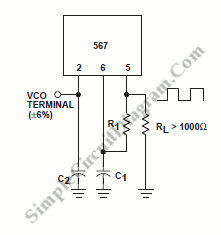
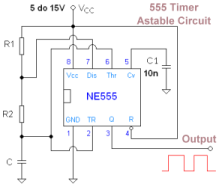
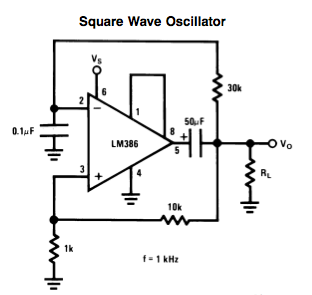
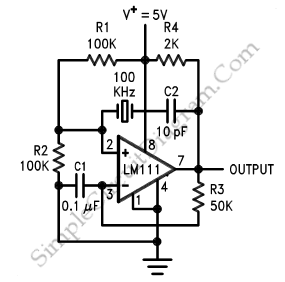
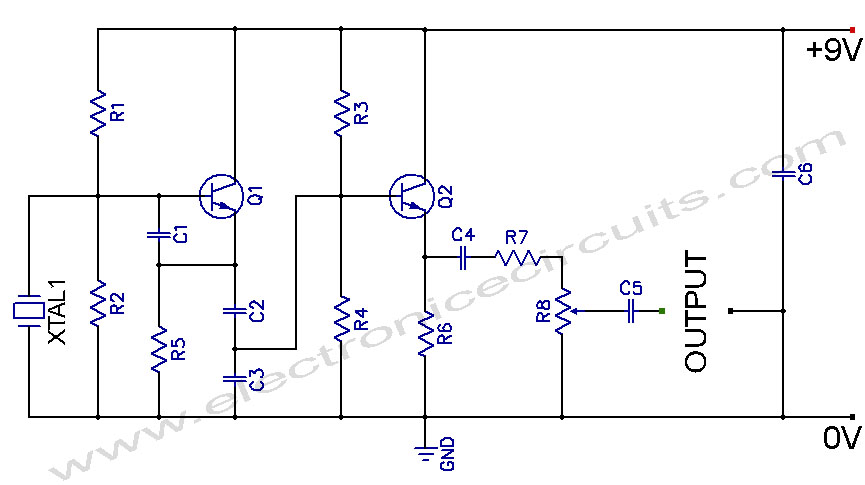
50Khz oscillator
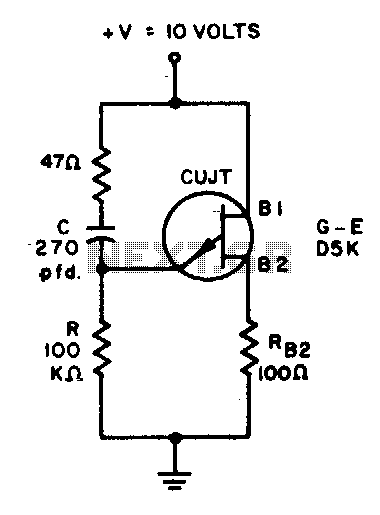
A 50 kHz circuit is feasible due to its nearly ideal characteristics.
The 50 kHz circuit is designed to operate effectively within that frequency range, leveraging components that exhibit minimal parasitic effects and optimal linearity. The circuit may include elements such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, carefully selected to ensure that they contribute to the desired frequency response without introducing significant distortion or attenuation.
In such a circuit, the choice of active components, such as operational amplifiers or transistors, is critical. These components should have high gain-bandwidth products, allowing them to maintain performance at higher frequencies. The layout of the circuit board is also essential; minimizing trace lengths and avoiding sharp corners can reduce inductive and capacitive coupling, which can adversely affect circuit performance at 50 kHz.
Additionally, the power supply design is crucial for maintaining stable operation. A well-regulated power supply can prevent voltage fluctuations that may lead to frequency drift or instability. Bypass capacitors should be placed close to the power pins of active devices to filter out high-frequency noise.
Overall, the design of a 50 kHz circuit requires careful consideration of component selection, layout, and power supply management to achieve the nearly ideal characteristics that enable reliable operation at this frequency.A 50 kHz circuit is possible because of the more nearly ideal characteristics. The circuit shown.
The 50 kHz circuit is designed to operate effectively within that frequency range, leveraging components that exhibit minimal parasitic effects and optimal linearity. The circuit may include elements such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, carefully selected to ensure that they contribute to the desired frequency response without introducing significant distortion or attenuation.
In such a circuit, the choice of active components, such as operational amplifiers or transistors, is critical. These components should have high gain-bandwidth products, allowing them to maintain performance at higher frequencies. The layout of the circuit board is also essential; minimizing trace lengths and avoiding sharp corners can reduce inductive and capacitive coupling, which can adversely affect circuit performance at 50 kHz.
Additionally, the power supply design is crucial for maintaining stable operation. A well-regulated power supply can prevent voltage fluctuations that may lead to frequency drift or instability. Bypass capacitors should be placed close to the power pins of active devices to filter out high-frequency noise.
Overall, the design of a 50 kHz circuit requires careful consideration of component selection, layout, and power supply management to achieve the nearly ideal characteristics that enable reliable operation at this frequency.A 50 kHz circuit is possible because of the more nearly ideal characteristics. The circuit shown.