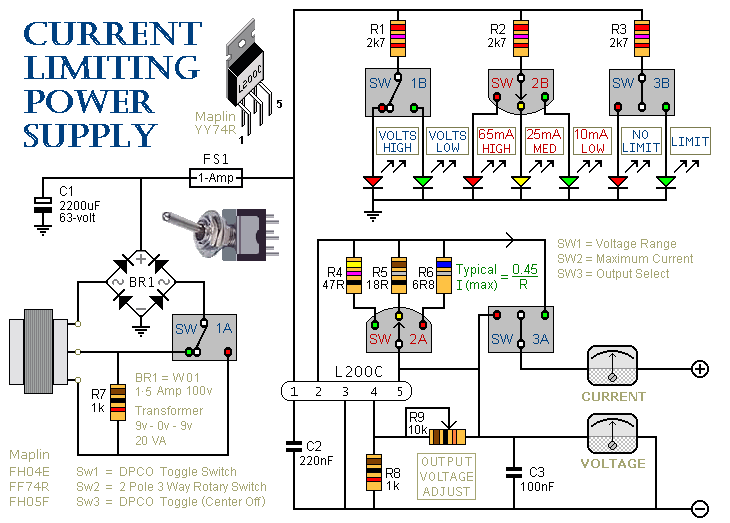
25W Class-A Hi-Fi Power Amplifier
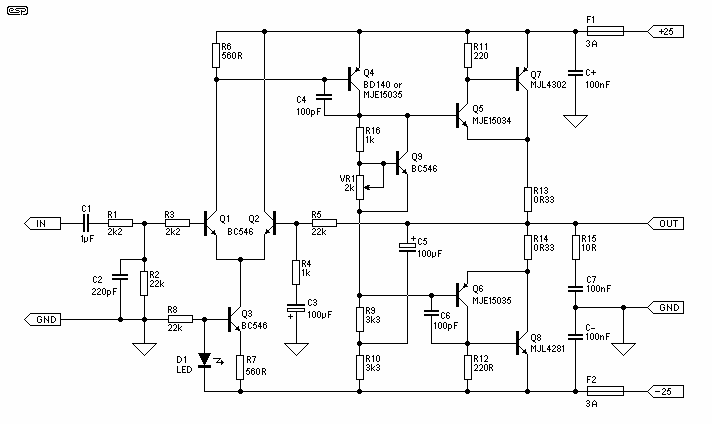
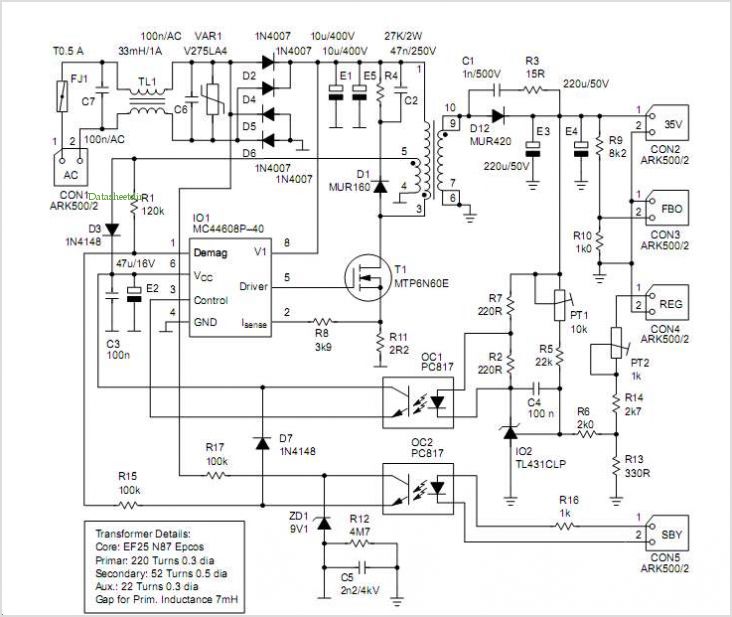
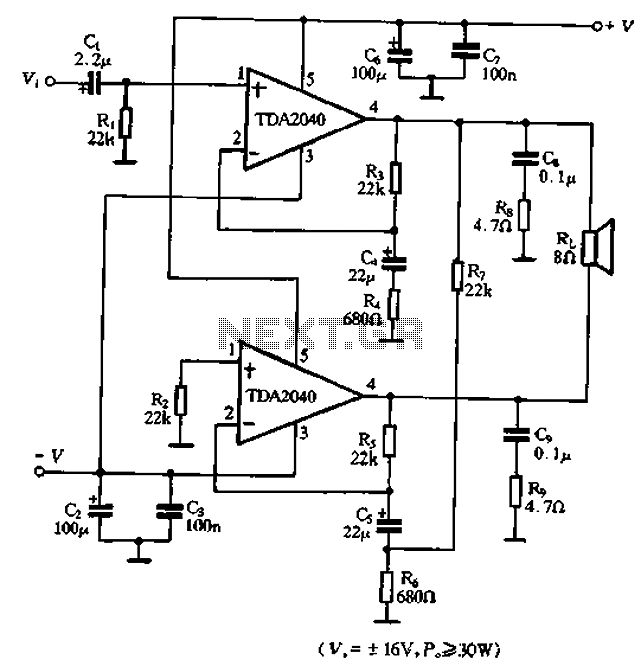
The basis for this amplifier has been around now for several years as Project 3A, and requires only relatively small modifications to be able to operate in Class-A. The biggest change is in output power (reduced dramatically from the 60-100W of the Class-AB version), but at 25W is still more than enough for many people.
The amplifier, known as Project 3A, has been designed to operate in Class-A mode with only minor adjustments necessary. Class-A amplifiers are characterized by their output devices always being active, regardless of the output signal amplitude. This leads to a very linear output but with lower efficiency compared to other classes of amplifiers.
The most significant alteration in this version of the amplifier is the reduction in output power. Originally, the Class-AB version of this amplifier could produce between 60-100W. However, in the Class-A version, this has been dramatically decreased to 25W. Despite this reduction, 25W is still a considerable amount of power and is more than sufficient for many users' needs.
The output power of an amplifier is a critical factor as it determines the maximum volume that can be achieved. However, it's worth noting that doubling the power does not double the volume. Therefore, while the output power of this Class-A version is significantly less than its Class-AB counterpart, the difference in perceived volume may not be as substantial as the numbers suggest.
This amplifier, therefore, represents a balance between performance and power consumption. While it may not deliver the same power as its Class-AB version, it provides a more linear output, which can result in a cleaner, more accurate sound reproduction. This makes it an ideal choice for audiophiles and those who prioritize sound quality over volume.The basis for this amplifier has been around now for several years as Project 3A, and requires only relatively small modifications to be able to operate in Class-A. The biggest change is in output power (reduced dramatically from the 60-100W of the Class-AB version), but at 25W is still more than enough for many people.
