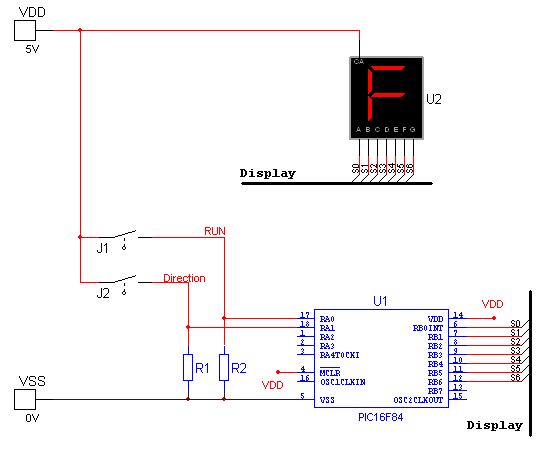
Wireless Headphones Transmitter Circuit
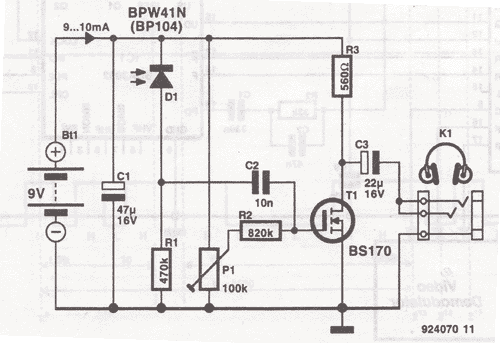
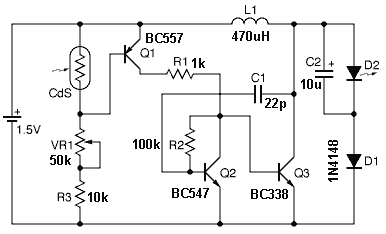
This wireless headphones transmitter ensures quality reception over a distance of 2 meters. The oscillator frequency ranges from 1750 kHz to 3500 kHz, and for the antenna, it...
The wireless headphones transmitter operates within a frequency range of 1750 kHz to 3500 kHz, making it suitable for various audio transmission applications. The system is designed to maintain a strong and clear signal over a distance of 2 meters, which is ideal for personal listening environments.
The transmitter utilizes an oscillator circuit to generate the carrier frequency, which is modulated with audio signals from a source device. This modulation process enables the audio information to be superimposed onto the carrier wave for transmission. The quality of reception is influenced by several factors, including the design of the antenna, the power output of the transmitter, and the surrounding environment.
An appropriate antenna design is crucial for optimal performance. Typically, a monopole or dipole antenna can be employed, tuned to the operating frequency range to maximize the radiation efficiency. The antenna should be positioned to minimize obstructions and interference, ensuring a clear line of sight between the transmitter and the receiving headphones.
The transmitter circuit may include additional components such as filters to minimize noise and enhance signal clarity, as well as amplifiers to boost the output signal strength. Power supply considerations are also essential; a stable voltage source is required to maintain consistent performance across the operational frequency range.
Overall, this wireless headphones transmitter provides a convenient solution for audio transmission, ensuring quality reception and user satisfaction within its specified range.This wireless headphones transmitter assures a quality reception over 2 meters. The oscillator frequency is between 1750KHz and 3500KHz and for antenna we.. 🔗 External reference
The wireless headphones transmitter operates within a frequency range of 1750 kHz to 3500 kHz, making it suitable for various audio transmission applications. The system is designed to maintain a strong and clear signal over a distance of 2 meters, which is ideal for personal listening environments.
The transmitter utilizes an oscillator circuit to generate the carrier frequency, which is modulated with audio signals from a source device. This modulation process enables the audio information to be superimposed onto the carrier wave for transmission. The quality of reception is influenced by several factors, including the design of the antenna, the power output of the transmitter, and the surrounding environment.
An appropriate antenna design is crucial for optimal performance. Typically, a monopole or dipole antenna can be employed, tuned to the operating frequency range to maximize the radiation efficiency. The antenna should be positioned to minimize obstructions and interference, ensuring a clear line of sight between the transmitter and the receiving headphones.
The transmitter circuit may include additional components such as filters to minimize noise and enhance signal clarity, as well as amplifiers to boost the output signal strength. Power supply considerations are also essential; a stable voltage source is required to maintain consistent performance across the operational frequency range.
Overall, this wireless headphones transmitter provides a convenient solution for audio transmission, ensuring quality reception and user satisfaction within its specified range.This wireless headphones transmitter assures a quality reception over 2 meters. The oscillator frequency is between 1750KHz and 3500KHz and for antenna we.. 🔗 External reference