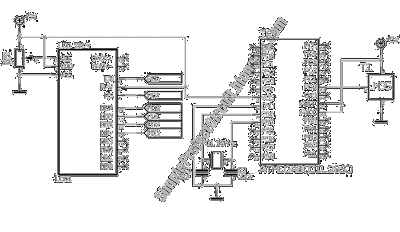
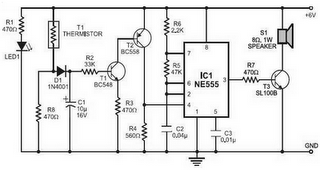
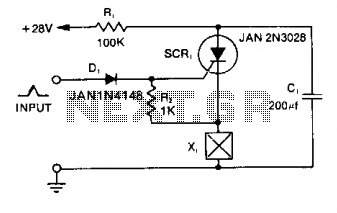
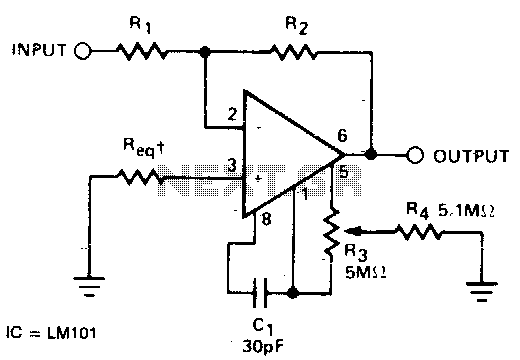
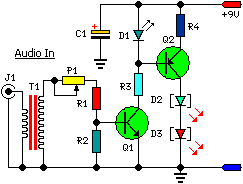
Small low-frequency drift polarity switching synchronous detector circuit
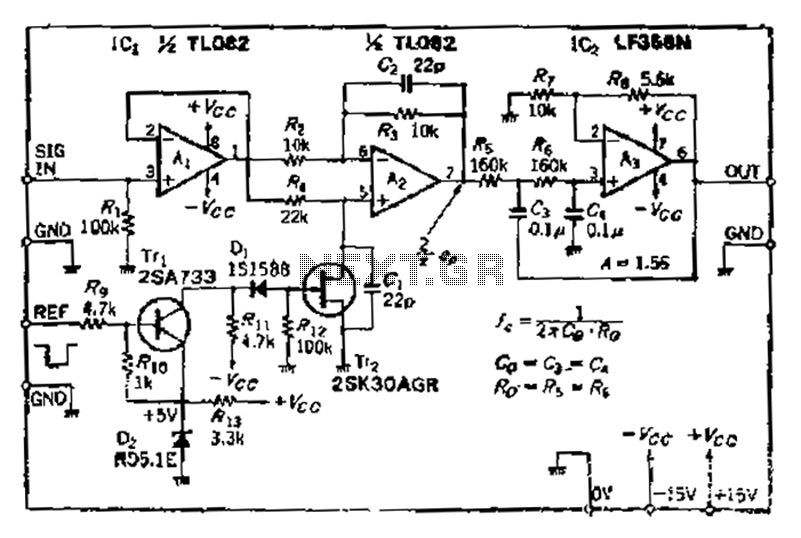
After turning off TT2, the input signal enters through chi Az, where the input resistance is very high and reaches the same potential. The inverting input terminal must also be associated with this movement. Therefore, Trr functions as a buffer amplifier. An analog switching circuit using transistor Tr must be configured between the gate electrode and the source. When the voltage is in the negative direction, it is positioned near the center of voltage vP. To utilize TTL level driving, +5V is replaced with -Vcc/+5V. Additionally, a C-MOS analog switch can be used, but cost considerations must be taken into account. Transistor Tr is a PNP type, with the emitter potential at +5V. When the TTL input power is off, the transistor is nearly off, and the telegraph voltage is set to -Vcc (thus disconnecting TT2). The TTL level input serves as a control signal, allowing Tr to produce base current, resulting in conduction. The collector potential is then close to +5V, turning diode Dj off, which leads to the output voltage being accounted for at Vout, with resistor Rz turned on.
