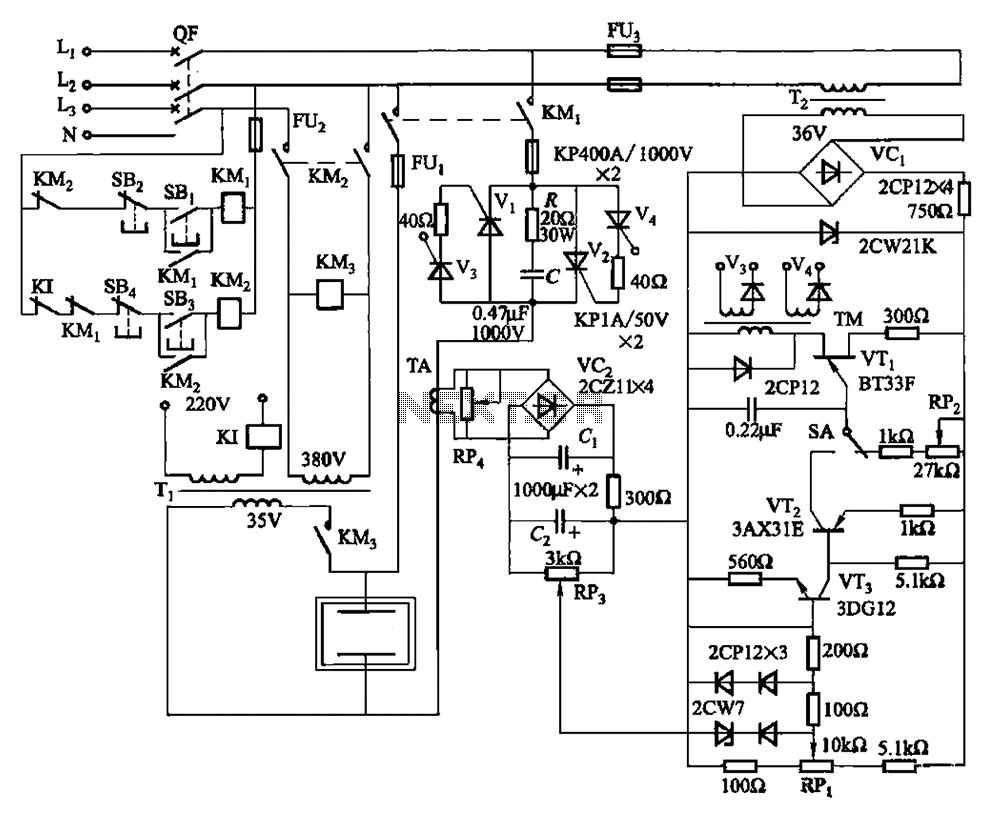
130kW induction motor synchronization control circuit operation
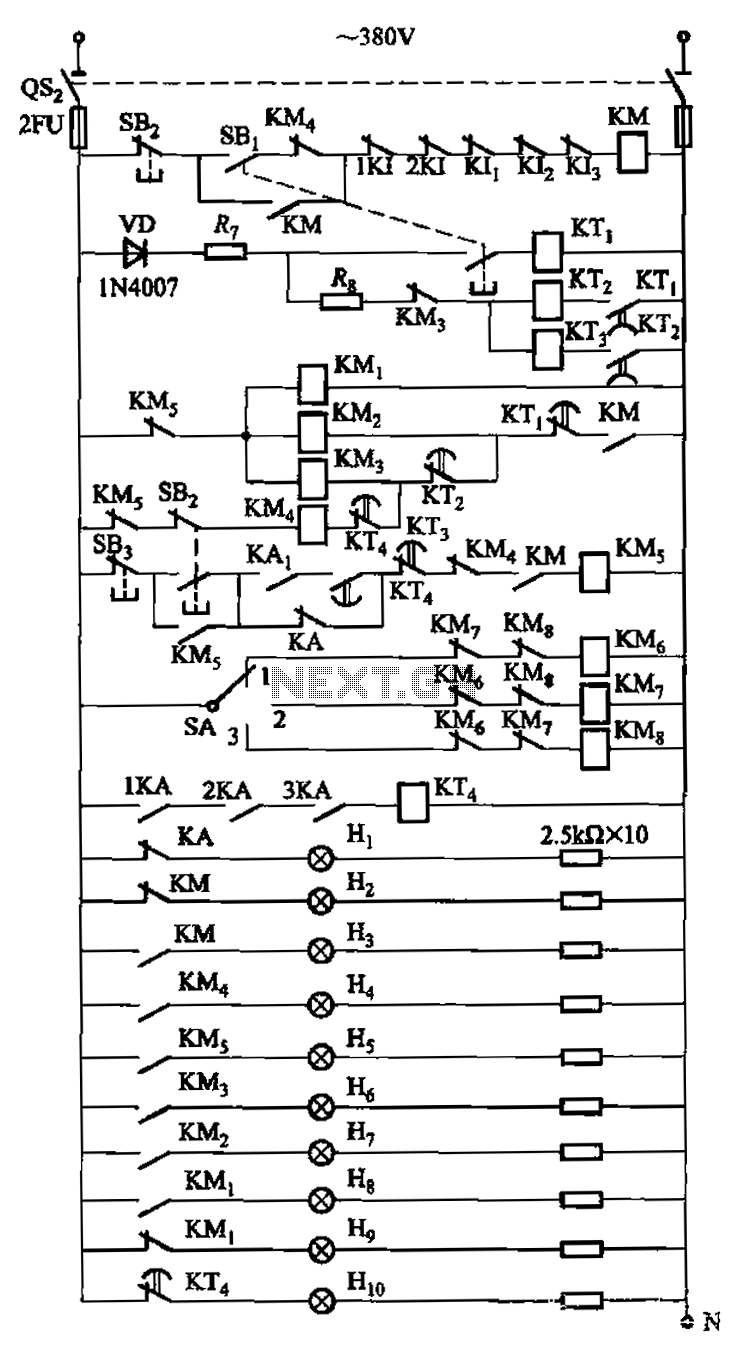
The circuit is illustrated. A motor utilizes series resistance in the rotor winding for starting. The drawing includes electrical velocity off the relay KIi ~ KI3 for motor short circuit protection and overcurrent. Additionally, relays 1KI and 2KI provide electrical overload protection. Voltage relays 1KA ~ 3KA and DC relay KAi ensure synchronous operation, requiring normal excitation voltage. The loss step relay KA2 guarantees that the motor can return to synchronous operation in the event of a loss of step.
