0.1 To 90 second timer
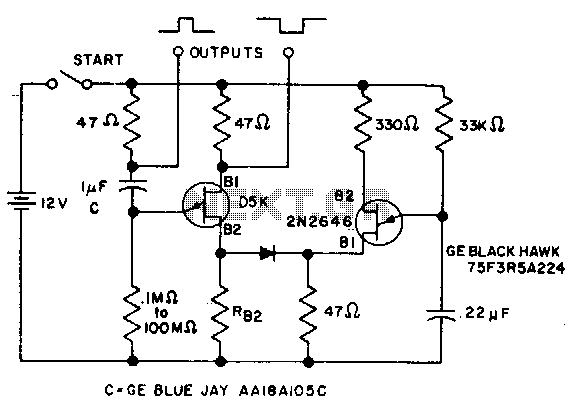
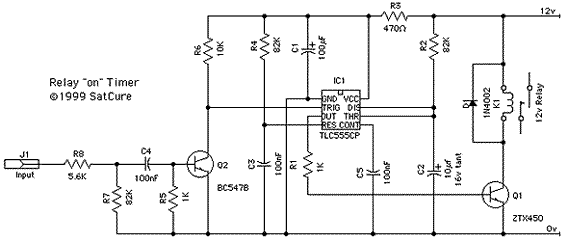
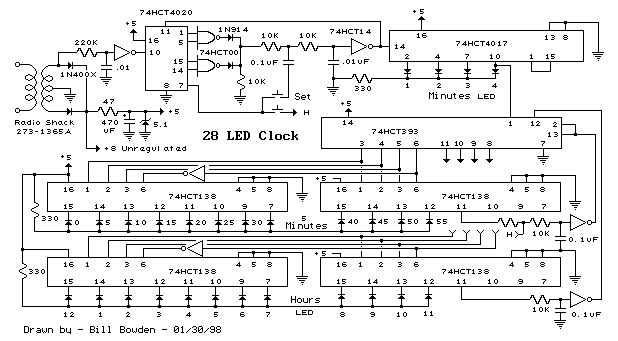
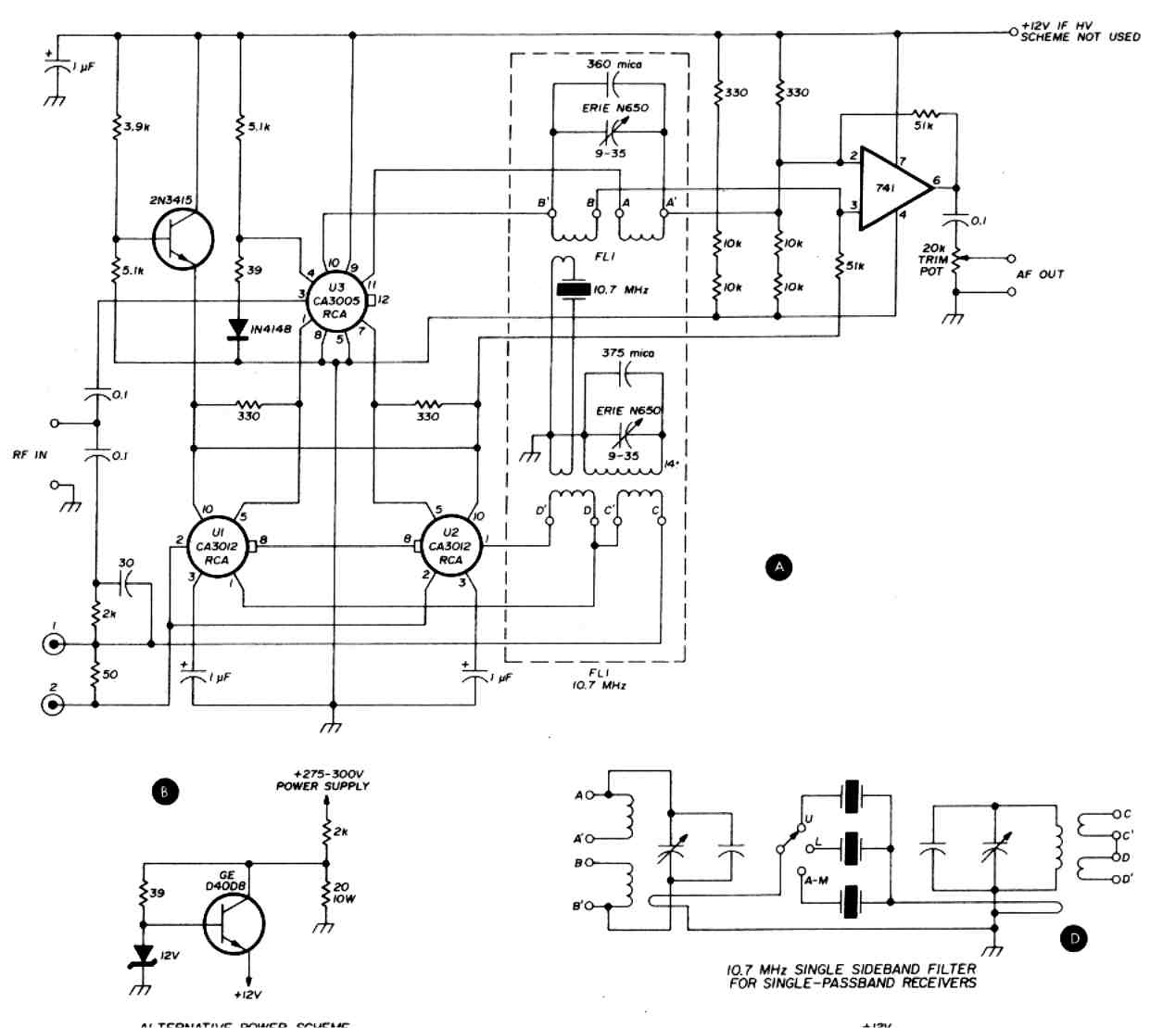
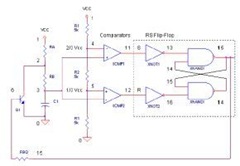
The timer interval begins when power is supplied to the circuit and ends when voltage is applied to the load. The 2N2646 transistor is utilized in the oscillator, which generates pulses to the base of the D5K. This configuration decreases the effective inductance (L) of the D5K, enabling the use of a significantly larger timing resistor and a smaller timing capacitor than would typically be feasible.
The circuit operates by initiating a timer interval upon the application of power, which is critical for timing applications. The 2N2646, a silicon NPN transistor, functions as a key component in the oscillator circuit. It is responsible for generating a square wave signal by rapidly switching on and off, which is then fed to the base of the D5K. The D5K, likely a type of digital logic IC or a similar device, responds to these pulses to control its output state.
The reduction in effective inductance (L) of the D5K is a significant design consideration. By manipulating the inductive characteristics, the circuit allows for a larger timing resistor, which can increase the timing interval as needed for specific applications. Concurrently, the ability to use a smaller timing capacitor is advantageous as it reduces the overall size of the circuit and can enhance performance by minimizing leakage currents and improving response times.
In practical terms, this means that the circuit can be tailored to achieve longer timing intervals without requiring large physical components, which can be a limitation in compact electronic designs. The design can be further optimized by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values based on the desired timing characteristics, ensuring efficient operation within the specified application parameters. Overall, this circuit exemplifies an effective use of component characteristics to achieve desired timing functions in electronic systems.The timer interval starts when power is applied to circuit and terminates when voltage is applied to load. 2N2646 is used in oscillator which pulses base 2 of D5K This reduces the effective L of D5K and allows a much larger timing resistor and smaller timing capacitor to be used than would otherwise be possible. