Pure CL B amplifier circuit
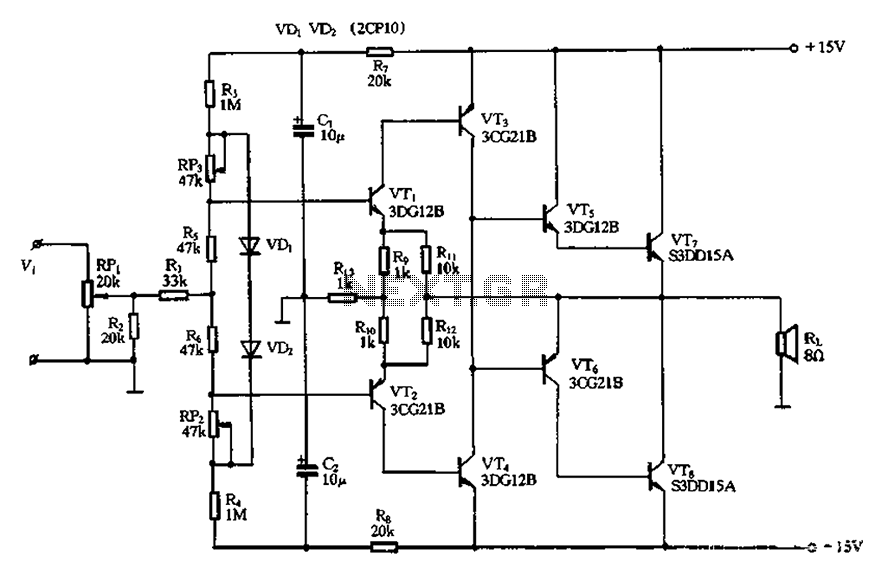
The circuit utilizes diode VDi, f Pooh to stabilize the base bias of transistors VTi and VT2, ensuring a more stable quiescent point when the supply voltage is within a specific range. In the event of temperature fluctuations, the two transistors, which are PN junction devices, will experience temperature changes in the same direction, providing compensation and protecting the circuit's temperature stability. Capacitors C1 and C2, along with resistor R7, form the input stage bias filter network designed to minimize hum noise in the input circuit. Experimental results indicate a significant difference in circuit performance with and without this filtering. Transistors VT3 to VT8 create a composite quasi-complementary push-pull output stage that has been calibrated to ensure that in the absence of an input signal, the output transistors remain in the OFF state, effectively maintaining a pure Class B operation. When a signal is present, transistors VT3 and VT4 supply current to the bases of VTs and VT6, thereby preventing distortion caused by input voltage dead zones in the transistors. For circuit debugging, two individuals utilize a power multimeter, one connected to the output terminals and the other to a speaker, while adjusting resistor RP1 to ground. Resistor RP3 is set to maximum resistance, and adjustments are made to RP2 and RP3 to ensure that the output circuit current reading remains at zero during the calibration process. The goal is to achieve a supply current reading of 2 to 2.5 mA.
The described circuit effectively stabilizes the operating conditions of the transistors through the use of temperature compensation and biasing techniques. The inclusion of diode VDi serves as a critical element in maintaining the base bias for VTi and VT2, which is essential for ensuring reliable transistor operation across varying supply voltages. The temperature stability offered by the circuit is particularly important in applications where ambient conditions may fluctuate, as it prevents performance degradation that could arise from thermal drift.
Capacitors C1 and C2, in conjunction with resistor R7, play a vital role in filtering out unwanted noise from the input signal. This noise reduction is crucial for high-fidelity audio applications, where any hum or interference can significantly impact sound quality. The experimental findings highlight the importance of this filtering stage, demonstrating that the circuit's performance can vary dramatically based on whether this filtering is implemented.
The quasi-complementary push-pull output stage formed by transistors VT3 through VT8 is designed to operate efficiently in a Class B configuration. This configuration is advantageous for audio amplification as it minimizes power dissipation during idle periods, thereby enhancing overall efficiency. The careful calibration of the output stage ensures that the transistors remain off when no signal is present, which is critical for preventing crossover distortion that can occur in push-pull amplifiers.
