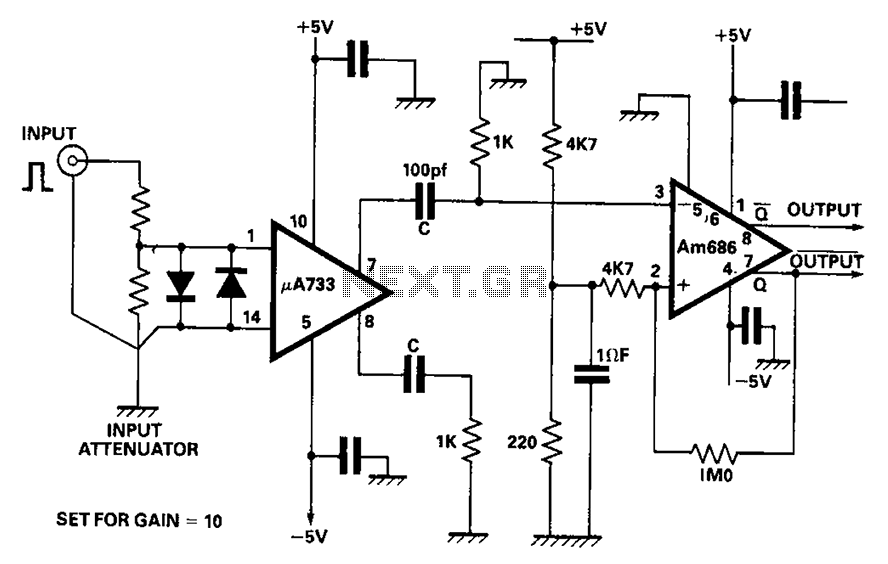
Walkman amplifier
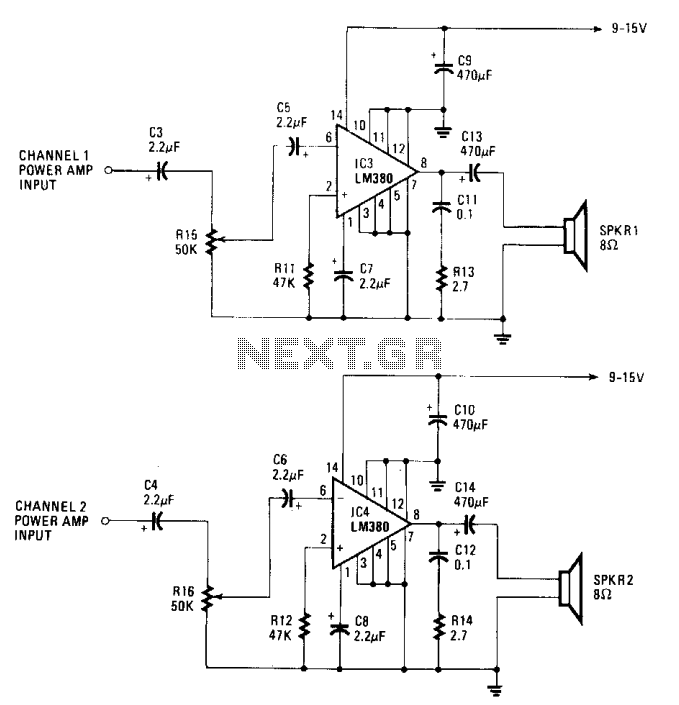
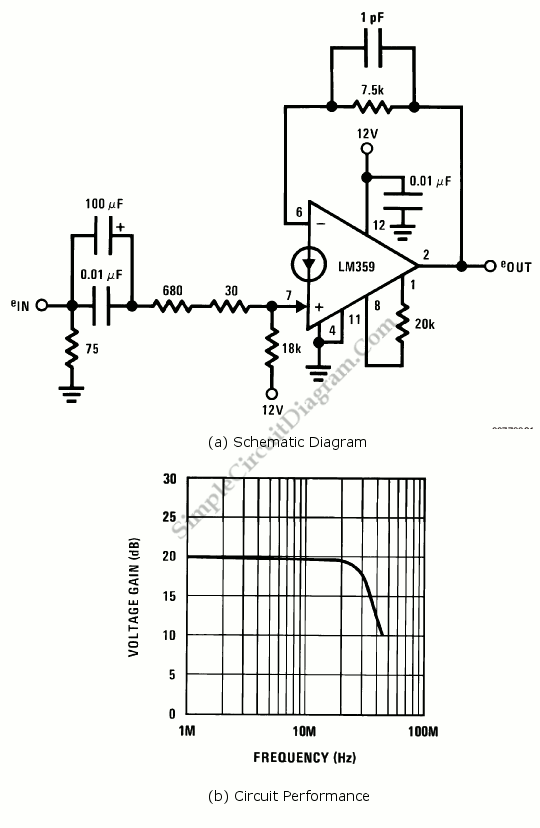
The gain of the low-cost IC is internally fixed at no less than 34 dB (50 times). A unique input stage allows input signals to be referenced to ground. The output is automatically self-centering to one-half the supply voltage and is short-circuit proof with internal thermal limiting. With a maximum supply of 15 volts and an 8-ohm load, the output is approximately 1.5 watts per channel. The input stage is usable with signals ranging from 50 mV to 500 mV rms. If the amplifier is to be used with a source other than a personal stereo, such as a phonograph or an electric guitar, some type of preamplifier is required. A suitable circuit is shown. In that circuit, two 741 op-amps have been configured as input amplifiers. Their input stages are referenced to a common point—half the supply voltage. This voltage is derived from a voltage divider made up of R1 and R2, two 2.2 kΩ resistors. The gain of each of the 741s has been fixed at 21 by the input resistors (R9, R10). Input capacitors C1 and C2 are used to filter out any DC component from the input signal.
The described circuit utilizes a low-cost integrated circuit (IC) amplifier with a fixed gain of 34 dB, making it suitable for various audio applications. The amplifier's design incorporates a unique input stage that allows for grounding of input signals, which is essential for eliminating noise and ensuring signal integrity. The output configuration is designed to self-center at half of the supply voltage, ensuring that the output signal remains within the linear operating range of the amplifier, thus preventing distortion.
The circuit is capable of delivering around 1.5 watts per channel when powered by a 15-volt supply and connected to an 8-ohm load, making it suitable for driving small speakers. The input stage is versatile, accepting signals from 50 mV to 500 mV rms, which covers a wide range of audio sources. However, for sources such as phonographs or electric guitars that typically output lower signal levels, a preamplifier is necessary to boost the signal before it reaches the main amplifier.
The preamplifier circuit employs two 741 operational amplifiers (op-amps), which are configured to amplify the input signals. The reference voltage for the input stages of these op-amps is established at half the supply voltage, achieved through a voltage divider composed of two 2.2 kΩ resistors (R1 and R2). This configuration allows for balanced operation of the op-amps, enhancing performance and stability.
The gain of each op-amp is set to 21, determined by the values of the input resistors (R9 and R10). This fixed gain ensures that the output from the preamplifier is adequate for the main amplifier stage. Additionally, input capacitors C1 and C2 are included to block any DC offset present in the incoming audio signals, allowing only the AC component to pass through for amplification. This filtering is crucial for maintaining audio quality and preventing unwanted DC levels from affecting the amplifier's operation.
