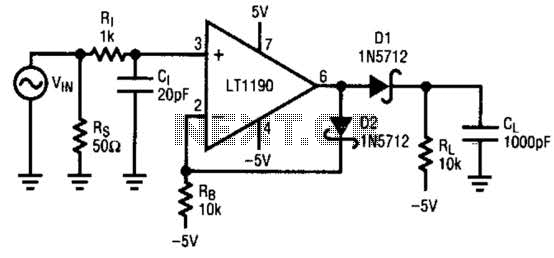
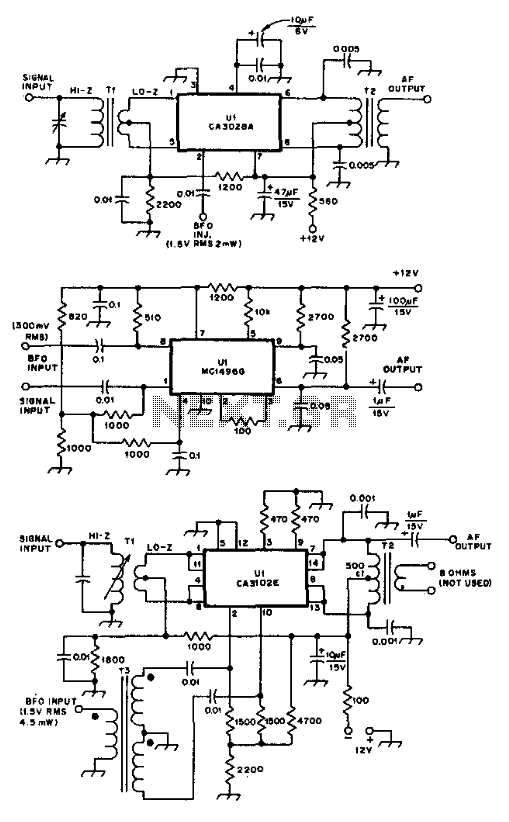
Zero crossing detector
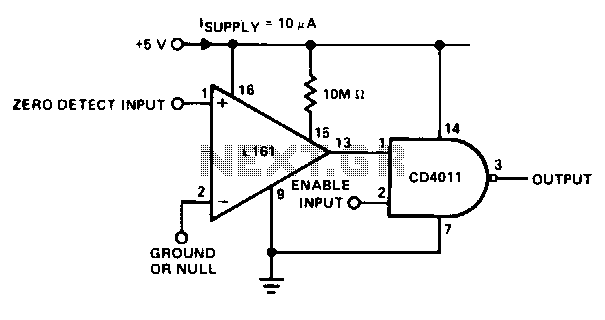
This detector is useful in sine wave squaring circuits and A/D converters. The positive input may either be grounded or connected to a nulling voltage that cancels input offsets and enables accuracy to within microvolts of ground. The CMOS output will switch to within a few millivolts of either rail for an input voltage change of less than 200 µV.
The described detector serves a critical role in applications involving sine wave squaring circuits and analog-to-digital (A/D) converters. Its functionality is primarily based on its ability to handle input offsets effectively, which is crucial for maintaining precision in high-resolution applications. The detector features a positive input that can be either grounded or connected to a nulling voltage. This nulling voltage is essential for compensating any inherent input offsets, thereby enhancing the accuracy of the measurements to within microvolt levels relative to ground.
In terms of performance, the CMOS output of the detector is designed to switch within a few millivolts of the supply rails, which signifies its capability to respond accurately to minor changes in input voltage. Specifically, it has a sensitivity threshold that allows it to detect input voltage variations of less than 200 µV. This high level of sensitivity is particularly advantageous in applications where precise voltage levels must be monitored or converted, such as in signal processing and digital data acquisition systems.
The integration of this detector into a circuit can significantly improve the overall performance of sine wave squaring and A/D conversion processes by ensuring that the output reflects the true characteristics of the input signal. This is especially important in high-frequency applications where signal integrity must be preserved. The ability to maintain accuracy in the presence of input offsets and minor voltage fluctuations makes this detector a valuable component in modern electronic design.This detector is useful in sine wave squaring circuits and A/D converters. The positive input may either be grounded or con-output nected a nulling voltage which cancels input offsets and enables accuracy to within microvolts of ground The CMOS output will switch to within a few millivolts of either rail for an input voltage change of less than 200 µV. 🔗 External reference
The described detector serves a critical role in applications involving sine wave squaring circuits and analog-to-digital (A/D) converters. Its functionality is primarily based on its ability to handle input offsets effectively, which is crucial for maintaining precision in high-resolution applications. The detector features a positive input that can be either grounded or connected to a nulling voltage. This nulling voltage is essential for compensating any inherent input offsets, thereby enhancing the accuracy of the measurements to within microvolt levels relative to ground.
In terms of performance, the CMOS output of the detector is designed to switch within a few millivolts of the supply rails, which signifies its capability to respond accurately to minor changes in input voltage. Specifically, it has a sensitivity threshold that allows it to detect input voltage variations of less than 200 µV. This high level of sensitivity is particularly advantageous in applications where precise voltage levels must be monitored or converted, such as in signal processing and digital data acquisition systems.
The integration of this detector into a circuit can significantly improve the overall performance of sine wave squaring and A/D conversion processes by ensuring that the output reflects the true characteristics of the input signal. This is especially important in high-frequency applications where signal integrity must be preserved. The ability to maintain accuracy in the presence of input offsets and minor voltage fluctuations makes this detector a valuable component in modern electronic design.This detector is useful in sine wave squaring circuits and A/D converters. The positive input may either be grounded or con-output nected a nulling voltage which cancels input offsets and enables accuracy to within microvolts of ground The CMOS output will switch to within a few millivolts of either rail for an input voltage change of less than 200 µV. 🔗 External reference