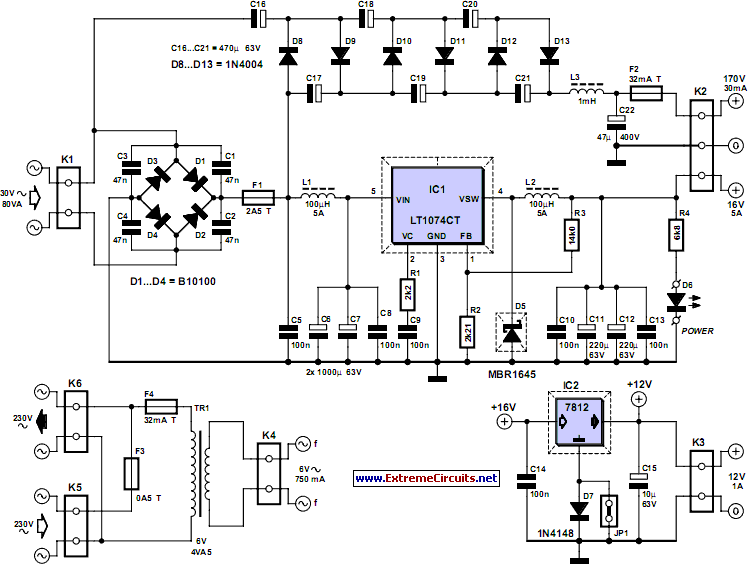
70 Watt MOSFET Audio Amplifier
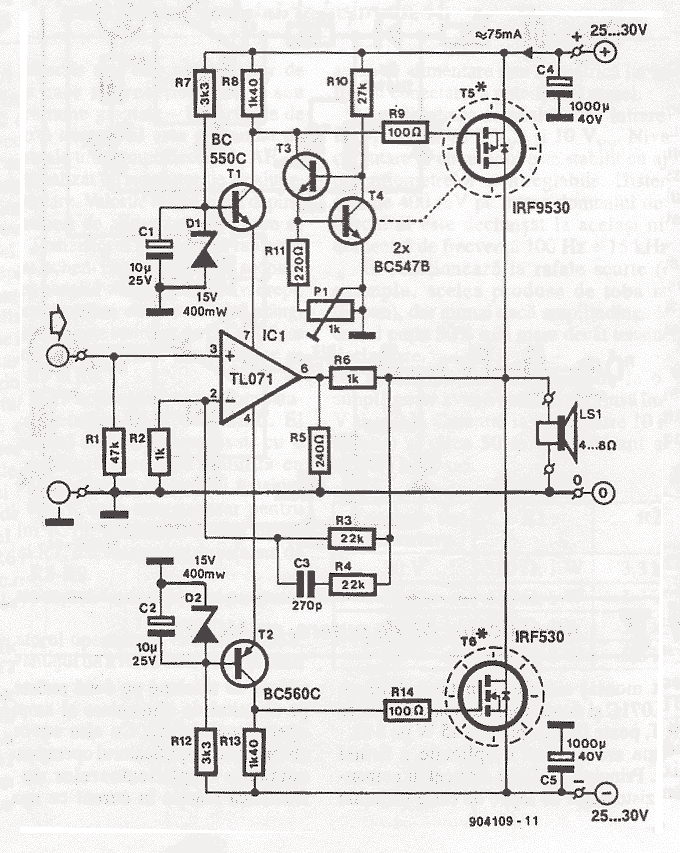
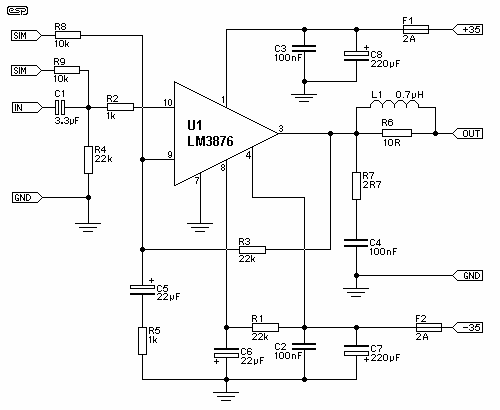
This simple power MOSFET audio amplifier circuit utilizes a TL071C operational amplifier and two MOSFETs (IRF9530 and IRF530), capable of delivering up to 45 Watts to an 8-ohm speaker. The schematic is based on a Siliconix application and incorporates variations in voltage across two resistors that are connected in series with the power supply of the operational amplifier driver. The MOSFET transistors must be mounted on a heatsink with a thermal resistance of at least 1K/W. The amplifier achieves an efficiency of 70%, with distortion at the cutoff frequency reaching a maximum of 0.2% at 20Hz with an 8-ohm load at 10W. With a power supply of ±30V, the MOSFET audio amplifier can provide 45W to an 8-ohm speaker and 70W to a 4-ohm speaker. It is important to note that this audio amplifier lacks short-circuit protection; therefore, it is essential to ensure the speaker is connected before powering on the device.
