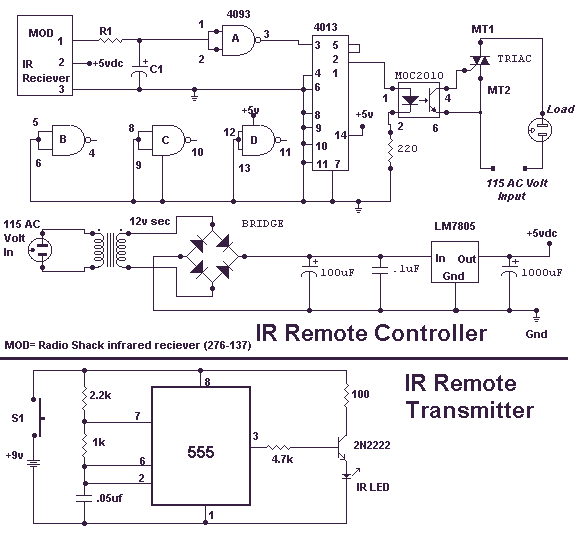
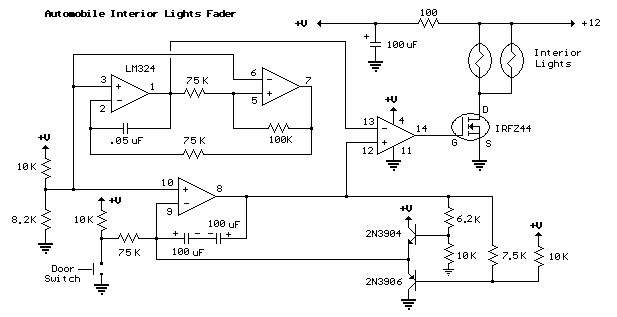
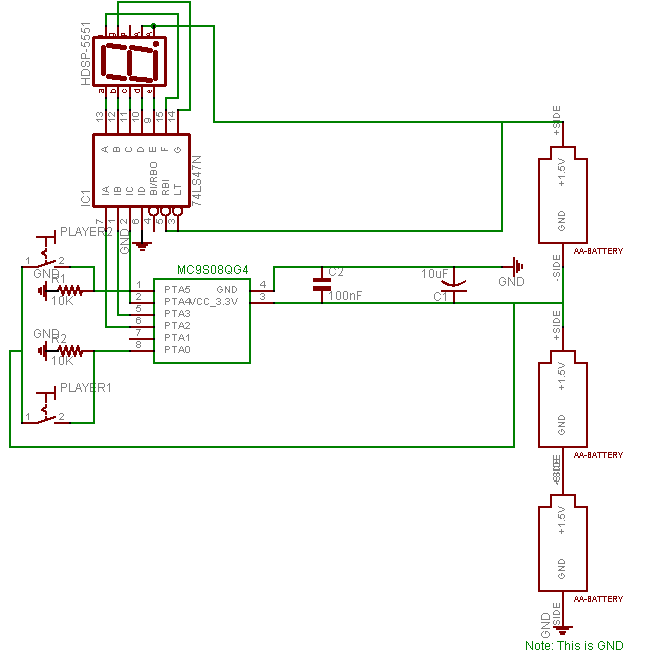
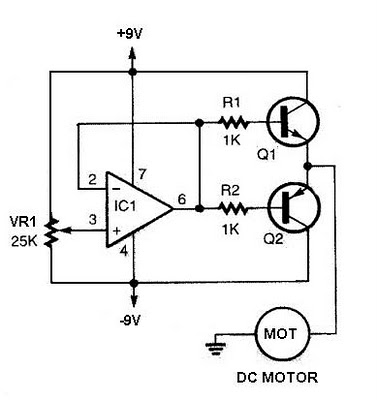
dancing light using 555 timer

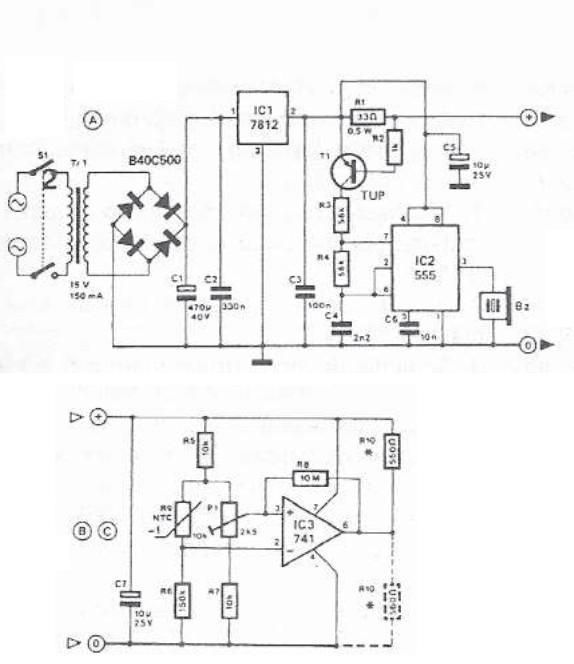
A dancing light can be easily constructed using a 555 timer wired in astable mode. This circuit alternately blinks two LEDs with a certain delay and can be modified to include additional LEDs or to control incandescent lamps. The oscillation time period is determined by the RC time constant of the circuit. The first and eighth pins of the 555 timer are used to provide power (Vcc) and ground (GND), respectively. The fourth pin is the reset pin, which is an active low input and is tied to Vcc to prevent accidental resets. The fifth pin is the control voltage pin, which is not utilized in this application and is therefore grounded through a 0.01 µF capacitor to eliminate high-frequency noise. When the output is high, the capacitor charges to Vcc through resistor R1 and a diode. Conversely, when the output is low, the capacitor discharges through resistor R2 and the discharge pin (pin 7) of the 555 timer. When the output is low (0V), the upper LED lights up, and when the output is high (5V), the lower LED lights up. Instead of current-limiting resistors R3 and R4, another LED may be used in series, allowing two LEDs to operate together. Higher supply voltages can be utilized if more LEDs need to be driven. The LM/NE555 can operate up to 16V, while the SE555 can function up to 18V. The 555 timer can source or sink up to 200mA of current; for higher current requirements, a transistor driver can be employed. This circuit can also be connected to a relay for controlling incandescent lamps. In this configuration, the transistor is wired as a switch; when the base input is high, the transistor turns on, energizing the relay. As the output of the 555 timer generates a square wave, the relay continuously energizes and de-energizes. The incandescent lamps turn on alternately since they are connected to the normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) terminals of the relay output. The LED on/off period is determined by resistors R1, R2, and capacitor C1. These components can be adjusted to modify the time period, which can be calculated using the equation T = 1.1 RC.
This circuit operates effectively in a variety of applications, including decorative lighting, indicators, and simple automated control systems. The 555 timer's versatility allows for easy adjustments to the frequency and duty cycle of the output signal by changing the values of the resistors and capacitor in the RC network. The inclusion of additional LEDs or the use of different types of loads, such as incandescent lamps, expands the potential applications of this circuit.
When implementing this design, careful consideration should be given to the power supply voltage and the current ratings of all components to ensure reliable operation. For instance, when using higher supply voltages, it is crucial to ensure that the 555 timer and any connected components can handle the increased voltage without damage. Additionally, when using the circuit to control larger loads through a relay, it is important to select a relay with appropriate ratings for the voltage and current of the load to be switched.
