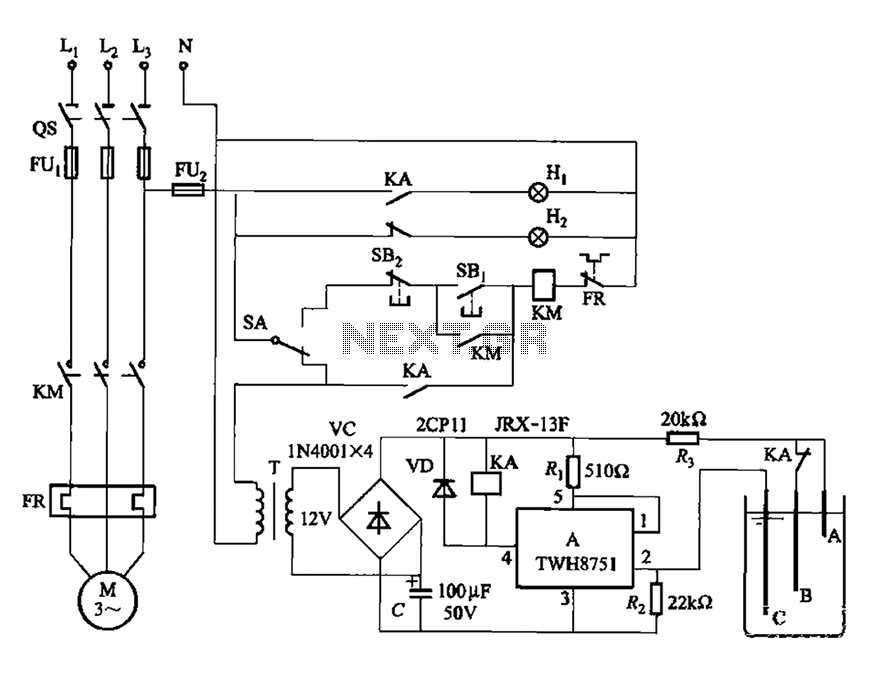
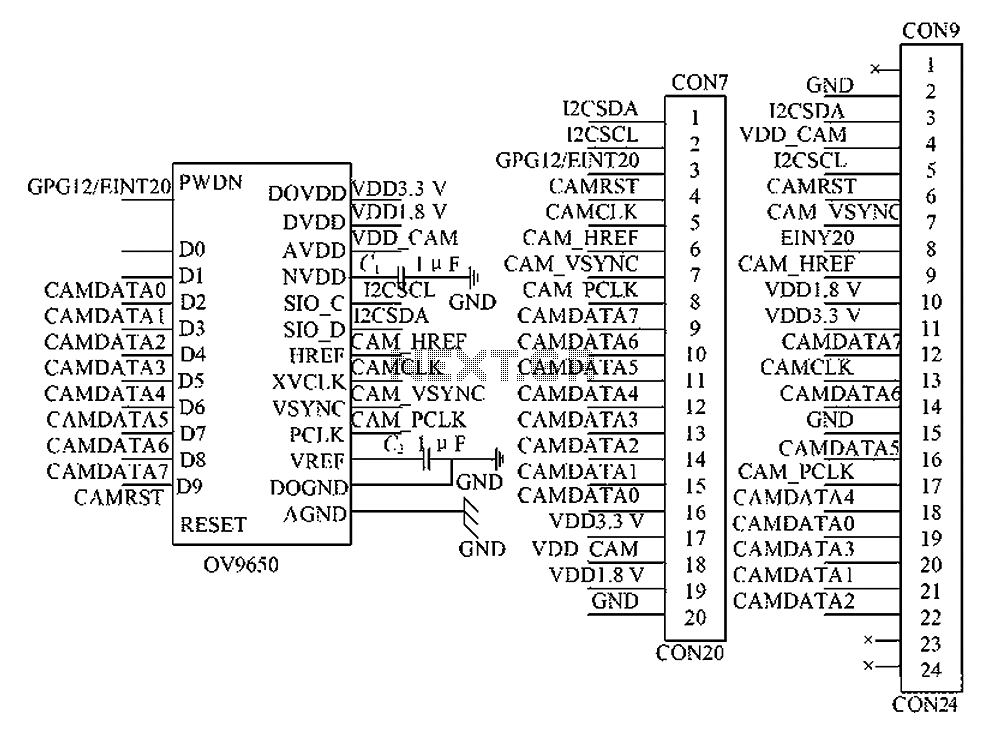
wire tracer circuit

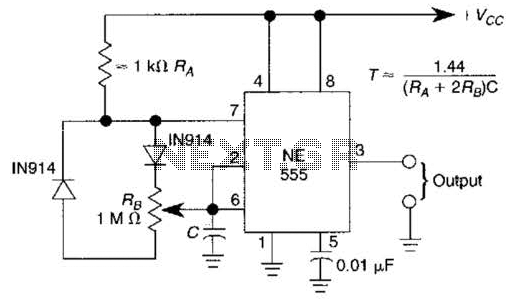
The output frequency alternates between approximately 2100 Hz and 2200 Hz. This unique test signal is easily distinguishable from other potential signals. Resistor R6 is connected to a wire, approximately ten centimeters long, which serves as the antenna. The ground connection (junction C2-C3) is tied to ground. When the antenna is directly connected to a cable, it is possible to identify the conductors at the other end of the cable using a receiver (this should not be done with live conductors). The schematic for the corresponding receiver can be found elsewhere on this website. The circuit illustrated here represents one half of a device that is extremely useful for tracing electrical wiring within a building or locating a wire break. The system is based on similar equipment used by technicians in telephone exchanges. The operation is straightforward: a generator that produces a recognizable signal is required, which is inductively coupled to a simple but high-gain receiver through a short antenna. To construct a functional transmitter, it would be sufficient to create a simple generator based on a 555 timer. However, as shown in the adjacent diagram, a 556 timer was chosen instead. The second timer (IC1a) is utilized to modulate the tone generated by IC1b.
