555 IC LED Flasher for Up To 10 LEDs
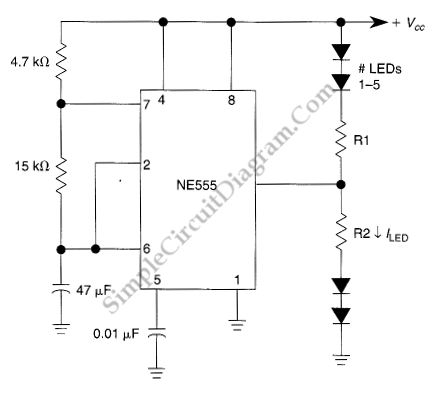
This LED flasher circuit utilizes a 555 integrated circuit (IC) and is designed to drive multiple LEDs. Notably, connecting several LEDs in series does not increase the power consumption.
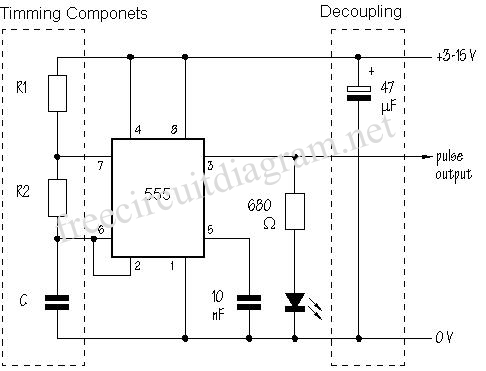
The LED flasher circuit based on the 555 timer IC is a versatile and efficient design suitable for various applications, including decorative lighting, indicators, and signaling devices. The 555 timer can be configured in astable mode to create a pulsing LED effect.
In this configuration, the circuit consists of a 555 timer, resistors, capacitors, and LEDs. The timer generates a square wave output, which alternates between high and low states, causing the connected LEDs to flash on and off. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values connected to the 555 timer.
The circuit typically includes two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C1) connected to the discharge and threshold pins of the 555 timer. The time period for which the output remains high (on) and low (off) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ T = 0.693 \times (R1 + 2R2) \times C1 \]
This formula allows for precise control over the flashing rate. For instance, increasing R1 or R2 will result in a longer on-time, while increasing C1 will also extend the duration of the flash.
The output pin of the 555 timer can drive a transistor to control larger currents, allowing the circuit to power multiple LEDs. When multiple LEDs are connected in series, the total forward voltage drop across the LEDs must be considered to ensure that the supply voltage is sufficient. However, the overall power consumption remains manageable, as the series configuration does not increase the total current drawn from the power supply.
In summary, this LED flasher circuit is an efficient design that leverages the capabilities of the 555 timer IC to provide a reliable and adjustable flashing LED output. The ability to connect multiple LEDs in series without increasing power consumption makes it a practical choice for various electronic projects.This LED flasher circuit uses 555 IC, and is capable of driving up to LEDs. The good news is, the use of multiple LEDs in series doesn`t increase the power.. 🔗 External reference
The LED flasher circuit based on the 555 timer IC is a versatile and efficient design suitable for various applications, including decorative lighting, indicators, and signaling devices. The 555 timer can be configured in astable mode to create a pulsing LED effect.
In this configuration, the circuit consists of a 555 timer, resistors, capacitors, and LEDs. The timer generates a square wave output, which alternates between high and low states, causing the connected LEDs to flash on and off. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values connected to the 555 timer.
The circuit typically includes two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C1) connected to the discharge and threshold pins of the 555 timer. The time period for which the output remains high (on) and low (off) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ T = 0.693 \times (R1 + 2R2) \times C1 \]
This formula allows for precise control over the flashing rate. For instance, increasing R1 or R2 will result in a longer on-time, while increasing C1 will also extend the duration of the flash.
The output pin of the 555 timer can drive a transistor to control larger currents, allowing the circuit to power multiple LEDs. When multiple LEDs are connected in series, the total forward voltage drop across the LEDs must be considered to ensure that the supply voltage is sufficient. However, the overall power consumption remains manageable, as the series configuration does not increase the total current drawn from the power supply.
In summary, this LED flasher circuit is an efficient design that leverages the capabilities of the 555 timer IC to provide a reliable and adjustable flashing LED output. The ability to connect multiple LEDs in series without increasing power consumption makes it a practical choice for various electronic projects.This LED flasher circuit uses 555 IC, and is capable of driving up to LEDs. The good news is, the use of multiple LEDs in series doesn`t increase the power.. 🔗 External reference