Overall, this dancing light circuit exemplifies the practical use of the 555 timer in creating dynamic lighting effects and controlling various types of electrical loads, demonstrating its utility in both hobbyist and professional electronic applications.A dancing light can be easily constructed using a 555 timer wired in astable mode. Please read the article Astable Multivibrator using 555 Timer before continuing. This circuit blinks two LEDsalternativelywith some delay and it can be easily modified to include more LEDs or for controllingincandescentlamps. Time period of oscillation is determined by RC time constant of the circuit. 1st and 8th pins of 555 timer are used to provide power, Vcc and GND respectively. 4th is the Reset pin which is a active low input and is tide to Vcc to avoid accidental resets. 5th is the Control Voltage pin which is not used in this application, hence it is grounded via 0. 01 F capacitor to avoid high frequency noises. When the output is HIGH capacitor charges to Vcc via resistor R1 and Diode. When the output is LOW capacitor discharges via resistor R2 and Discharge pin (7th) of 555 timer. When the output is LOW (0V) upper LED glows and when the output is HIGH (5v) lower LED glows. Instead of current limiting resistors R3, R4 you may use another LED, such that two LEDs will come in series. You can use higher supply voltages if you need to drive more LEDs. LM/NE555 can work upto 16V and SE555 can work upto 18V. 555 can source or sinkup to200mA current, if you need more current use a transistor driver. You can also connect this circuit to relay for controllingincandescentlamps as shown below. Here transistor is wired as a switch, when the base input is HIGH transistor turns ON and therelayisenergized.
Since the output of the 555 timer is square wave, the relay energizes and de-energizes continuously. Incandescentlamps turns ON alternatively since they are connected to Normally Open (NO) and Normally Closed (NC) of the realy output. LED ON OFF period is determined by theresistorsR1, R2 and the capacitor C1. You can change these resistors or capacitors to adjust the time period and can be determined by the equation, T = 1.
1RC. 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates effectively in a variety of applications, including decorative lighting, indicators, and simple automated control systems. The 555 timer's versatility allows for easy adjustments to the frequency and duty cycle of the output signal by changing the values of the resistors and capacitor in the RC network. The inclusion of additional LEDs or the use of different types of loads, such as incandescent lamps, expands the potential applications of this circuit.
When implementing this design, careful consideration should be given to the power supply voltage and the current ratings of all components to ensure reliable operation. For instance, when using higher supply voltages, it is crucial to ensure that the 555 timer and any connected components can handle the increased voltage without damage. Additionally, when using the circuit to control larger loads through a relay, it is important to select a relay with appropriate ratings for the voltage and current of the load to be switched.
Overall, this dancing light circuit exemplifies the practical use of the 555 timer in creating dynamic lighting effects and controlling various types of electrical loads, demonstrating its utility in both hobbyist and professional electronic applications.A dancing light can be easily constructed using a 555 timer wired in astable mode. Please read the article Astable Multivibrator using 555 Timer before continuing. This circuit blinks two LEDsalternativelywith some delay and it can be easily modified to include more LEDs or for controllingincandescentlamps. Time period of oscillation is determined by RC time constant of the circuit. 1st and 8th pins of 555 timer are used to provide power, Vcc and GND respectively. 4th is the Reset pin which is a active low input and is tide to Vcc to avoid accidental resets. 5th is the Control Voltage pin which is not used in this application, hence it is grounded via 0. 01 F capacitor to avoid high frequency noises. When the output is HIGH capacitor charges to Vcc via resistor R1 and Diode. When the output is LOW capacitor discharges via resistor R2 and Discharge pin (7th) of 555 timer. When the output is LOW (0V) upper LED glows and when the output is HIGH (5v) lower LED glows. Instead of current limiting resistors R3, R4 you may use another LED, such that two LEDs will come in series. You can use higher supply voltages if you need to drive more LEDs. LM/NE555 can work upto 16V and SE555 can work upto 18V. 555 can source or sinkup to200mA current, if you need more current use a transistor driver. You can also connect this circuit to relay for controllingincandescentlamps as shown below. Here transistor is wired as a switch, when the base input is HIGH transistor turns ON and therelayisenergized.
Since the output of the 555 timer is square wave, the relay energizes and de-energizes continuously. Incandescentlamps turns ON alternatively since they are connected to Normally Open (NO) and Normally Closed (NC) of the realy output. LED ON OFF period is determined by theresistorsR1, R2 and the capacitor C1. You can change these resistors or capacitors to adjust the time period and can be determined by the equation, T = 1.
1RC. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713