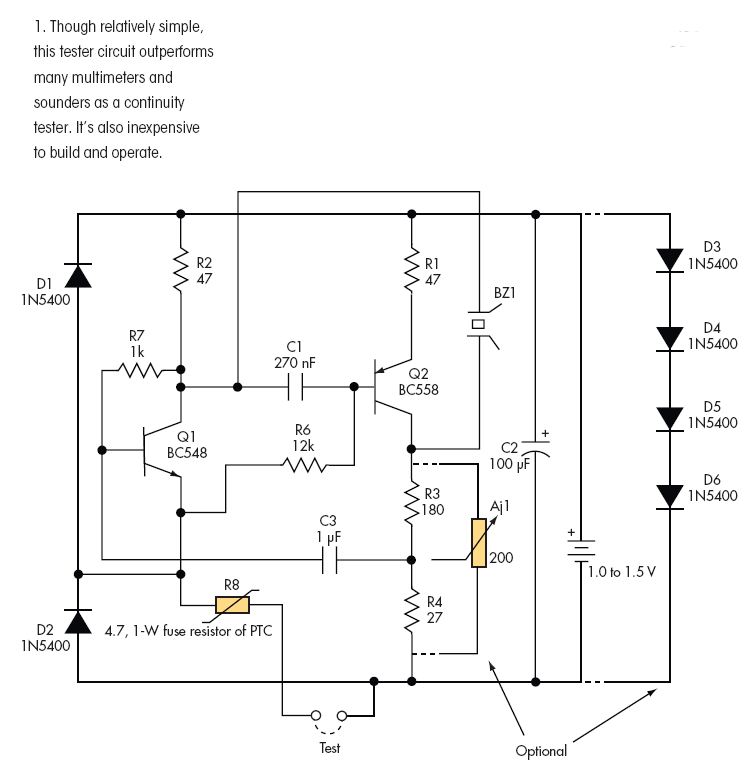
Zener diode tester
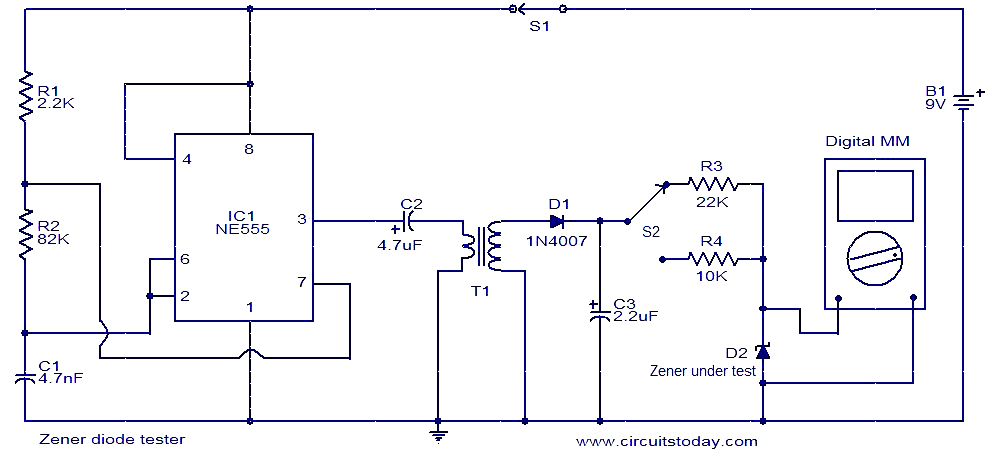
This circuit is designed for testing Zener diodes. The NE555 integrated circuit (IC1) is configured as an astable multivibrator, generating a square wave output. This output is transformed into a high voltage alternating current (AC) by transformer T1, with an unloaded AC voltage of approximately 120V. The AC voltage is then rectified by diode D1 and smoothed using capacitor C3. This filtered voltage is applied across the Zener diode through current limiting resistors R2 or R3, which can be selected via switch S2 to test the diode at currents of 1mA or 2mA, respectively. A digital multimeter set to DC voltage mode is connected across the Zener diode under test, allowing for the measurement of the Zener voltage as specified by the manufacturer.