An electronic circuit utilizing a PNP transistor as a switch or amplifier can be designed based on the described operation. The circuit consists of a PNP transistor (Tr) configured in a common-emitter configuration. The emitter of the transistor is connected to +5V, while the collector is linked to the load, which may be a diode (Dj) and a resistor (Rz) in series. The base of the transistor receives a control signal from a TTL logic level input, which determines the on/off state of the transistor.
When the TTL input is high (logic 1), the base current flows into the transistor, turning it on and allowing current to flow from the emitter to the collector. This causes the output voltage at the collector to rise close to +5V, effectively turning off the diode Dj. Conversely, when the TTL input is low (logic 0), the base current ceases, and the transistor turns off, resulting in the collector voltage dropping towards ground potential, which allows diode Dj to conduct if the load conditions permit.
The analog switching circuit can be further refined by integrating a CMOS analog switch for applications requiring lower power consumption and higher switching speeds. However, the selection of components must be balanced with cost constraints, as CMOS devices may be more expensive than traditional bipolar junction transistors (BJTs).
Overall, this circuit configuration provides a reliable method for controlling analog signals using digital logic levels, enabling seamless integration into larger electronic systems. Proper attention to component specifications and circuit layout will ensure optimal performance and reliability in various applications.After TT2 off, the input signal input via chi Az, dry white [input resistance is very high, becomes the same potential, the inverting input terminal must also be associated wit h the move, so Trr play the role of a magnification of the follower 1. Analog switching circuit Tr soap must be formed between the gate electrode a source off when the voltage v. J negative direction placed near the center off voltage vP. To use TTL level drive, the + s/ov replaced - vcc/+ Sv, in addition can also be replaced C-MOS analog switch, but must consider the cost element.
Tr. It is a PNP transistor, the emitter potential of Sv, T TL input power when oH- almost off, then set the telegraph voltage - vcc (TT2 so disconnected). TTL level input as labor hours, so that Tr, produce base current, r, conduction, the collector potential placed near + sv, diode Dj off, then v accounted s FO, rz turned on.
An electronic circuit utilizing a PNP transistor as a switch or amplifier can be designed based on the described operation. The circuit consists of a PNP transistor (Tr) configured in a common-emitter configuration. The emitter of the transistor is connected to +5V, while the collector is linked to the load, which may be a diode (Dj) and a resistor (Rz) in series. The base of the transistor receives a control signal from a TTL logic level input, which determines the on/off state of the transistor.
When the TTL input is high (logic 1), the base current flows into the transistor, turning it on and allowing current to flow from the emitter to the collector. This causes the output voltage at the collector to rise close to +5V, effectively turning off the diode Dj. Conversely, when the TTL input is low (logic 0), the base current ceases, and the transistor turns off, resulting in the collector voltage dropping towards ground potential, which allows diode Dj to conduct if the load conditions permit.
The analog switching circuit can be further refined by integrating a CMOS analog switch for applications requiring lower power consumption and higher switching speeds. However, the selection of components must be balanced with cost constraints, as CMOS devices may be more expensive than traditional bipolar junction transistors (BJTs).
Overall, this circuit configuration provides a reliable method for controlling analog signals using digital logic levels, enabling seamless integration into larger electronic systems. Proper attention to component specifications and circuit layout will ensure optimal performance and reliability in various applications.After TT2 off, the input signal input via chi Az, dry white [input resistance is very high, becomes the same potential, the inverting input terminal must also be associated wit h the move, so Trr play the role of a magnification of the follower 1. Analog switching circuit Tr soap must be formed between the gate electrode a source off when the voltage v. J negative direction placed near the center off voltage vP. To use TTL level drive, the + s/ov replaced - vcc/+ Sv, in addition can also be replaced C-MOS analog switch, but must consider the cost element.
Tr. It is a PNP transistor, the emitter potential of Sv, T TL input power when oH- almost off, then set the telegraph voltage - vcc (TT2 so disconnected). TTL level input as labor hours, so that Tr, produce base current, r, conduction, the collector potential placed near + sv, diode Dj off, then v accounted s FO, rz turned on.