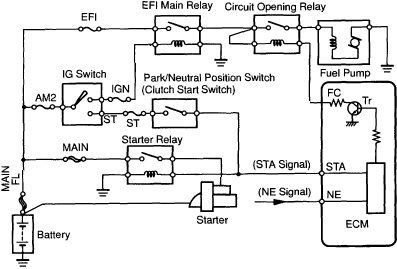
Off TV with reed elimination circuit diagram highlights
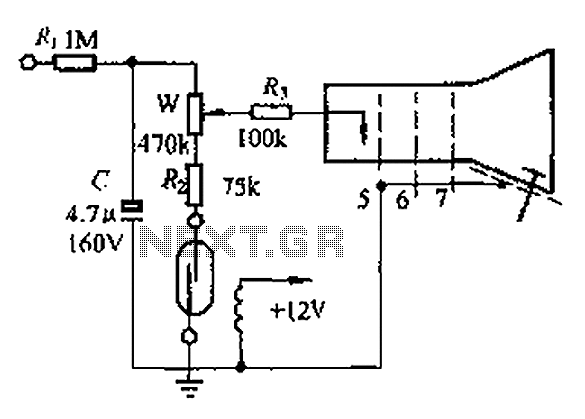
A reed switch is utilized in a TV highlights cancellation circuit. A brightness potentiometer is grounded in series with the reed switch. Under normal operation, the reed contact remains closed, allowing the capacitor C to charge to approximately 160V. When the circuit is shut down, the reed contacts open. Due to the large capacitance of C, and the interruption of the main discharge path, the cathode voltage of the CRT is maintained for a period of time, effectively cutting off the electron beam to eliminate highlights. A coil should be added around the reed switch; this coil frame should be constructed with 0.1mm enameled wire, tightly wound with 5200 turns. One end of the coil should be grounded, while the other end connects to a +12V power supply.
The circuit operates by integrating a reed switch, which acts as a control element to regulate the brightness of a CRT display. The brightness potentiometer allows for user-adjustable control over the circuit's operation. When the reed switch is closed, the capacitor C accumulates a high voltage, which is essential for maintaining the required cathode voltage in the CRT. This voltage enables the display to function correctly by allowing the electron beam to strike the phosphorescent screen.
Upon deactivation of the circuit, the opening of the reed switch interrupts the charging path of the capacitor. The significant capacitance of C plays a crucial role in sustaining the cathode voltage momentarily even after the power is removed. This retention of voltage ensures that the electron beam is effectively cut off, thereby preventing any residual highlights from appearing on the screen.
The inclusion of a coil around the reed switch serves to enhance the magnetic field interaction, which can improve the reliability and responsiveness of the reed switch operation. The use of 0.1mm enameled wire with 5200 turns allows for a compact yet effective design, optimizing the inductance and ensuring that the coil generates a sufficient magnetic field when energized. One terminal of the coil is grounded, providing a return path, while the other is connected to the +12V power supply, ensuring that the circuit operates within the appropriate voltage range.
Overall, this circuit design effectively addresses the issue of highlight elimination in CRT displays, leveraging the properties of capacitors and reed switches in conjunction with a carefully designed coil to achieve desired performance outcomes. As shown by a reed switch off the TV highlights cancellation circuit. Brightness potentiometer W ground a series reed, normally watch TV, the reed contact is closed, the capaci tor C charging voltage of about 160V. Shutdown, reed contacts open, since the larger capacity C, and its main tributary discharge has been cut off, so that the CRT cathode voltage will be retained for a period of time to cut an electron beam to achieve the purpose of eliminating the highlights. Reed should be added around the outside of a coil, the coil frame including enamelled with 0.1MM tightly wound 5200 turns coil end of the ground, and the other termination power + 12V.
The circuit operates by integrating a reed switch, which acts as a control element to regulate the brightness of a CRT display. The brightness potentiometer allows for user-adjustable control over the circuit's operation. When the reed switch is closed, the capacitor C accumulates a high voltage, which is essential for maintaining the required cathode voltage in the CRT. This voltage enables the display to function correctly by allowing the electron beam to strike the phosphorescent screen.
Upon deactivation of the circuit, the opening of the reed switch interrupts the charging path of the capacitor. The significant capacitance of C plays a crucial role in sustaining the cathode voltage momentarily even after the power is removed. This retention of voltage ensures that the electron beam is effectively cut off, thereby preventing any residual highlights from appearing on the screen.
The inclusion of a coil around the reed switch serves to enhance the magnetic field interaction, which can improve the reliability and responsiveness of the reed switch operation. The use of 0.1mm enameled wire with 5200 turns allows for a compact yet effective design, optimizing the inductance and ensuring that the coil generates a sufficient magnetic field when energized. One terminal of the coil is grounded, providing a return path, while the other is connected to the +12V power supply, ensuring that the circuit operates within the appropriate voltage range.
Overall, this circuit design effectively addresses the issue of highlight elimination in CRT displays, leveraging the properties of capacitors and reed switches in conjunction with a carefully designed coil to achieve desired performance outcomes. As shown by a reed switch off the TV highlights cancellation circuit. Brightness potentiometer W ground a series reed, normally watch TV, the reed contact is closed, the capaci tor C charging voltage of about 160V. Shutdown, reed contacts open, since the larger capacity C, and its main tributary discharge has been cut off, so that the CRT cathode voltage will be retained for a period of time to cut an electron beam to achieve the purpose of eliminating the highlights. Reed should be added around the outside of a coil, the coil frame including enamelled with 0.1MM tightly wound 5200 turns coil end of the ground, and the other termination power + 12V.