The described power MOSFET audio amplifier circuit features a TL071C operational amplifier, which is known for its low noise and high performance, making it suitable for audio applications. The use of IRF9530 and IRF530 MOSFETs allows for efficient switching and amplification of audio signals. The circuit is designed to operate with a dual power supply providing ±30V, which is essential for achieving the desired output power levels.
The two resistors in series with the operational amplifier's power supply are critical for setting the biasing conditions of the amplifier, ensuring optimal performance and stability. The choice of a heatsink with a thermal resistance of at least 1K/W is crucial for maintaining the junction temperature of the MOSFETs within safe limits during operation, especially at higher output levels where thermal dissipation is significant.
The amplifier's efficiency rating of 70% indicates that a substantial portion of the input power is converted into useful audio output, while the remaining power is dissipated as heat. The low distortion figure of 0.2% at 20Hz signifies that the amplifier can reproduce low-frequency audio signals with high fidelity, which is vital for music reproduction.
It is important to implement proper circuit protection measures, as the absence of short-circuit protection can lead to potential damage to the amplifier and connected speakers. Regular checks before powering on the amplifier, ensuring correct speaker connections, and monitoring for any signs of overheating will help maintain the longevity and reliability of the circuit.This simple power mosfet audio amplifier circuit, with TL071C and 2 MOSFETs (IRF9530 and IRF530) can deliver up to 45 Watts on 8 © speaker. This schematic is based on Siliconix application and on variations of voltage on the 2 resistors that are serial inserted on the voltage supplier of the operational amplifier driver.
The MosFet transistor mus t be mounted on a heatsink with at least 1K/W. Amplifier`s efficiency is 70%, distortions at cut frequency were at most 0. 2% at 20Hz on 8 © and 10W. With a power supply of ± 30V the mosfet audio amplifier can deliver 45W on 8 © and 70w on 4 ©. Remember that this audio amplifier is not protected on shortcircuits so everytime you switch on check to see if the speaker is connected. 🔗 External reference
The described power MOSFET audio amplifier circuit features a TL071C operational amplifier, which is known for its low noise and high performance, making it suitable for audio applications. The use of IRF9530 and IRF530 MOSFETs allows for efficient switching and amplification of audio signals. The circuit is designed to operate with a dual power supply providing ±30V, which is essential for achieving the desired output power levels.
The two resistors in series with the operational amplifier's power supply are critical for setting the biasing conditions of the amplifier, ensuring optimal performance and stability. The choice of a heatsink with a thermal resistance of at least 1K/W is crucial for maintaining the junction temperature of the MOSFETs within safe limits during operation, especially at higher output levels where thermal dissipation is significant.
The amplifier's efficiency rating of 70% indicates that a substantial portion of the input power is converted into useful audio output, while the remaining power is dissipated as heat. The low distortion figure of 0.2% at 20Hz signifies that the amplifier can reproduce low-frequency audio signals with high fidelity, which is vital for music reproduction.
It is important to implement proper circuit protection measures, as the absence of short-circuit protection can lead to potential damage to the amplifier and connected speakers. Regular checks before powering on the amplifier, ensuring correct speaker connections, and monitoring for any signs of overheating will help maintain the longevity and reliability of the circuit.This simple power mosfet audio amplifier circuit, with TL071C and 2 MOSFETs (IRF9530 and IRF530) can deliver up to 45 Watts on 8 © speaker. This schematic is based on Siliconix application and on variations of voltage on the 2 resistors that are serial inserted on the voltage supplier of the operational amplifier driver.
The MosFet transistor mus t be mounted on a heatsink with at least 1K/W. Amplifier`s efficiency is 70%, distortions at cut frequency were at most 0. 2% at 20Hz on 8 © and 10W. With a power supply of ± 30V the mosfet audio amplifier can deliver 45W on 8 © and 70w on 4 ©. Remember that this audio amplifier is not protected on shortcircuits so everytime you switch on check to see if the speaker is connected. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713