Wire Loop AlarmCircuit Project
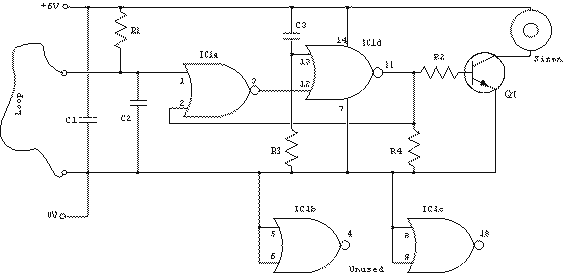
The loop can be any type of hookup wire, with a maximum resistance of about 90K. Using very thin wire (40AWG, for example) will create a highly sensitive trip wire, but will reduce the distance it can be strung due to the high resistance.
In the context of electronic circuits, a trip wire is an essential component often used in alarm systems, security devices, or automated triggering mechanisms. The choice of wire type for the loop is critical, as it directly influences the circuit's performance. Hookup wire can vary in gauge, with thinner wires, such as 40AWG, providing increased sensitivity due to their higher resistance. This sensitivity makes them ideal for applications where even minor disturbances need to be detected. However, the trade-off is that thinner wires can only be strung over limited distances before the resistance becomes too high, potentially leading to false triggers or failure to complete the circuit.
When designing a trip wire system, it is important to consider the maximum resistance of 90K ohms. This limitation ensures that the circuit remains functional while maintaining the desired sensitivity. The circuit can be configured to include a resistor in parallel with the trip wire to help manage the overall resistance and improve performance over longer distances. Additionally, the use of a suitable microcontroller or comparator circuit can enhance the detection capabilities, allowing for precise monitoring of the trip wire's status.
In summary, the selection of hookup wire gauge, along with proper circuit design considerations, plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of a trip wire system. By balancing sensitivity and operational range, a reliable and efficient triggering mechanism can be achieved.The loop can be any type of hookup wire, with a maximum resistance of about 90K. Using very thin wire (40AWG, for example) will make a very sensitive trip wire, but will shorten the distance it can be strung due to the high resistance. 🔗 External reference
In the context of electronic circuits, a trip wire is an essential component often used in alarm systems, security devices, or automated triggering mechanisms. The choice of wire type for the loop is critical, as it directly influences the circuit's performance. Hookup wire can vary in gauge, with thinner wires, such as 40AWG, providing increased sensitivity due to their higher resistance. This sensitivity makes them ideal for applications where even minor disturbances need to be detected. However, the trade-off is that thinner wires can only be strung over limited distances before the resistance becomes too high, potentially leading to false triggers or failure to complete the circuit.
When designing a trip wire system, it is important to consider the maximum resistance of 90K ohms. This limitation ensures that the circuit remains functional while maintaining the desired sensitivity. The circuit can be configured to include a resistor in parallel with the trip wire to help manage the overall resistance and improve performance over longer distances. Additionally, the use of a suitable microcontroller or comparator circuit can enhance the detection capabilities, allowing for precise monitoring of the trip wire's status.
In summary, the selection of hookup wire gauge, along with proper circuit design considerations, plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of a trip wire system. By balancing sensitivity and operational range, a reliable and efficient triggering mechanism can be achieved.The loop can be any type of hookup wire, with a maximum resistance of about 90K. Using very thin wire (40AWG, for example) will make a very sensitive trip wire, but will shorten the distance it can be strung due to the high resistance. 🔗 External reference