The circuit utilizes the NE555 timer in an astable configuration, which continuously oscillates between high and low states, producing a square wave output. This output is fed into transformer T1, which steps up the voltage to a high level suitable for testing Zener diodes. The transformer is crucial for isolating the high voltage from the low voltage components, ensuring safety during operation.
Diode D1 plays a vital role in converting the high voltage AC output from the transformer into a pulsating DC voltage. The rectification process is essential for providing a stable voltage to the Zener diode under test. Capacitor C3 acts as a filter, smoothing out the pulsating DC to provide a more constant voltage level, which is necessary for accurate testing.
The current limiting resistors R2 and R3 are critical for protecting the Zener diode from excessive current, which could lead to damage or inaccurate readings. The selection of either resistor is facilitated by switch S2, allowing the user to choose between testing at 1mA or 2mA, depending on the specifications of the Zener diode being tested.
The digital multimeter, configured in DC voltage mode, is connected in parallel with the Zener diode. This setup enables the user to measure the voltage across the diode, which should correspond to the specified Zener voltage provided by the manufacturer. The circuit is designed to provide a simple yet effective means of testing Zener diodes, ensuring that they function within their specified voltage range. Overall, this circuit is a valuable tool for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike, facilitating the testing and verification of Zener diode performance.Here is a very simple circuit that can be used for testing Zener diodes. The IC1 NE555 is wired as an astable multivibrator and the output of the IC is stepped up to a high voltage AC using the transformer T1. The unloaded AC voltage will be around 120V. The AC voltage is rectified by the diode D1 and filtered by the capacitor C3. This voltage is ap plied across the Zener diode through the current limiting resistors R2 or R3 which can be selected by switch S2 for testing the diode at 1mA or 2mA respectively. The digital multimeter in DC voltage mode is connected across the Zener diode under test. The Zener diode is a fine one; the meter will show the correct Zener voltage specified by the manufacturer.
🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the NE555 timer in an astable configuration, which continuously oscillates between high and low states, producing a square wave output. This output is fed into transformer T1, which steps up the voltage to a high level suitable for testing Zener diodes. The transformer is crucial for isolating the high voltage from the low voltage components, ensuring safety during operation.
Diode D1 plays a vital role in converting the high voltage AC output from the transformer into a pulsating DC voltage. The rectification process is essential for providing a stable voltage to the Zener diode under test. Capacitor C3 acts as a filter, smoothing out the pulsating DC to provide a more constant voltage level, which is necessary for accurate testing.
The current limiting resistors R2 and R3 are critical for protecting the Zener diode from excessive current, which could lead to damage or inaccurate readings. The selection of either resistor is facilitated by switch S2, allowing the user to choose between testing at 1mA or 2mA, depending on the specifications of the Zener diode being tested.
The digital multimeter, configured in DC voltage mode, is connected in parallel with the Zener diode. This setup enables the user to measure the voltage across the diode, which should correspond to the specified Zener voltage provided by the manufacturer. The circuit is designed to provide a simple yet effective means of testing Zener diodes, ensuring that they function within their specified voltage range. Overall, this circuit is a valuable tool for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike, facilitating the testing and verification of Zener diode performance.Here is a very simple circuit that can be used for testing Zener diodes. The IC1 NE555 is wired as an astable multivibrator and the output of the IC is stepped up to a high voltage AC using the transformer T1. The unloaded AC voltage will be around 120V. The AC voltage is rectified by the diode D1 and filtered by the capacitor C3. This voltage is ap plied across the Zener diode through the current limiting resistors R2 or R3 which can be selected by switch S2 for testing the diode at 1mA or 2mA respectively. The digital multimeter in DC voltage mode is connected across the Zener diode under test. The Zener diode is a fine one; the meter will show the correct Zener voltage specified by the manufacturer.
🔗 External reference