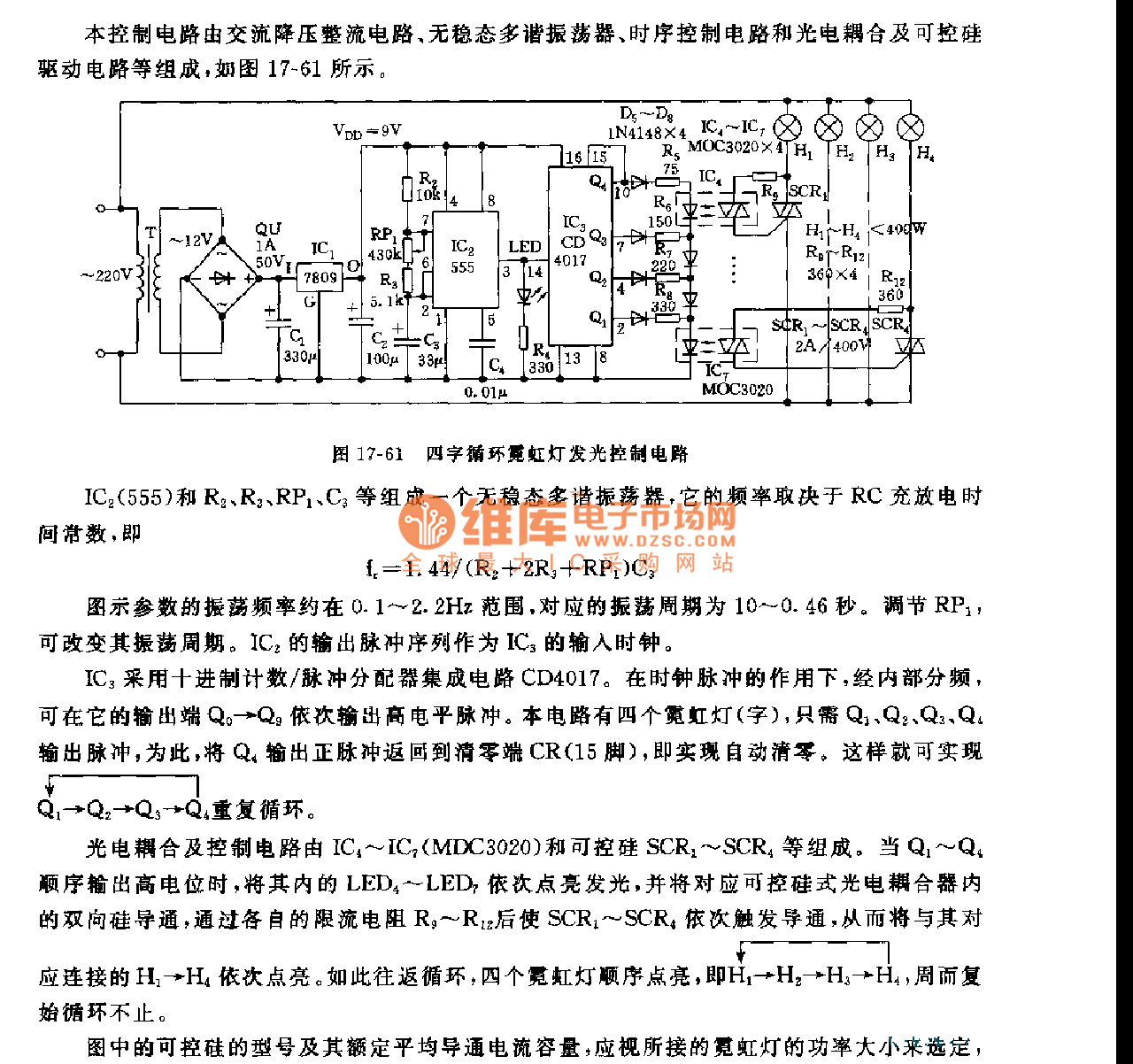
50 watt power MOSFET amplifier circuit diagram
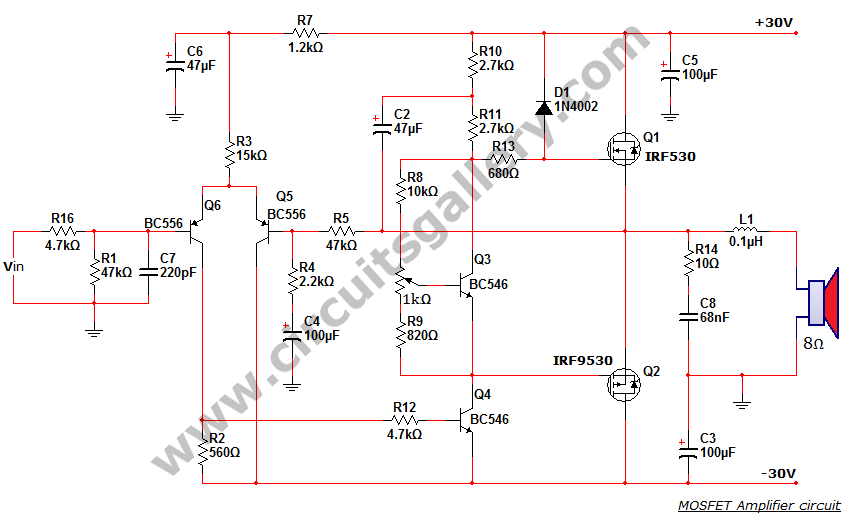
This is a MOSFET transistor-based power amplifier circuit that operates within a voltage range of +35V to -35V. The input voltage is pre-filtered and pre-amplified before being applied to the MOSFET switch. The pre-audio amplifier consists of a differential amplifier section utilizing a PNP transistor. A differential amplifier is a type of power amplifier with two differential inputs that amplify the difference between two input signals. This discussion focuses on the circuit diagram and operation of a high-voltage differential amplifier using the IRF9530 and IRF530 MOSFETs. A dual power supply circuit is required for this amplifier, which has been posted previously.
