The triangular wave carrier generator circuit diagram
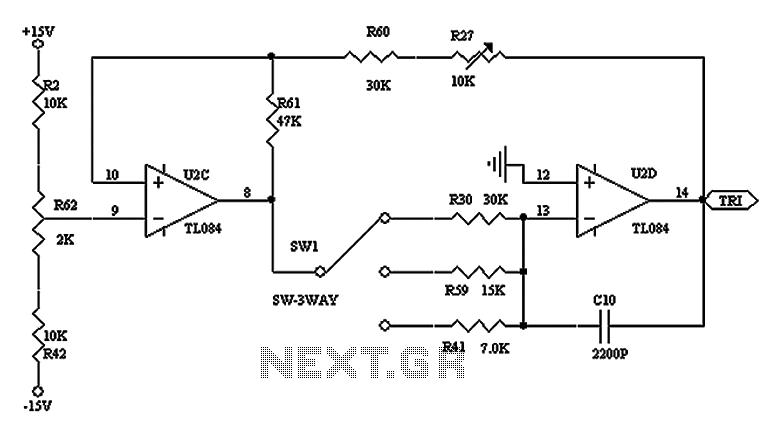
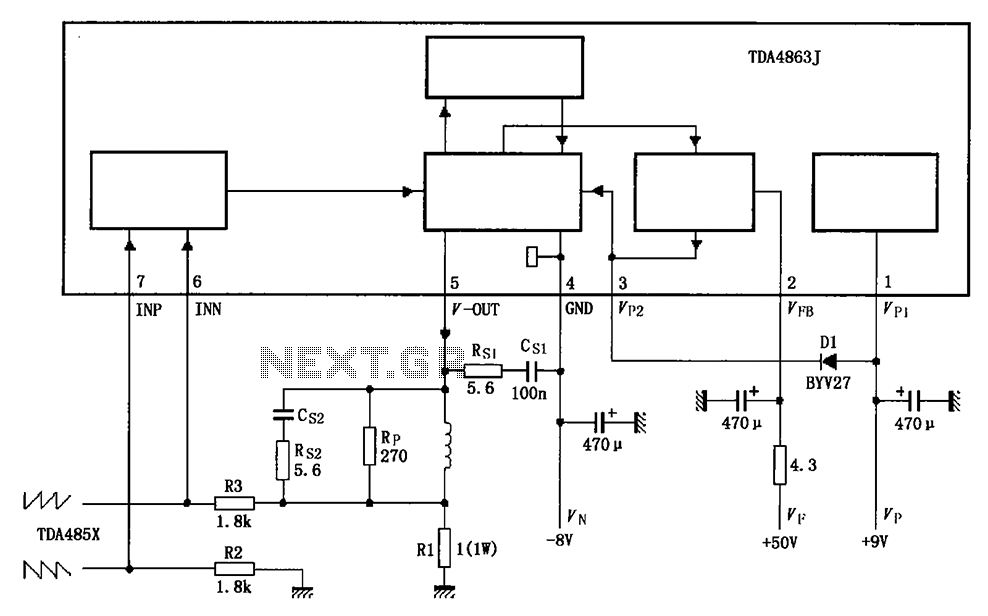
The triangular wave circuit consists of two operational amplifiers (OPs). R62 serves as the offset adjustment, while R27 is utilized for peak adjustment. A switch is included to select different resistances, allowing for the generation of triangular waves at varying frequencies.
The triangular wave generator circuit described employs two operational amplifiers configured in a feedback loop to produce a stable triangular waveform. The use of operational amplifiers is advantageous due to their high input impedance and low output impedance, which facilitate effective signal processing.
R62, the offset adjustment resistor, plays a crucial role in calibrating the output waveform to ensure that it oscillates symmetrically around a desired voltage level. By adjusting R62, the user can fine-tune the baseline voltage of the triangular wave, accommodating variations in power supply or desired output levels.
R27, the peak adjustment resistor, allows for the modification of the amplitude of the triangular waveform. This adjustment is essential for applications that require specific voltage levels or for interfacing with other circuit components that may have varying input requirements.
The inclusion of a switch to select different resistances enhances the circuit's versatility. By changing the resistance values, the frequency of the output triangular wave can be altered. This feature is particularly useful in applications such as signal modulation, waveform generation for testing purposes, or in audio synthesis where different frequencies are needed.
Overall, this triangular wave circuit is designed for flexibility and precision, making it suitable for various electronic applications where a stable and adjustable waveform is required. As shown by the triangular wave circuit composed of two OP, R62 is OFFSET adjustment, R27 for the adjustment of the peak, with the switch to select different resistance obtaine d triangular waves of different frequencies.
The triangular wave generator circuit described employs two operational amplifiers configured in a feedback loop to produce a stable triangular waveform. The use of operational amplifiers is advantageous due to their high input impedance and low output impedance, which facilitate effective signal processing.
R62, the offset adjustment resistor, plays a crucial role in calibrating the output waveform to ensure that it oscillates symmetrically around a desired voltage level. By adjusting R62, the user can fine-tune the baseline voltage of the triangular wave, accommodating variations in power supply or desired output levels.
R27, the peak adjustment resistor, allows for the modification of the amplitude of the triangular waveform. This adjustment is essential for applications that require specific voltage levels or for interfacing with other circuit components that may have varying input requirements.
The inclusion of a switch to select different resistances enhances the circuit's versatility. By changing the resistance values, the frequency of the output triangular wave can be altered. This feature is particularly useful in applications such as signal modulation, waveform generation for testing purposes, or in audio synthesis where different frequencies are needed.
Overall, this triangular wave circuit is designed for flexibility and precision, making it suitable for various electronic applications where a stable and adjustable waveform is required. As shown by the triangular wave circuit composed of two OP, R62 is OFFSET adjustment, R27 for the adjustment of the peak, with the switch to select different resistance obtaine d triangular waves of different frequencies.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713