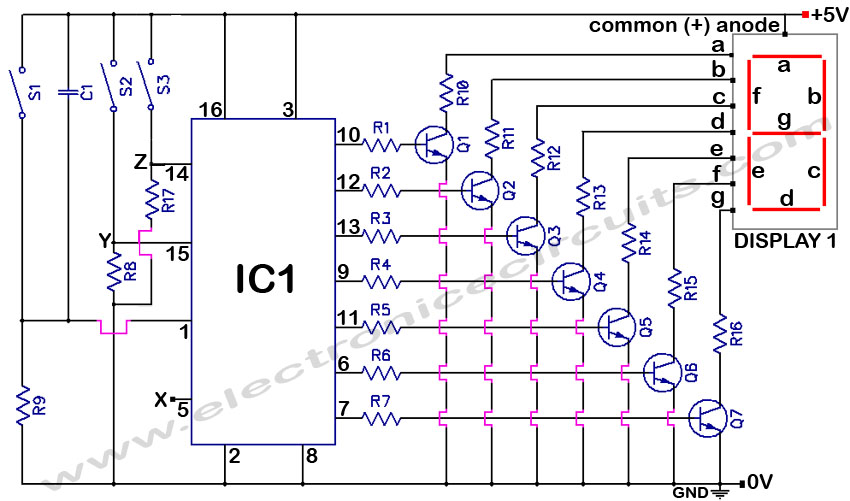
6 to 35kV substation cable entry into the segment of Lightning b
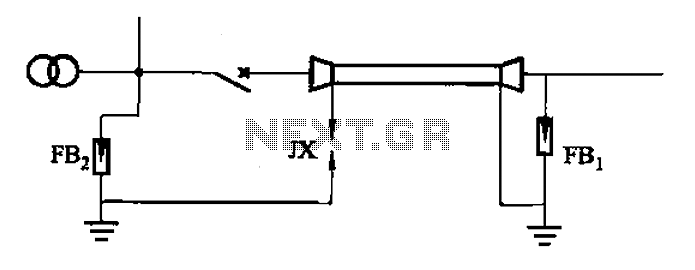
A 6-35kV cable line substation includes a lightning protection system, which is illustrated in Figure (a). This system protects the access lines; for single-core cables, the end of the metal sheath must adhere to the ground clearance protection standards, as shown in Figure (b).
The 6-35kV cable line substation is designed to manage high-voltage electrical distribution while ensuring safety against lightning strikes. The lightning protection system is a critical component that safeguards the integrity of the electrical infrastructure. It involves the installation of surge arresters and grounding systems that divert excessive voltage away from sensitive equipment and structures.
In the case of single-core cables, particular attention must be paid to the termination of the metal sheath. This metal sheath serves as a protective barrier against electromagnetic interference and physical damage. The proper grounding of this sheath is essential to prevent potential electrical hazards. The ground clearance, denoted as JX, must comply with local regulations and standards to ensure adequate protection against lightning-induced surges.
The design of the substation should include a detailed schematic that outlines the placement of lightning rods, grounding electrodes, and surge protective devices. The schematic should also indicate the routing of cables, the connection points for grounding, and the specifications for the materials used in the construction of the lightning protection system. Proper implementation of these elements will enhance the reliability and safety of the substation, ensuring uninterrupted service in adverse weather conditions.6-35kV cable line substation, into its line of lightning protection can be Figure (a), the protection of access lines; for single-core cable, the end of the metal sheath shall be subject to the protection of ground clearance JX, as ( b). 6 to 35kV substation cable entry into the segment of Lightning b
The 6-35kV cable line substation is designed to manage high-voltage electrical distribution while ensuring safety against lightning strikes. The lightning protection system is a critical component that safeguards the integrity of the electrical infrastructure. It involves the installation of surge arresters and grounding systems that divert excessive voltage away from sensitive equipment and structures.
In the case of single-core cables, particular attention must be paid to the termination of the metal sheath. This metal sheath serves as a protective barrier against electromagnetic interference and physical damage. The proper grounding of this sheath is essential to prevent potential electrical hazards. The ground clearance, denoted as JX, must comply with local regulations and standards to ensure adequate protection against lightning-induced surges.
The design of the substation should include a detailed schematic that outlines the placement of lightning rods, grounding electrodes, and surge protective devices. The schematic should also indicate the routing of cables, the connection points for grounding, and the specifications for the materials used in the construction of the lightning protection system. Proper implementation of these elements will enhance the reliability and safety of the substation, ensuring uninterrupted service in adverse weather conditions.6-35kV cable line substation, into its line of lightning protection can be Figure (a), the protection of access lines; for single-core cable, the end of the metal sheath shall be subject to the protection of ground clearance JX, as ( b). 6 to 35kV substation cable entry into the segment of Lightning b