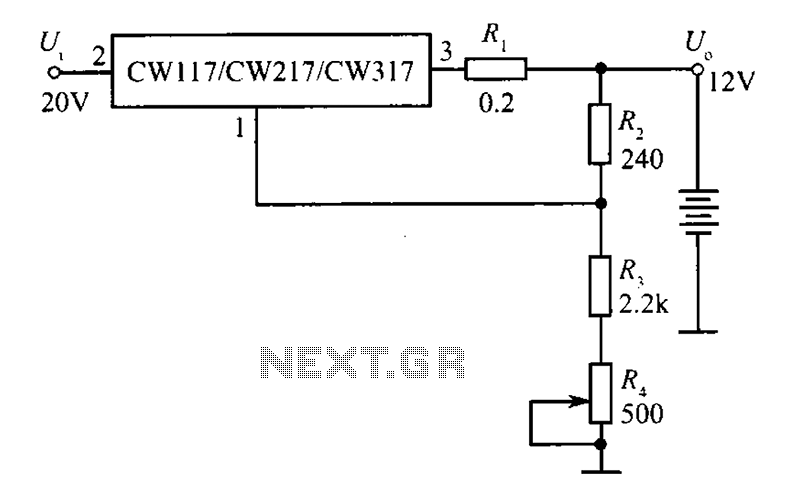
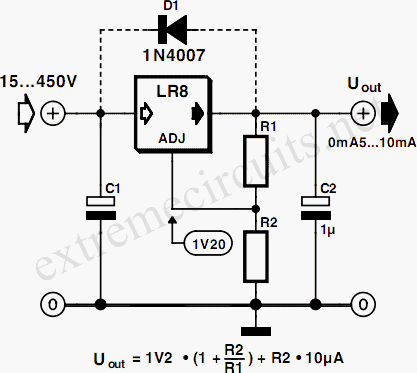
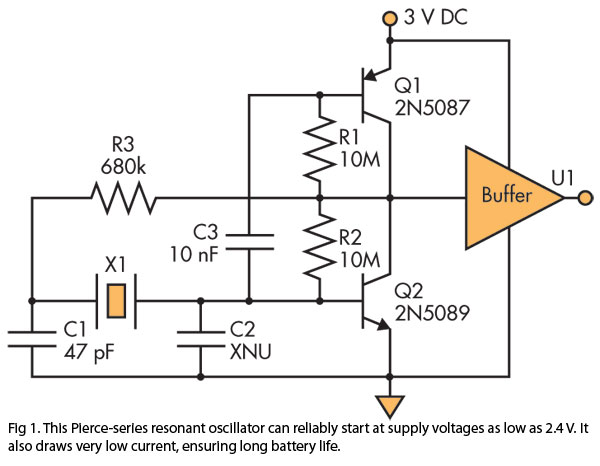
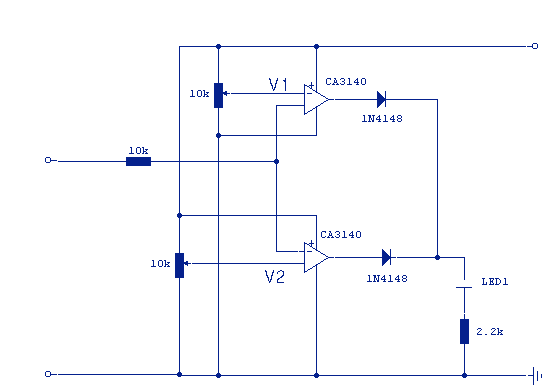
Voltage multiplier
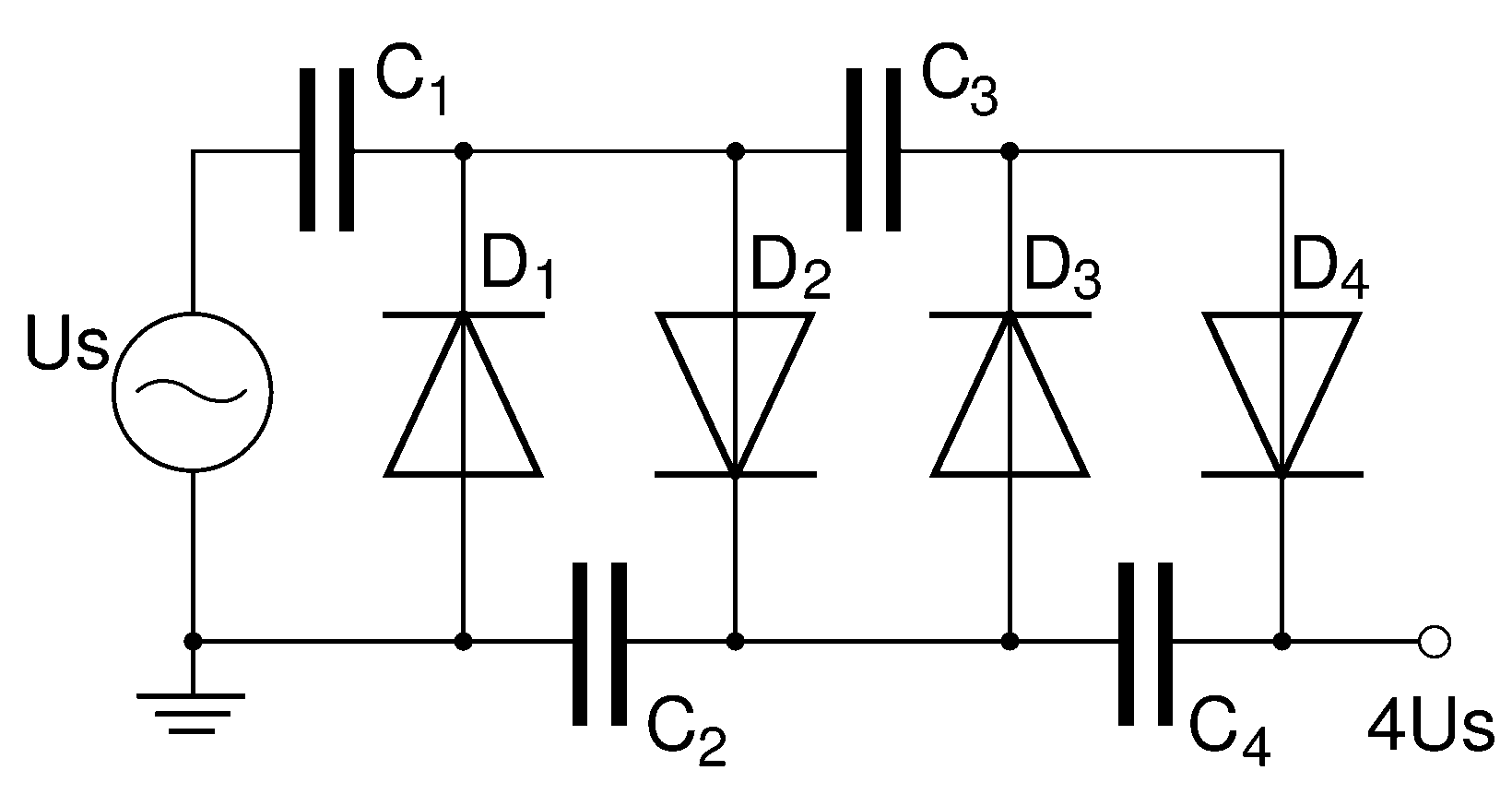
Villard cascade voltage multiplier. A voltage multiplier is an electrical circuit that converts AC electrical power from a lower voltage to a higher DC voltage, typically by means of a network of capacitors and diodes. Voltage multipliers can be used in various applications where higher voltages are required from a lower voltage source.
The Villard cascade voltage multiplier operates by utilizing a series of stages, each consisting of a diode and a capacitor. The basic principle involves charging the capacitors during the positive half-cycle of the AC input voltage and discharging them to produce a higher DC output during the negative half-cycle.
In a typical configuration, the input AC voltage is applied to the first diode-capacitor pair. During the positive cycle, the diode conducts, allowing the capacitor to charge to the peak value of the input voltage. In the subsequent negative cycle, the diode becomes reverse-biased, preventing discharge. The charged capacitor then contributes to the voltage seen at the output.
The output voltage can be calculated as a function of the input voltage and the number of stages in the multiplier. For a single-stage Villard multiplier, the output voltage is approximately equal to the input voltage multiplied by a factor of two. As additional stages are added, the output voltage increases, following the formula V_out = n * V_in, where n is the number of stages.
It is important to note that the efficiency of the voltage multiplier decreases with increased load, and the ripple voltage can also become significant at higher output voltages. Therefore, careful consideration of the load characteristics and the choice of components is essential for optimal performance.
Applications of the Villard cascade voltage multiplier include power supplies for high-voltage equipment, photomultiplier tubes, and other devices requiring elevated DC voltages. The design must ensure that the components can withstand the increased voltage levels and that the layout minimizes parasitic capacitances and inductances that could affect performance.Villard cascade voltage multiplier. A voltage multiplier is an electrical circuit that converts AC electrical power from a lower voltage to a higher DC voltage, typically by means of a network of capacitors and diodes. Voltage multipliers can be.. 🔗 External reference
