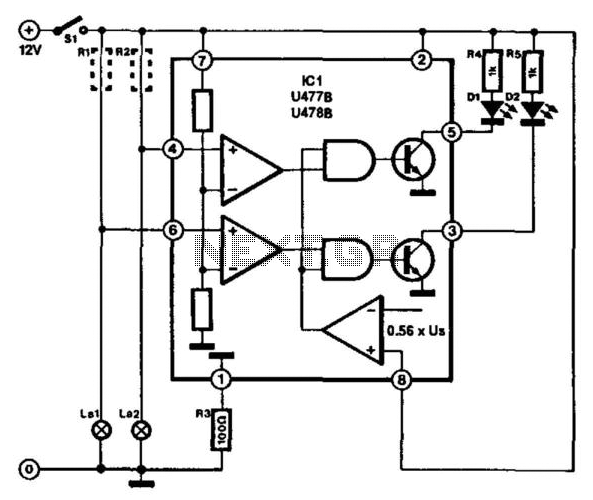
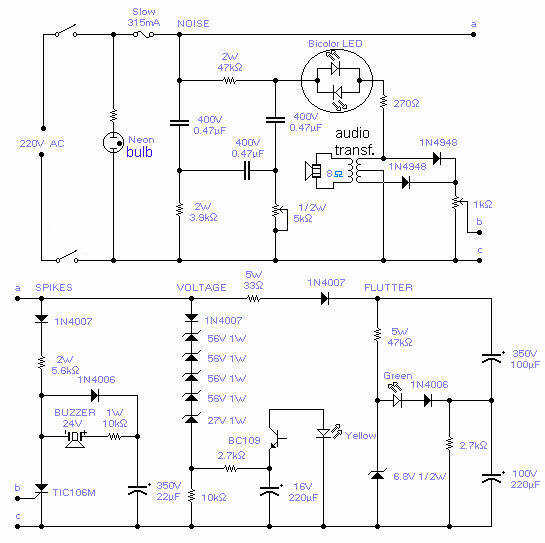
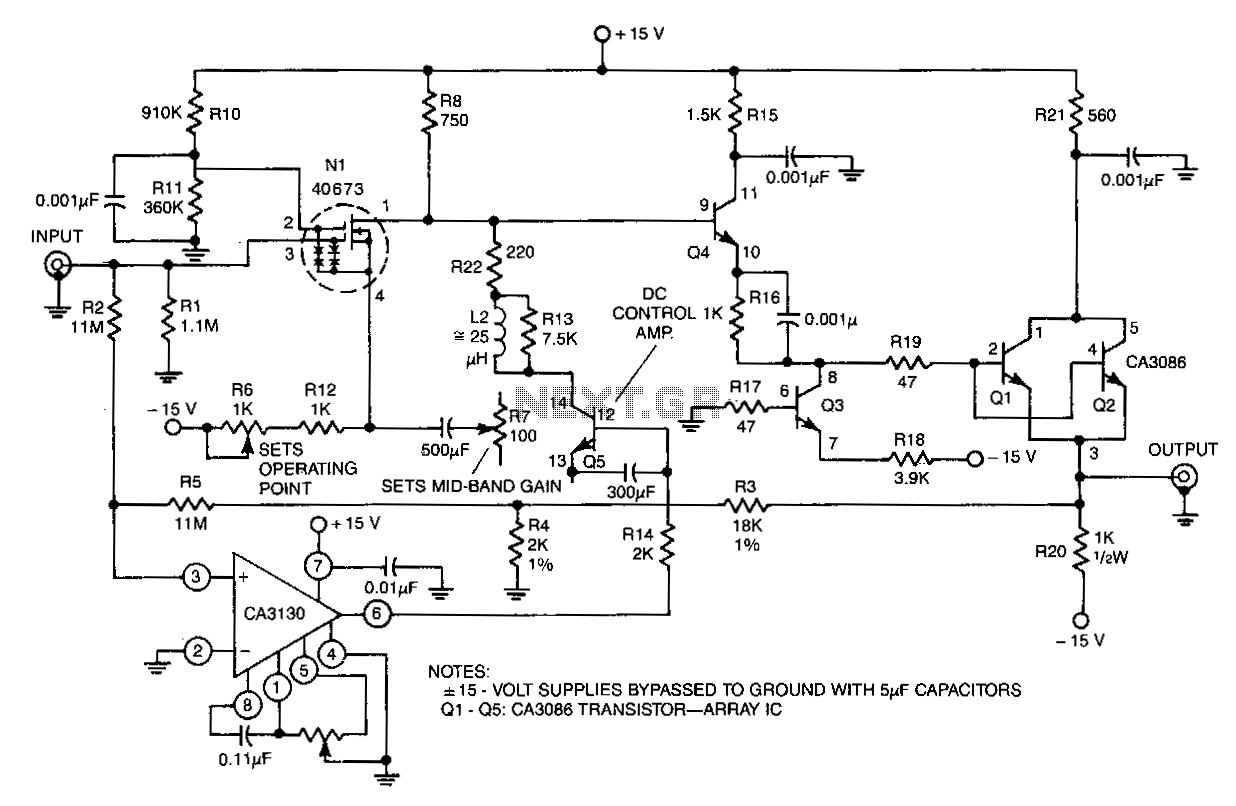
Wideband radiation monitor
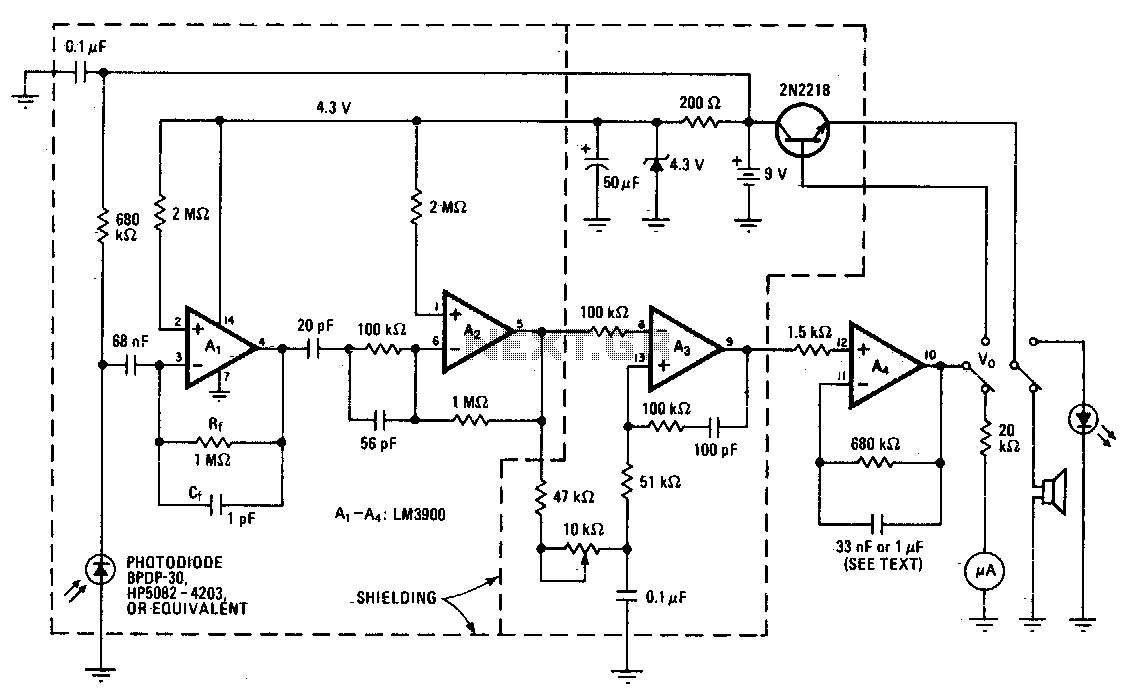
A sensitive radiation monitor can be constructed using a large-area photodiode in conjunction with a quad operational amplifier. By replacing the glass window of the diode with Mylar foil, it is shielded from light and infrared energy, allowing it to detect nuclear radiation such as alpha and beta particles, as well as gamma rays. Operational amplifier A4 integrates the output from A3 to drive a microammeter. Additionally, a 1 microfarad capacitor is utilized in the integrating network, while a smaller capacitor, such as 33 nanofarads, can be employed to drive a small loudspeaker, producing a 50-hertz output signal, or a light-emitting diode.