The described circuit integrates a motor control system that employs several protective and operational relays to ensure safe and efficient motor performance. The use of series resistance in the rotor winding is a common method for controlling the starting current of the motor, allowing for a gradual increase in speed and torque while minimizing the initial inrush current.
The relays KIi through KI3 function as critical components for motor protection. Specifically, these relays monitor the electrical velocity and are designed to disconnect the motor in case of a short circuit or overcurrent situation, thereby preventing potential damage to the motor and associated circuitry. The inclusion of overload protection relays 1KI and 2KI further enhances the safety of the system by ensuring that the motor does not operate beyond its rated capacity, which could lead to overheating and failure.
Voltage relays 1KA to 3KA and the DC relay KAi are essential for maintaining synchronous operation of the motor. These relays monitor the excitation voltage, which is crucial for the motor to function correctly in synchronous mode. If the excitation voltage falls below the required level, these relays can initiate corrective actions to maintain operational stability.
The loss step relay KA2 plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the motor system. In scenarios where the motor experiences a loss of step—often due to mechanical overload or sudden changes in load—it is imperative that the system can recover quickly. The KA2 relay ensures that the motor can return to its synchronous operation state, thereby enhancing the reliability and performance of the system.
Overall, this circuit design reflects a comprehensive approach to motor control, combining protective measures with operational stability to ensure efficient and safe motor operation in various applications. Circuit is shown. Motor using series resistance in the rotor winding start. Drawing, electrical velocity off the relay KIi ~ KI3 for motor short circuit protection; overcurrent relay 1KI, 2KI electrically motive overload protection; voltage relay 1KA ~ 3KA and DC relay KAi ensure synchronous operation must have normal excitation voltage; loss step relay KA2 ensure that the motor in case of losing step into synchronous operation.
The described circuit integrates a motor control system that employs several protective and operational relays to ensure safe and efficient motor performance. The use of series resistance in the rotor winding is a common method for controlling the starting current of the motor, allowing for a gradual increase in speed and torque while minimizing the initial inrush current.
The relays KIi through KI3 function as critical components for motor protection. Specifically, these relays monitor the electrical velocity and are designed to disconnect the motor in case of a short circuit or overcurrent situation, thereby preventing potential damage to the motor and associated circuitry. The inclusion of overload protection relays 1KI and 2KI further enhances the safety of the system by ensuring that the motor does not operate beyond its rated capacity, which could lead to overheating and failure.
Voltage relays 1KA to 3KA and the DC relay KAi are essential for maintaining synchronous operation of the motor. These relays monitor the excitation voltage, which is crucial for the motor to function correctly in synchronous mode. If the excitation voltage falls below the required level, these relays can initiate corrective actions to maintain operational stability.
The loss step relay KA2 plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the motor system. In scenarios where the motor experiences a loss of step—often due to mechanical overload or sudden changes in load—it is imperative that the system can recover quickly. The KA2 relay ensures that the motor can return to its synchronous operation state, thereby enhancing the reliability and performance of the system.
Overall, this circuit design reflects a comprehensive approach to motor control, combining protective measures with operational stability to ensure efficient and safe motor operation in various applications. Circuit is shown. Motor using series resistance in the rotor winding start. Drawing, electrical velocity off the relay KIi ~ KI3 for motor short circuit protection; overcurrent relay 1KI, 2KI electrically motive overload protection; voltage relay 1KA ~ 3KA and DC relay KAi ensure synchronous operation must have normal excitation voltage; loss step relay KA2 ensure that the motor in case of losing step into synchronous operation.