The Villard cascade voltage multiplier operates by utilizing a series of stages, each consisting of a diode and a capacitor. The basic principle involves charging the capacitors during the positive half-cycle of the AC input voltage and discharging them to produce a higher DC output during the negative half-cycle.
In a typical configuration, the input AC voltage is applied to the first diode-capacitor pair. During the positive cycle, the diode conducts, allowing the capacitor to charge to the peak value of the input voltage. In the subsequent negative cycle, the diode becomes reverse-biased, preventing discharge. The charged capacitor then contributes to the voltage seen at the output.
The output voltage can be calculated as a function of the input voltage and the number of stages in the multiplier. For a single-stage Villard multiplier, the output voltage is approximately equal to the input voltage multiplied by a factor of two. As additional stages are added, the output voltage increases, following the formula V_out = n * V_in, where n is the number of stages.
It is important to note that the efficiency of the voltage multiplier decreases with increased load, and the ripple voltage can also become significant at higher output voltages. Therefore, careful consideration of the load characteristics and the choice of components is essential for optimal performance.
Applications of the Villard cascade voltage multiplier include power supplies for high-voltage equipment, photomultiplier tubes, and other devices requiring elevated DC voltages. The design must ensure that the components can withstand the increased voltage levels and that the layout minimizes parasitic capacitances and inductances that could affect performance.Villard cascade voltage multiplier. A voltage multiplier is an electrical circuit that converts AC electrical power from a lower voltage to a higher DC voltage, typically by means of a network of capacitors and diodes. Voltage multipliers can be.. 🔗 External reference