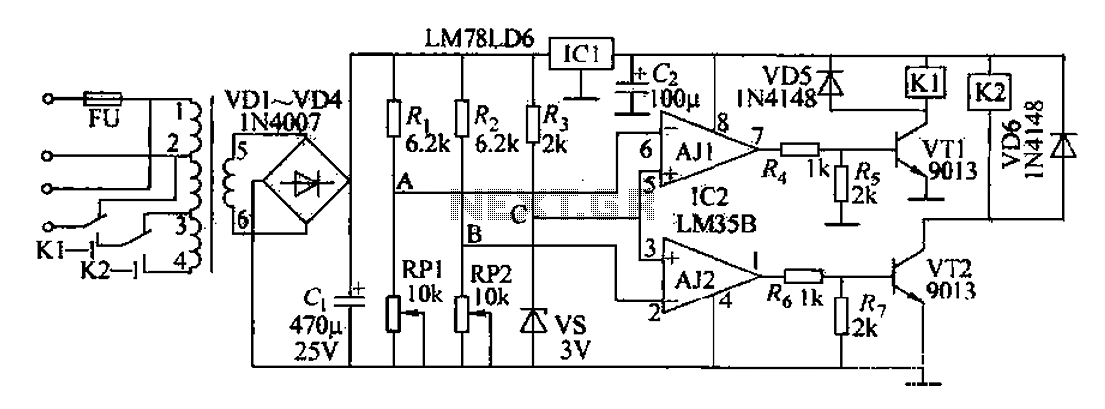
24V to 36V Battery Charger Circuit
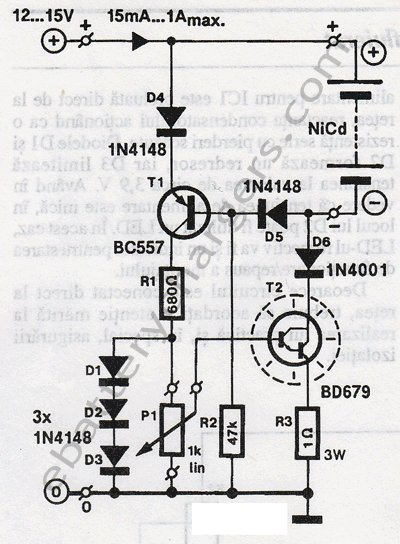
This 24V to 36V linear battery charger is long overdue. While this is an old circuit technique, it is optimized for charging higher voltage lead-acid batteries.
The 24V to 36V linear battery charger is designed to provide a stable charging voltage suitable for higher voltage lead-acid batteries. The circuit employs a linear regulation method, which, despite being an older technique, offers advantages such as simplicity and reliability.
The charger typically comprises a transformer, rectifier, filter capacitors, and a linear voltage regulator. The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging. The rectifier, usually a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage to DC. Filter capacitors smooth out the rectified voltage to minimize ripple, ensuring a steady DC output.
The linear voltage regulator is the core component that maintains the output voltage within the specified range of 24V to 36V. It operates by dissipating excess voltage as heat, which necessitates the use of a heat sink to prevent overheating during operation. The output voltage can be adjusted using a feedback mechanism, allowing for precise control over the charging process.
Additionally, incorporating protection mechanisms such as over-voltage, over-current, and thermal shutdown features is essential to safeguard both the charger and the battery being charged. These safety features help prevent damage due to incorrect voltage levels or excessive current flow, which can lead to battery degradation or failure.
Overall, this linear battery charger design is suitable for applications requiring reliable and efficient charging of higher voltage lead-acid batteries, making it a valuable solution in various electronic and automotive applications.This 24V to 36V linear battery charger is long overdue. While this is an old circuit technique, it is optimized for charging higher voltage lead-acid batte.. 🔗 External reference
The 24V to 36V linear battery charger is designed to provide a stable charging voltage suitable for higher voltage lead-acid batteries. The circuit employs a linear regulation method, which, despite being an older technique, offers advantages such as simplicity and reliability.
The charger typically comprises a transformer, rectifier, filter capacitors, and a linear voltage regulator. The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging. The rectifier, usually a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage to DC. Filter capacitors smooth out the rectified voltage to minimize ripple, ensuring a steady DC output.
The linear voltage regulator is the core component that maintains the output voltage within the specified range of 24V to 36V. It operates by dissipating excess voltage as heat, which necessitates the use of a heat sink to prevent overheating during operation. The output voltage can be adjusted using a feedback mechanism, allowing for precise control over the charging process.
Additionally, incorporating protection mechanisms such as over-voltage, over-current, and thermal shutdown features is essential to safeguard both the charger and the battery being charged. These safety features help prevent damage due to incorrect voltage levels or excessive current flow, which can lead to battery degradation or failure.
Overall, this linear battery charger design is suitable for applications requiring reliable and efficient charging of higher voltage lead-acid batteries, making it a valuable solution in various electronic and automotive applications.This 24V to 36V linear battery charger is long overdue. While this is an old circuit technique, it is optimized for charging higher voltage lead-acid batte.. 🔗 External reference