The radiation monitor circuit is designed to be sensitive and responsive to various types of nuclear radiation. The large-area photodiode serves as the primary sensor, detecting the ionizing radiation. The Mylar foil acts as an effective barrier against unwanted light and infrared radiation, ensuring that the photodiode's output is solely due to the nuclear radiation it encounters.
The quad operational amplifier configuration is critical for processing the weak signals generated by the photodiode. The first stage of the amplifier amplifies the photodiode's current output, converting it into a more manageable voltage signal. The integration process performed by operational amplifier A4 takes the amplified signal from A3 and produces a steady output that can be easily read on a microammeter, providing a clear indication of the radiation levels.
Incorporating a 1 microfarad capacitor in the integrating network helps to smooth out the output signal, allowing for accurate readings over time. For applications requiring sound or visual alerts, a smaller capacitor value of 33 nanofarads can be used to produce a 50-hertz signal, driving a small loudspeaker or light-emitting diode. This feature adds a layer of functionality to the radiation monitor, enabling it to provide immediate feedback in response to detected radiation levels.
The design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, making it accessible for various applications in radiation monitoring, whether for educational purposes, research, or safety monitoring in environments where radiation exposure is a concern.A sensitive radiation monitor may be simply constructed with a large-area photodiode and a quad operational amplifier. Replacing the glass window of the diode with Mylar foil will shield it from light and infrared energy, enabling it to respond to such nuclear radiation as alpha and beta particles and gamma rays.
A4 integrates the output of A3 in order to drive a microammeter A1 microfarad capacitor is used in the integrating network. A lower value, say, 33 nanofarads, will make it possible to drive a small loudspeaker (50-hertz output signal) or light-emitting diode.
The radiation monitor circuit is designed to be sensitive and responsive to various types of nuclear radiation. The large-area photodiode serves as the primary sensor, detecting the ionizing radiation. The Mylar foil acts as an effective barrier against unwanted light and infrared radiation, ensuring that the photodiode's output is solely due to the nuclear radiation it encounters.
The quad operational amplifier configuration is critical for processing the weak signals generated by the photodiode. The first stage of the amplifier amplifies the photodiode's current output, converting it into a more manageable voltage signal. The integration process performed by operational amplifier A4 takes the amplified signal from A3 and produces a steady output that can be easily read on a microammeter, providing a clear indication of the radiation levels.
Incorporating a 1 microfarad capacitor in the integrating network helps to smooth out the output signal, allowing for accurate readings over time. For applications requiring sound or visual alerts, a smaller capacitor value of 33 nanofarads can be used to produce a 50-hertz signal, driving a small loudspeaker or light-emitting diode. This feature adds a layer of functionality to the radiation monitor, enabling it to provide immediate feedback in response to detected radiation levels.
The design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, making it accessible for various applications in radiation monitoring, whether for educational purposes, research, or safety monitoring in environments where radiation exposure is a concern.A sensitive radiation monitor may be simply constructed with a large-area photodiode and a quad operational amplifier. Replacing the glass window of the diode with Mylar foil will shield it from light and infrared energy, enabling it to respond to such nuclear radiation as alpha and beta particles and gamma rays.
A4 integrates the output of A3 in order to drive a microammeter A1 microfarad capacitor is used in the integrating network. A lower value, say, 33 nanofarads, will make it possible to drive a small loudspeaker (50-hertz output signal) or light-emitting diode.