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by initiating a timer interval upon the application of power, which is critical for timing applications. The 2N2646, a silicon NPN transistor, functions as a key component in the oscillator circuit. It is responsible for generating a square wave signal by rapidly switching on and off, which is then fed to the base of the D5K. The D5K, likely a type of digital logic IC or a similar device, responds to these pulses to control its output state.
The reduction in effective inductance (L) of the D5K is a significant design consideration. By manipulating the inductive characteristics, the circuit allows for a larger timing resistor, which can increase the timing interval as needed for specific applications. Concurrently, the ability to use a smaller timing capacitor is advantageous as it reduces the overall size of the circuit and can enhance performance by minimizing leakage currents and improving response times.
In practical terms, this means that the circuit can be tailored to achieve longer timing intervals without requiring large physical components, which can be a limitation in compact electronic designs. The design can be further optimized by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values based on the desired timing characteristics, ensuring efficient operation within the specified application parameters. Overall, this circuit exemplifies an effective use of component characteristics to achieve desired timing functions in electronic systems.The timer interval starts when power is applied to circuit and terminates when voltage is applied to load. 2N2646 is used in oscillator which pulses base 2 of D5K This reduces the effective L of D5K and allows a much larger timing resistor and smaller timing capacitor to be used than would otherwise be possible. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713