3 Band Graphic Equalizer
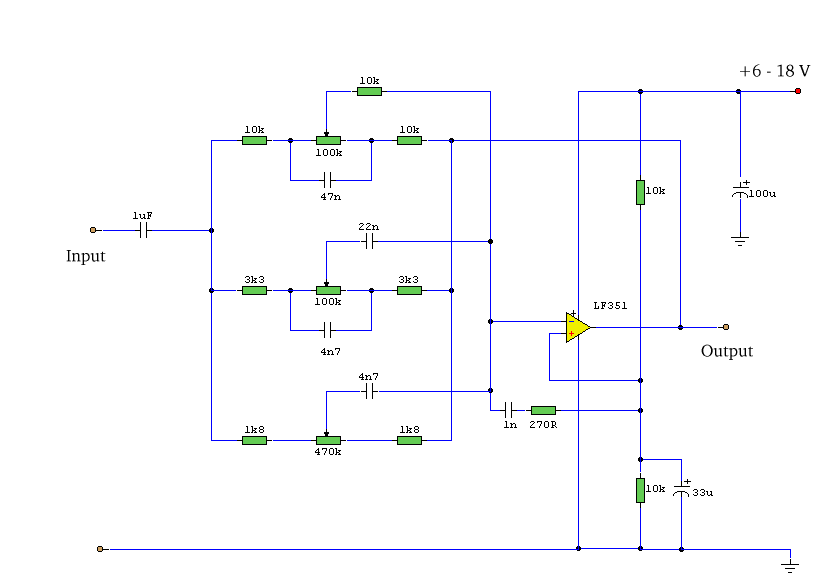
This simple equalizer utilizes a single operational amplifier (op-amp) and provides three frequency ranges: low frequency, mid frequency, and high frequency. With the specified component values, it achieves approximately ±20 dB of gain or attenuation at frequencies of 50 Hz, 1 kHz, and 10 kHz. The supply voltage can range from 6 to 30 volts, with the maximum boost of 20 dB being attainable only at a supply voltage of 18 volts.
The circuit employs a single op-amp configured in a non-inverting amplifier configuration, allowing for both gain and attenuation adjustments. The frequency response is shaped by passive components, including resistors and capacitors, which define the cutoff frequencies for each band. The low-frequency range is centered around 50 Hz, the mid-frequency range is centered around 1 kHz, and the high-frequency range is centered around 10 kHz.
The design incorporates a potentiometer for each frequency band, enabling users to adjust the gain or cut smoothly. This allows for fine-tuning of the audio signal based on personal preference or specific audio requirements. The op-amp's feedback network is configured to achieve the desired gain levels while maintaining stability and minimizing distortion.
Power supply considerations are crucial in this design. The op-amp can operate within a wide voltage range, making it versatile for various applications. However, to achieve the full ±20 dB boost, an 18-volt supply is necessary. Lower supply voltages will reduce the maximum achievable gain, which should be taken into account during circuit implementation.
In summary, this equalizer circuit is an effective solution for audio signal processing, providing adjustable gain across three distinct frequency ranges while being simple to construct and adaptable to different power supply conditions.Using a single op-amp this easy to make equalizer offers three ranges, low frequency, mid frequency, and high. With component values shown there is approximately +/-20dB of boost or cut at frequencies of 50Hz, 1kHz and 10kHz.
Supply voltage may be anything from 6 to 30 Volts. Maximum boost 20dB is only realized with maximum supply voltage of 18 Volt . 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs a single op-amp configured in a non-inverting amplifier configuration, allowing for both gain and attenuation adjustments. The frequency response is shaped by passive components, including resistors and capacitors, which define the cutoff frequencies for each band. The low-frequency range is centered around 50 Hz, the mid-frequency range is centered around 1 kHz, and the high-frequency range is centered around 10 kHz.
The design incorporates a potentiometer for each frequency band, enabling users to adjust the gain or cut smoothly. This allows for fine-tuning of the audio signal based on personal preference or specific audio requirements. The op-amp's feedback network is configured to achieve the desired gain levels while maintaining stability and minimizing distortion.
Power supply considerations are crucial in this design. The op-amp can operate within a wide voltage range, making it versatile for various applications. However, to achieve the full ±20 dB boost, an 18-volt supply is necessary. Lower supply voltages will reduce the maximum achievable gain, which should be taken into account during circuit implementation.
In summary, this equalizer circuit is an effective solution for audio signal processing, providing adjustable gain across three distinct frequency ranges while being simple to construct and adaptable to different power supply conditions.Using a single op-amp this easy to make equalizer offers three ranges, low frequency, mid frequency, and high. With component values shown there is approximately +/-20dB of boost or cut at frequencies of 50Hz, 1kHz and 10kHz.
Supply voltage may be anything from 6 to 30 Volts. Maximum boost 20dB is only realized with maximum supply voltage of 18 Volt . 🔗 External reference