The described MOSFET-based power amplifier circuit is designed to efficiently amplify audio signals while maintaining high fidelity and low distortion. The operational range of +35V to -35V allows for significant headroom, making the circuit suitable for high-power applications.
At the input stage, the pre-filtering and pre-amplification processes are critical for ensuring that the signal fed into the MOSFET switch is clean and free from noise. The differential amplifier section, which employs a PNP transistor, serves to amplify the difference between two input signals, effectively enhancing the overall signal quality. This is particularly advantageous in audio applications where signal integrity is paramount.
The choice of MOSFETs, specifically the IRF9530 and IRF530, is essential for the amplifier's performance. These components are known for their high efficiency and capability to handle substantial power levels, making them ideal for use in a high-voltage differential amplifier configuration. The IRF9530 is a P-channel MOSFET, while the IRF530 is an N-channel MOSFET, allowing for complementary operation in the amplifier circuit.
To implement this amplifier, a dual power supply circuit is necessary to provide the required positive and negative voltage rails. This dual supply configuration is crucial for the proper biasing of the MOSFETs and ensures that the amplifier can handle both the positive and negative cycles of the input audio signal without distortion.
In summary, this MOSFET power amplifier circuit is a sophisticated design that leverages a differential amplifier configuration to enhance audio signal quality. The use of high-performance MOSFETs and a dual power supply makes it suitable for demanding audio amplification tasks, ensuring reliable operation across its specified voltage range.This is a MOSFET transistor based power amplifier circuit that can be operated between +35V to -35V range. The input voltage is pre filtered and pre amplified before applying to the MOSFET switch. The pre audio amplifier is a differential amplifier section with PNP transistor. What is differential amplifier A difference amplifier is a type of powe r amp with two differential inputs which amplify the difference between two input signals. Here we are dealing with the circuit diagram and working of high voltage differential amplifier using IRF9530 and IRF530 MOSFET. You need a dual power supply circuit for this amplifier which I had posted earlier. 🔗 External reference
The described MOSFET-based power amplifier circuit is designed to efficiently amplify audio signals while maintaining high fidelity and low distortion. The operational range of +35V to -35V allows for significant headroom, making the circuit suitable for high-power applications.
At the input stage, the pre-filtering and pre-amplification processes are critical for ensuring that the signal fed into the MOSFET switch is clean and free from noise. The differential amplifier section, which employs a PNP transistor, serves to amplify the difference between two input signals, effectively enhancing the overall signal quality. This is particularly advantageous in audio applications where signal integrity is paramount.
The choice of MOSFETs, specifically the IRF9530 and IRF530, is essential for the amplifier's performance. These components are known for their high efficiency and capability to handle substantial power levels, making them ideal for use in a high-voltage differential amplifier configuration. The IRF9530 is a P-channel MOSFET, while the IRF530 is an N-channel MOSFET, allowing for complementary operation in the amplifier circuit.
To implement this amplifier, a dual power supply circuit is necessary to provide the required positive and negative voltage rails. This dual supply configuration is crucial for the proper biasing of the MOSFETs and ensures that the amplifier can handle both the positive and negative cycles of the input audio signal without distortion.
In summary, this MOSFET power amplifier circuit is a sophisticated design that leverages a differential amplifier configuration to enhance audio signal quality. The use of high-performance MOSFETs and a dual power supply makes it suitable for demanding audio amplification tasks, ensuring reliable operation across its specified voltage range.This is a MOSFET transistor based power amplifier circuit that can be operated between +35V to -35V range. The input voltage is pre filtered and pre amplified before applying to the MOSFET switch. The pre audio amplifier is a differential amplifier section with PNP transistor. What is differential amplifier A difference amplifier is a type of powe r amp with two differential inputs which amplify the difference between two input signals. Here we are dealing with the circuit diagram and working of high voltage differential amplifier using IRF9530 and IRF530 MOSFET. You need a dual power supply circuit for this amplifier which I had posted earlier. 🔗 External reference