During the debugging process, the use of a multimeter allows for precise monitoring of output current, ensuring that adjustments to the circuit do not lead to unintended consequences. Setting RP3 to maximum resistance and adjusting RP2 and RP3 to achieve a zero output current serves as a methodical approach to calibrating the circuit, ensuring that it operates within the desired parameters. The target supply current of 2 to 2.5 mA is indicative of the circuit's readiness for optimal performance, balancing power consumption with the need for effective amplification. Circuit, the diode VDi, f Pooh is used to stabilize VTi, VT2 base bias, so that when the supply voltage in a certain range, VTi, VT2 a more stable quiescent point. If there is a temperature change at the same time, since the two grant tube PN junction transistor PN junction temperature changes and changes in the same direction, can play a role in compensation, protection temperature stability of the circuit. C1, R7 and C2, who constitute the input stage bias strip of filter networks to reduce hum noise input circuit.
Experiments show that the circuit access or not, the effect is quite different. VTs ~ VT8 constituting the composite quasi-complementary push-pull output stage, has been adjusted so that the static Jo /C4, therefore, in the absence of the letter when, and outputs the tubes are in the OFF state, that is pure B state. When a signal is output VT3, VT4 the form of a current applied to the VTs, VT6 base, thus avoiding the post due to the transistor input voltage dead zone caused by the distortion.
Circuit debug: two people are the power multimeter a string, a string of people between the output terminals and the speaker will RPi rotation to ground, build) 2, RP3 maximum resistance to rotation end power. While adjusting RP2, RP3t and adjusted so that the process has remained the string table in the output circuit current reading is zero.
When adjusted to supply current table is 2- 2 5mA to o
The described circuit effectively stabilizes the operating conditions of the transistors through the use of temperature compensation and biasing techniques. The inclusion of diode VDi serves as a critical element in maintaining the base bias for VTi and VT2, which is essential for ensuring reliable transistor operation across varying supply voltages. The temperature stability offered by the circuit is particularly important in applications where ambient conditions may fluctuate, as it prevents performance degradation that could arise from thermal drift.
Capacitors C1 and C2, in conjunction with resistor R7, play a vital role in filtering out unwanted noise from the input signal. This noise reduction is crucial for high-fidelity audio applications, where any hum or interference can significantly impact sound quality. The experimental findings highlight the importance of this filtering stage, demonstrating that the circuit's performance can vary dramatically based on whether this filtering is implemented.
The quasi-complementary push-pull output stage formed by transistors VT3 through VT8 is designed to operate efficiently in a Class B configuration. This configuration is advantageous for audio amplification as it minimizes power dissipation during idle periods, thereby enhancing overall efficiency. The careful calibration of the output stage ensures that the transistors remain off when no signal is present, which is critical for preventing crossover distortion that can occur in push-pull amplifiers.
During the debugging process, the use of a multimeter allows for precise monitoring of output current, ensuring that adjustments to the circuit do not lead to unintended consequences. Setting RP3 to maximum resistance and adjusting RP2 and RP3 to achieve a zero output current serves as a methodical approach to calibrating the circuit, ensuring that it operates within the desired parameters. The target supply current of 2 to 2.5 mA is indicative of the circuit's readiness for optimal performance, balancing power consumption with the need for effective amplification. Circuit, the diode VDi, f Pooh is used to stabilize VTi, VT2 base bias, so that when the supply voltage in a certain range, VTi, VT2 a more stable quiescent point. If there is a temperature change at the same time, since the two grant tube PN junction transistor PN junction temperature changes and changes in the same direction, can play a role in compensation, protection temperature stability of the circuit. C1, R7 and C2, who constitute the input stage bias strip of filter networks to reduce hum noise input circuit.
Experiments show that the circuit access or not, the effect is quite different. VTs ~ VT8 constituting the composite quasi-complementary push-pull output stage, has been adjusted so that the static Jo /C4, therefore, in the absence of the letter when, and outputs the tubes are in the OFF state, that is pure B state. When a signal is output VT3, VT4 the form of a current applied to the VTs, VT6 base, thus avoiding the post due to the transistor input voltage dead zone caused by the distortion.
Circuit debug: two people are the power multimeter a string, a string of people between the output terminals and the speaker will RPi rotation to ground, build) 2, RP3 maximum resistance to rotation end power. While adjusting RP2, RP3t and adjusted so that the process has remained the string table in the output circuit current reading is zero.
When adjusted to supply current table is 2- 2 5mA to o