555 car circuit diagram of the device
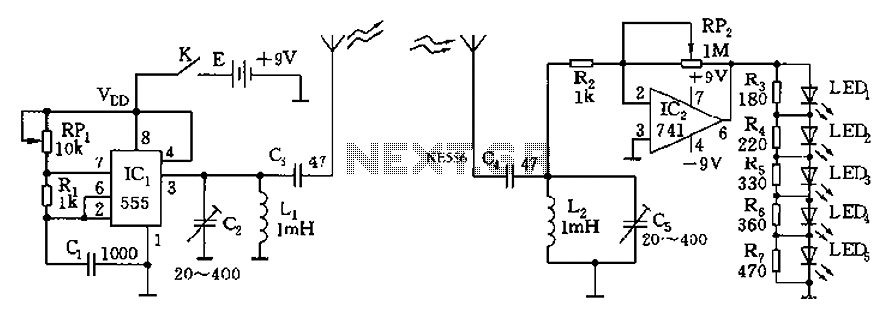
The circuit diagram of the device features a 555 timer IC configured as a transmitter and a receiver, divided into two sections. The 555 timer in the transmitter section serves as the core component of a frequency oscillator. The oscillation frequency should be slightly lower than the AM broadcast carrier frequency of 535 kHz. The frequency is determined by the equation f = 1.44 / ((RP1 + 2R1) * C1). The output resonant circuit is formed by L1 and C2, which is used for frequency selection, while C3 is responsible for emission through the antenna. The receiving circuit consists of a frequency selective network and a 741 operational amplifier; the amplification factor is dependent on the ratio of RP2 to R2. LEDs LED1 to LED5 function as a received signal strength indicator, illuminating sequentially as the signal strength increases.
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer IC in astable mode to generate a continuous square wave signal, which serves as the carrier frequency for the transmission. The selection of components RP1, R1, and C1 is critical as they define the oscillation frequency of the transmitter. Specifically, RP1 and R1 form a voltage divider network that, along with capacitor C1, sets the timing intervals for the oscillation. The output from the 555 timer is coupled to an antenna via capacitor C3, which allows the transmission of the modulated signal.
In the receiver section, the incoming signal is routed through a frequency selective network that filters out unwanted frequencies, allowing only the desired frequency to pass through. The filtered signal is then amplified by the 741 operational amplifier, where the gain is set by the feedback resistor RP2 and the input resistor R2. This gain can be adjusted to optimize the signal for further processing.
The received signal strength is indicated through a series of LEDs (LED1 to LED5). These LEDs light up in sequence as the strength of the received signal increases, providing a visual representation of the signal quality. This feature is particularly useful in applications where monitoring signal strength is crucial for effective communication. The overall design of this circuit is compact and efficient, making it suitable for various applications in wireless communication systems. As shown in the circuit diagram of the device is looking for 555 cars, including a transmitter and a receiver in two parts. The transmitter 555 is a core component of the wave frequency oscillator, the oscillation frequency should be selected than the AM broadcast carrier frequency 535kHz slightly lower frequency value, RP1, C1 is determined by R1, that is, f 1.44/(RP1 + 2R1) C1, L1, C2 form the output resonant circuit, frequency selection, and then by C3 emitted by the antenna. Receiving circuit by the input frequency selective network and 741 op amp, amplifier magnification depends on the ratio RP2/R2s.
LED1 ~ LED5 received signal strength indicator is used, and as the signal strength, the arc tube is lit sequentially.
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer IC in astable mode to generate a continuous square wave signal, which serves as the carrier frequency for the transmission. The selection of components RP1, R1, and C1 is critical as they define the oscillation frequency of the transmitter. Specifically, RP1 and R1 form a voltage divider network that, along with capacitor C1, sets the timing intervals for the oscillation. The output from the 555 timer is coupled to an antenna via capacitor C3, which allows the transmission of the modulated signal.
In the receiver section, the incoming signal is routed through a frequency selective network that filters out unwanted frequencies, allowing only the desired frequency to pass through. The filtered signal is then amplified by the 741 operational amplifier, where the gain is set by the feedback resistor RP2 and the input resistor R2. This gain can be adjusted to optimize the signal for further processing.
The received signal strength is indicated through a series of LEDs (LED1 to LED5). These LEDs light up in sequence as the strength of the received signal increases, providing a visual representation of the signal quality. This feature is particularly useful in applications where monitoring signal strength is crucial for effective communication. The overall design of this circuit is compact and efficient, making it suitable for various applications in wireless communication systems. As shown in the circuit diagram of the device is looking for 555 cars, including a transmitter and a receiver in two parts. The transmitter 555 is a core component of the wave frequency oscillator, the oscillation frequency should be selected than the AM broadcast carrier frequency 535kHz slightly lower frequency value, RP1, C1 is determined by R1, that is, f 1.44/(RP1 + 2R1) C1, L1, C2 form the output resonant circuit, frequency selection, and then by C3 emitted by the antenna. Receiving circuit by the input frequency selective network and 741 op amp, amplifier magnification depends on the ratio RP2/R2s.
LED1 ~ LED5 received signal strength indicator is used, and as the signal strength, the arc tube is lit sequentially.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713