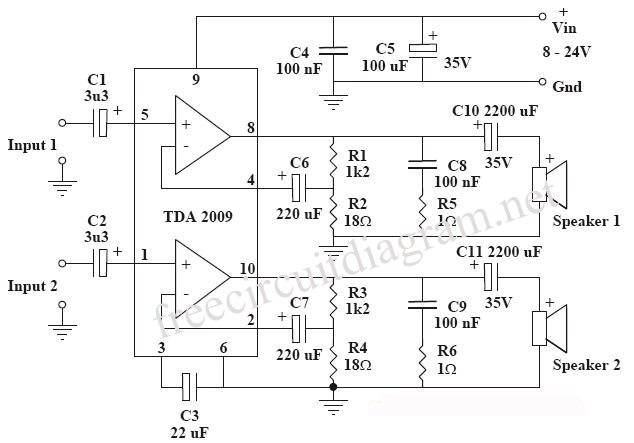
24 Watt Audio Amplifier
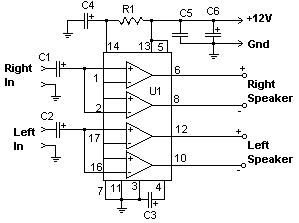
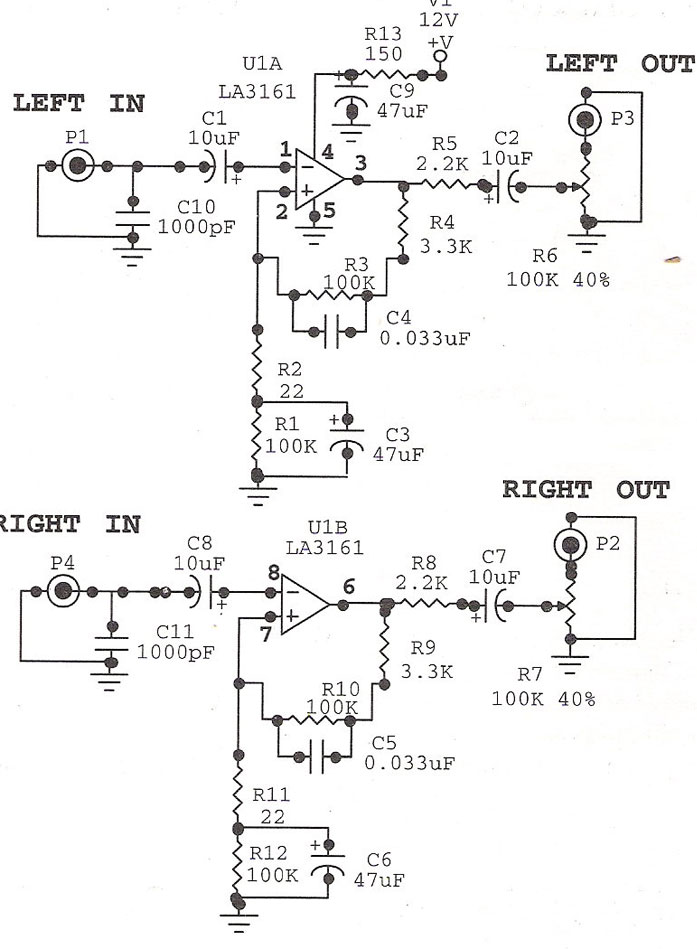
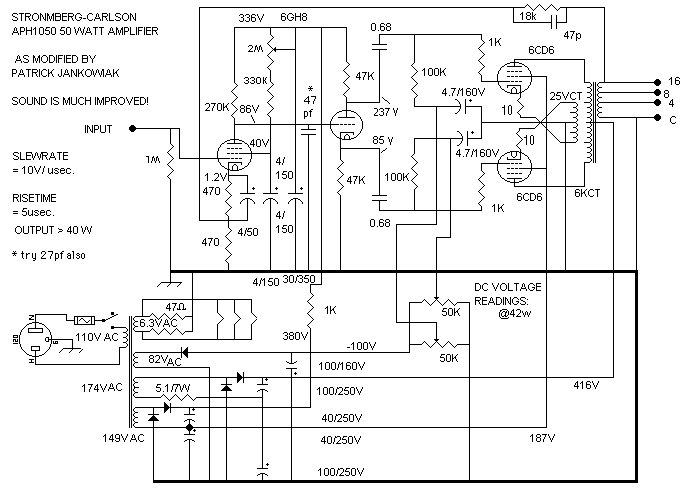
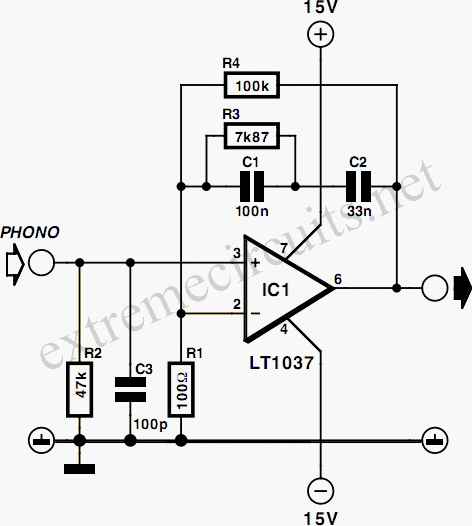
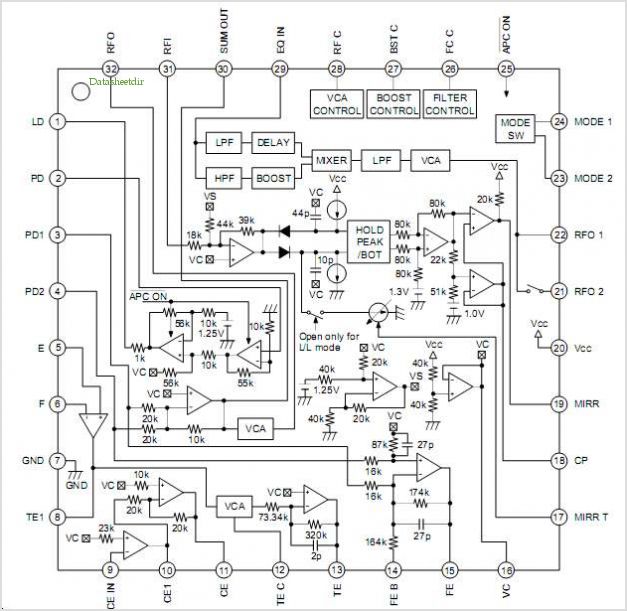
The 24 watt amp is easy to build, and very inexpensive. The circuit can be used as a booster in a car audio system, an amp for satellite speakers in a surround sound or home theater system, or as an amp for computer speakers. The circuit is quite compact and uses only about 60 watts. The circuit works best with 4 ohm speakers, but 8 ohm units will do. The circuit dissipates roughly 28 watts of heat, so a good heatsink is necessary. The chip should run cool enough to touch with the proper heatsink installed.
The 24 watt amplifier circuit is designed to provide efficient audio amplification while maintaining a compact form factor. This amplifier is suitable for various applications, including automotive audio systems, home theater setups, and computer audio enhancements. The circuit operates optimally with 4-ohm speakers, ensuring maximum power transfer and sound quality. However, it is also compatible with 8-ohm speakers, albeit with slightly reduced output power.
The amplifier's design incorporates a power supply that consumes approximately 60 watts to deliver the desired 24 watts of output power. This indicates a relatively efficient design, but it also results in significant heat generation, approximately 28 watts. To manage this thermal output, the use of a robust heatsink is essential. The heatsink must be designed to dissipate heat effectively, allowing the amplifier to operate within safe temperature limits while ensuring it remains cool enough to touch.
Key components of the circuit may include an operational amplifier or a dedicated audio amplifier IC, along with passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and possibly inductors to filter and stabilize the audio signal. The layout of these components should be carefully considered to minimize signal interference and maximize performance. Additionally, the power supply design should be capable of delivering stable voltage and current to prevent distortion during operation.