Overall, the described circuit represents a robust solution for audio amplification, integrating effective gain stages and signal conditioning to accommodate a variety of audio sources.The gain of the low-cost IC is internally fixed so that it is not less than 34 dB (50 times). A unique input stage allows input signals to be referenced to ground. The output is automatically self centering to one half the supply voltage. The output is also short-circuit proof with internal thermal limiting. With a maximum supply of 15 volts and an 8 ohm load, the output is around 1.5 watts per channel. The input stage is usable with signals from 50 mV to 500 mV rms. If the amplifier is to be used with a source other than a personal stereo, such as a phonograph or an electric guitar, some type of preamplifier is required. A suitable circuit is shown. In that circuit, two 741 op amps have been configured as input amplifiers. Their input stages referenced to a common point—half the supply voltage. That voltage is derived from a voltage divider made up of Rl and R2, two 2.2 k resistors. The gain of each of the 741's has been fixed at 21 by the input resistors (R9, RIO). Input capacitors; Cl and C2, are used to-filter out any dc component from the input signal than a personal stereo, such as a phonograph or an electric guitar, some type of preamplifier is required. A suitable circuit is shown. In that circuit, two 741 op amps have been configured as input amplifiers. Their input stages referenced to a common point—half the supply voltage. That voltage is derived from a voltage divider made up of Rl and R2, two 2.2 k resistors. The gain of each of the 741's has been fixed at 21 by the input resistors (R9, RIO). Input capacitors; Cl and C2, are used to-filter out any dc component from the input signal.
The described circuit utilizes a low-cost integrated circuit (IC) amplifier with a fixed gain of 34 dB, making it suitable for various audio applications. The amplifier's design incorporates a unique input stage that allows for grounding of input signals, which is essential for eliminating noise and ensuring signal integrity. The output configuration is designed to self-center at half of the supply voltage, ensuring that the output signal remains within the linear operating range of the amplifier, thus preventing distortion.
The circuit is capable of delivering around 1.5 watts per channel when powered by a 15-volt supply and connected to an 8-ohm load, making it suitable for driving small speakers. The input stage is versatile, accepting signals from 50 mV to 500 mV rms, which covers a wide range of audio sources. However, for sources such as phonographs or electric guitars that typically output lower signal levels, a preamplifier is necessary to boost the signal before it reaches the main amplifier.
The preamplifier circuit employs two 741 operational amplifiers (op-amps), which are configured to amplify the input signals. The reference voltage for the input stages of these op-amps is established at half the supply voltage, achieved through a voltage divider composed of two 2.2 kΩ resistors (R1 and R2). This configuration allows for balanced operation of the op-amps, enhancing performance and stability.
The gain of each op-amp is set to 21, determined by the values of the input resistors (R9 and R10). This fixed gain ensures that the output from the preamplifier is adequate for the main amplifier stage. Additionally, input capacitors C1 and C2 are included to block any DC offset present in the incoming audio signals, allowing only the AC component to pass through for amplification. This filtering is crucial for maintaining audio quality and preventing unwanted DC levels from affecting the amplifier's operation.
Overall, the described circuit represents a robust solution for audio amplification, integrating effective gain stages and signal conditioning to accommodate a variety of audio sources.The gain of the low-cost IC is internally fixed so that it is not less than 34 dB (50 times). A unique input stage allows input signals to be referenced to ground. The output is automatically self centering to one half the supply voltage. The output is also short-circuit proof with internal thermal limiting. With a maximum supply of 15 volts and an 8 ohm load, the output is around 1.5 watts per channel. The input stage is usable with signals from 50 mV to 500 mV rms. If the amplifier is to be used with a source other than a personal stereo, such as a phonograph or an electric guitar, some type of preamplifier is required. A suitable circuit is shown. In that circuit, two 741 op amps have been configured as input amplifiers. Their input stages referenced to a common point—half the supply voltage. That voltage is derived from a voltage divider made up of Rl and R2, two 2.2 k resistors. The gain of each of the 741's has been fixed at 21 by the input resistors (R9, RIO). Input capacitors; Cl and C2, are used to-filter out any dc component from the input signal than a personal stereo, such as a phonograph or an electric guitar, some type of preamplifier is required. A suitable circuit is shown. In that circuit, two 741 op amps have been configured as input amplifiers. Their input stages referenced to a common point—half the supply voltage. That voltage is derived from a voltage divider made up of Rl and R2, two 2.2 k resistors. The gain of each of the 741's has been fixed at 21 by the input resistors (R9, RIO). Input capacitors; Cl and C2, are used to-filter out any dc component from the input signal.