🔗 External reference
The amplifier, known as Project 3A, has been designed to operate in Class-A mode with only minor adjustments necessary. Class-A amplifiers are characterized by their output devices always being active, regardless of the output signal amplitude. This leads to a very linear output but with lower efficiency compared to other classes of amplifiers.
The most significant alteration in this version of the amplifier is the reduction in output power. Originally, the Class-AB version of this amplifier could produce between 60-100W. However, in the Class-A version, this has been dramatically decreased to 25W. Despite this reduction, 25W is still a considerable amount of power and is more than sufficient for many users' needs.
The output power of an amplifier is a critical factor as it determines the maximum volume that can be achieved. However, it's worth noting that doubling the power does not double the volume. Therefore, while the output power of this Class-A version is significantly less than its Class-AB counterpart, the difference in perceived volume may not be as substantial as the numbers suggest.
This amplifier, therefore, represents a balance between performance and power consumption. While it may not deliver the same power as its Class-AB version, it provides a more linear output, which can result in a cleaner, more accurate sound reproduction. This makes it an ideal choice for audiophiles and those who prioritize sound quality over volume.The basis for this amplifier has been around now for several years as Project 3A, and requires only relatively small modifications to be able to operate in Class-A. The biggest change is in output power (reduced dramatically from the 60-100W of the Class-AB version), but at 25W is still more than enough for many people.
🔗 External reference