220v LED DIMMER
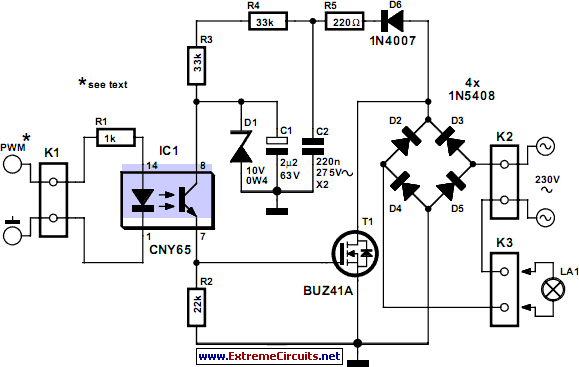
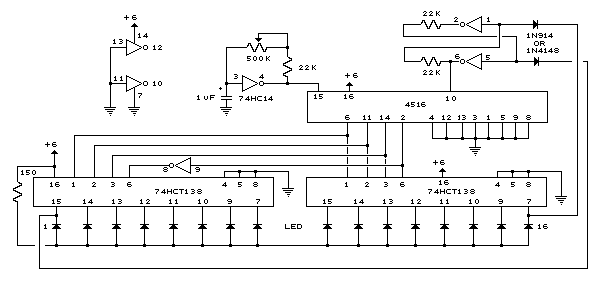
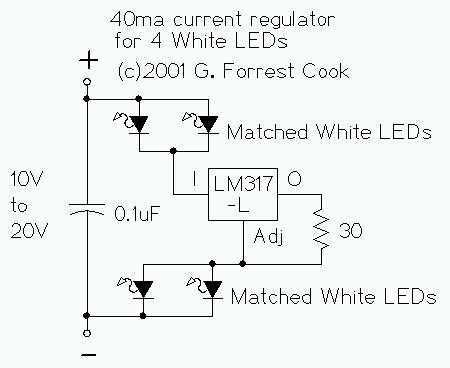
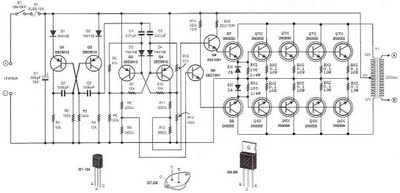
A circuit was discovered in a computer, and there is uncertainty regarding its origin and functionality. The main inquiry is whether this circuit can effectively dim 220V LED bulbs.
The circuit in question likely utilizes a phase control method for dimming, which is a common technique for adjusting the brightness of LED bulbs operating at high voltage levels such as 220V. This method involves controlling the amount of power delivered to the load (in this case, the LED bulbs) by altering the phase of the AC waveform.
A typical dimmer circuit for 220V LED bulbs may consist of several key components: a triac, an opto-isolator, a zero-crossing detector, and a variable resistor (potentiometer). The triac acts as a switch that can be turned on and off at specific points in the AC cycle, allowing for the control of the power delivered to the LED bulbs. The opto-isolator provides electrical isolation between the high-voltage side and the control side of the circuit, ensuring safety and preventing damage to low-voltage components.
The zero-crossing detector is crucial for ensuring that the triac is triggered at the appropriate moment in the AC cycle, which minimizes electrical noise and reduces the risk of flickering in the LED bulbs. The potentiometer allows the user to adjust the resistance, thereby varying the phase angle at which the triac is triggered and enabling smooth dimming of the connected LED bulbs.
It is important to note that not all LED bulbs are compatible with dimming circuits; therefore, it is advisable to use LED bulbs specifically designed for dimming applications to achieve optimal performance. Additionally, the circuit design should be verified for compliance with electrical safety standards to ensure reliable and safe operation when connected to high voltage.Hi everyone! I found this circuit in my computer (i don`t remember where i got it and when) and i was wandering if it`s able to dim 220V LED BULBS? it .. 🔗 External reference
The circuit in question likely utilizes a phase control method for dimming, which is a common technique for adjusting the brightness of LED bulbs operating at high voltage levels such as 220V. This method involves controlling the amount of power delivered to the load (in this case, the LED bulbs) by altering the phase of the AC waveform.
A typical dimmer circuit for 220V LED bulbs may consist of several key components: a triac, an opto-isolator, a zero-crossing detector, and a variable resistor (potentiometer). The triac acts as a switch that can be turned on and off at specific points in the AC cycle, allowing for the control of the power delivered to the LED bulbs. The opto-isolator provides electrical isolation between the high-voltage side and the control side of the circuit, ensuring safety and preventing damage to low-voltage components.
The zero-crossing detector is crucial for ensuring that the triac is triggered at the appropriate moment in the AC cycle, which minimizes electrical noise and reduces the risk of flickering in the LED bulbs. The potentiometer allows the user to adjust the resistance, thereby varying the phase angle at which the triac is triggered and enabling smooth dimming of the connected LED bulbs.
It is important to note that not all LED bulbs are compatible with dimming circuits; therefore, it is advisable to use LED bulbs specifically designed for dimming applications to achieve optimal performance. Additionally, the circuit design should be verified for compliance with electrical safety standards to ensure reliable and safe operation when connected to high voltage.Hi everyone! I found this circuit in my computer (i don`t remember where i got it and when) and i was wandering if it`s able to dim 220V LED BULBS? it .. 🔗 External reference