The circuit described operates within a frequency range that allows for effective signal transmission and reception, which is critical for applications such as wire tracing and fault detection. The use of a 556 timer, which contains two timing circuits, enhances the functionality of the transmitter by enabling frequency modulation. The first timer (IC1b) generates a square wave signal, while the second timer (IC1a) modulates this signal, providing a variable output frequency that can be adjusted for optimal performance based on the specific requirements of the testing environment.
The antenna, a simple wire connected to resistor R6, plays a crucial role in radiating the generated signal. Its length is carefully chosen to optimize the transmission characteristics at the frequencies being used. The ground connection ensures that the circuit operates effectively by providing a stable reference point, which is essential for accurate signal transmission and reception.
This device is particularly beneficial for technicians and electricians who need to trace wiring paths or locate breaks without the need for invasive methods. The straightforward design allows for easy assembly and use, making it accessible for both professionals and hobbyists. By employing this circuit, users can efficiently identify and troubleshoot wiring issues, improving overall maintenance and repair processes in electrical systems.The output frequency alternates between about 2100 Hz and 2200 Hz. This is a very distinctive test signal that is easily distinguished from any other signals that may be present. Resistor R6 is connected to a piece of wire, about ten centimeters long, that functions as the antenna. The ground connection (junction C2-C3) is connected to ground. When the antenna is connected directly to a cable, it is possible to determine at the other end of the cable, with the aid of the receiver, which conductor is which (don`t do this with live conductors!).
The schematic for the matching receiver may be found elsewhere in this website. The circuit depicted here forms one half of a device that will prove extremely handy when tracing the path of electrical wiring in a building or to locate a break in a wire. The system is based on similar equipment that is used by technicians in telephone exchanges. The operation is straightforward. You require a generator that delivers an easily recognizable signal which, using a short antenna, is inductively coupled to a simple, but high gain, receiver.
To create a useful transmitter it would suffice to build a simple generator based on a 555. But as the adjacent diagram shows, a 556 was selected instead. The second timer (IC1a) is used to modulate the tone produced by IC1b. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described operates within a frequency range that allows for effective signal transmission and reception, which is critical for applications such as wire tracing and fault detection. The use of a 556 timer, which contains two timing circuits, enhances the functionality of the transmitter by enabling frequency modulation. The first timer (IC1b) generates a square wave signal, while the second timer (IC1a) modulates this signal, providing a variable output frequency that can be adjusted for optimal performance based on the specific requirements of the testing environment.
The antenna, a simple wire connected to resistor R6, plays a crucial role in radiating the generated signal. Its length is carefully chosen to optimize the transmission characteristics at the frequencies being used. The ground connection ensures that the circuit operates effectively by providing a stable reference point, which is essential for accurate signal transmission and reception.
This device is particularly beneficial for technicians and electricians who need to trace wiring paths or locate breaks without the need for invasive methods. The straightforward design allows for easy assembly and use, making it accessible for both professionals and hobbyists. By employing this circuit, users can efficiently identify and troubleshoot wiring issues, improving overall maintenance and repair processes in electrical systems.The output frequency alternates between about 2100 Hz and 2200 Hz. This is a very distinctive test signal that is easily distinguished from any other signals that may be present. Resistor R6 is connected to a piece of wire, about ten centimeters long, that functions as the antenna. The ground connection (junction C2-C3) is connected to ground. When the antenna is connected directly to a cable, it is possible to determine at the other end of the cable, with the aid of the receiver, which conductor is which (don`t do this with live conductors!).
The schematic for the matching receiver may be found elsewhere in this website. The circuit depicted here forms one half of a device that will prove extremely handy when tracing the path of electrical wiring in a building or to locate a break in a wire. The system is based on similar equipment that is used by technicians in telephone exchanges. The operation is straightforward. You require a generator that delivers an easily recognizable signal which, using a short antenna, is inductively coupled to a simple, but high gain, receiver.
To create a useful transmitter it would suffice to build a simple generator based on a 555. But as the adjacent diagram shows, a 556 was selected instead. The second timer (IC1a) is used to modulate the tone produced by IC1b. 🔗 External reference