Overall, this amplifier circuit represents an economical and efficient solution for enhancing audio systems across various platforms, providing users with a reliable means to achieve high-quality sound reproduction.The 24 watt amp is easy to build, and very inexpensive. The circuit can be used as a booster in a car audio system, an amp for satellite speakers in a surround sound or home theater system, or as an amp for computer speakers. The circuit is quite compact and uses only about 60 watts. 1. The circuit works best with 4 ohm speakers, but 8 ohm units will do. 2. The circuit dissipates roughly 28 watts of heat, so a good heatsink is necessary. The chip should run cool enough to touch with the proper heatsink installed. 3. The circuit 🔗 External reference
The 24 watt amplifier circuit is designed to provide efficient audio amplification while maintaining a compact form factor. This amplifier is suitable for various applications, including automotive audio systems, home theater setups, and computer audio enhancements. The circuit operates optimally with 4-ohm speakers, ensuring maximum power transfer and sound quality. However, it is also compatible with 8-ohm speakers, albeit with slightly reduced output power.
The amplifier's design incorporates a power supply that consumes approximately 60 watts to deliver the desired 24 watts of output power. This indicates a relatively efficient design, but it also results in significant heat generation, approximately 28 watts. To manage this thermal output, the use of a robust heatsink is essential. The heatsink must be designed to dissipate heat effectively, allowing the amplifier to operate within safe temperature limits while ensuring it remains cool enough to touch.
Key components of the circuit may include an operational amplifier or a dedicated audio amplifier IC, along with passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and possibly inductors to filter and stabilize the audio signal. The layout of these components should be carefully considered to minimize signal interference and maximize performance. Additionally, the power supply design should be capable of delivering stable voltage and current to prevent distortion during operation.
Overall, this amplifier circuit represents an economical and efficient solution for enhancing audio systems across various platforms, providing users with a reliable means to achieve high-quality sound reproduction.The 24 watt amp is easy to build, and very inexpensive. The circuit can be used as a booster in a car audio system, an amp for satellite speakers in a surround sound or home theater system, or as an amp for computer speakers. The circuit is quite compact and uses only about 60 watts. 1. The circuit works best with 4 ohm speakers, but 8 ohm units will do. 2. The circuit dissipates roughly 28 watts of heat, so a good heatsink is necessary. The chip should run cool enough to touch with the proper heatsink installed. 3. The circuit 🔗 External reference