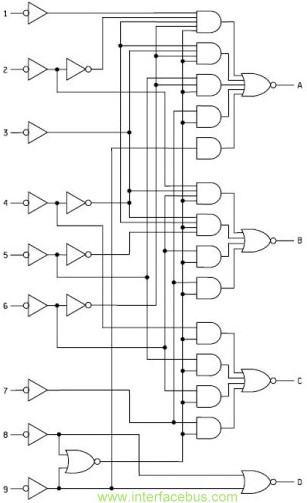
8-Channel DTMF Link: Encoder
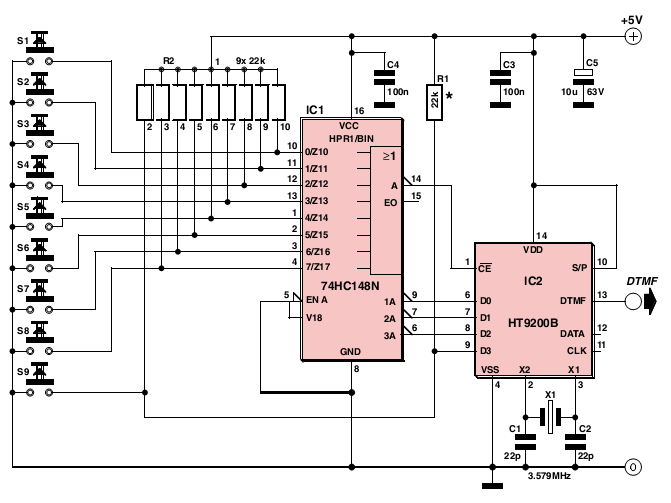
The signal is encoded as a pair of sine waves, ensuring that no frequency is a multiple of the other, and that the sum and difference between the two frequencies do not match any single tone, which contributes to the unpleasant sound of DTMF. The DTMF encoder circuit presented here is based on the HT9200B tone generator device produced by Holtek and distributed by Futurlec, among others. The encoder is complemented by a decoder elsewhere in this publication. The HT9200B is provided as a traditional 14-pin device. It can be controlled by a microcontroller to generate 16 dual tones and, in serial mode only, 8 single tones from the DTMF pin output. Its 8-pin counterpart, the HT9200A, operates only in serial mode, while the HT9200B features a selectable serial/parallel mode interface suitable for various applications such as security systems, home automation, and remote control via telephone lines. A 74HC148 8-to-3 priority encoder is utilized to convert the keypad information from switches S1 to S8 into 3-bit tone selection words that the HT9200B requires as input. The ninth switch, S9, is connected to input D3 on the encoder chip. Activating one of the switches S1 to S8 produces a complementary 3-bit binary output at A0, A1, and A2 of IC1. IC2 then generates the corresponding dual tones based on these binary codes. Pressing S1 to S8 generates dual tones for DTMF digits C, B, A, #, *, 0, 9, and 8. Holding down S9 generates the DTMF digits 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, and D. To accurately generate the eight single frequencies, a 3.58 MHz crystal quartz is connected to pins 2 and 3 of IC2. Pin 13 of the HT9200B outputs a DTMF signal of approximately 150 mV at a 5 kΩ load.
The DTMF encoder circuit leverages the HT9200B tone generator to produce dual-tone multi-frequency signals, which are essential for telecommunications. The design ensures that the generated frequencies are distinct and do not interfere with one another, thereby avoiding harmonic distortion. The circuit is structured to allow for easy interfacing with microcontrollers, enabling versatile applications in various electronic systems.
The 74HC148 priority encoder plays a crucial role in interpreting the keypad inputs, converting the pressed switch states into binary codes that the HT9200B can process. This allows for a user-friendly interface where each button corresponds to a specific DTMF tone, facilitating effective communication in automated systems.
Connections to the crystal oscillator are vital for maintaining the accuracy of the generated frequencies. The 3.58 MHz crystal ensures precise timing, which is critical for the generation of reliable DTMF signals. The output from the HT9200B is designed to be compatible with standard telecommunications equipment, providing a clean signal at a manageable voltage level.
The overall design of the DTMF encoder circuit is robust, making it suitable for integration into various applications, including security systems that require remote activation via telephone, home automation systems that utilize DTMF signals for control, and communication systems that rely on reliable tone generation for user input. The combination of the HT9200B with other components like the 74HC148 and the crystal oscillator creates a comprehensive solution for generating and decoding DTMF signals effectively.The signal is encoded as a pair of sine waves, ensuring that no frequency is a multiple of the other and the sum and difference between two frequencies does not match any single tone and that`s why DTMF sounds so ugly!T he DTMF encoder circuit show n here is based on the HT9200B tone generator device produced by Holtek and distributed by Futurlec (. com) among others. The encoder is complemented by a decoder elsew her e in this publication. The HT2900B is supplied as a nice old fashioned 14-pin device. It can be instructed by a microcontroller to generate 16 dual tones and (in serial mode only) 8 single tones from the DTMF pin output. It s 8 - pin younger brother` the HT9200A provides a serial mode only whereas the HT9200B contains a select-able serial/parallel mode interface for various applications such as security systems, home automation, remote control through telephone lines, communication systems, etc.
A 74HC148 8-to-3 priority encoder is used to convert the keypad` information from S1 S8 into 3-bit tone selection words the HT9200B wants to see at its input. The ninth switch, S9, is connected to input D3 on the encoder chip. Pressing one of the switches S1 S8 generates a complementary 3-bit binary word at outputs A0, A1, A2 of IC1.
IC2 then generates the dual tones accordingly to these binary codes. Pressing S1 S8 generates the dual tones for DTMF digits C, B, A, #, *, 0, 9 and 8. By pressing and holding down S9 the DTMF digits 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and D are generated. To generate the eight single frequencies accurately a 3. 58 MHz crystal quartz is connected to pin 2 and 3 of IC2. Pin 13 of the HT9200B supplies a DTMF signal of about 150 mV at a 5 KO load. 🔗 External reference
The DTMF encoder circuit leverages the HT9200B tone generator to produce dual-tone multi-frequency signals, which are essential for telecommunications. The design ensures that the generated frequencies are distinct and do not interfere with one another, thereby avoiding harmonic distortion. The circuit is structured to allow for easy interfacing with microcontrollers, enabling versatile applications in various electronic systems.
The 74HC148 priority encoder plays a crucial role in interpreting the keypad inputs, converting the pressed switch states into binary codes that the HT9200B can process. This allows for a user-friendly interface where each button corresponds to a specific DTMF tone, facilitating effective communication in automated systems.
Connections to the crystal oscillator are vital for maintaining the accuracy of the generated frequencies. The 3.58 MHz crystal ensures precise timing, which is critical for the generation of reliable DTMF signals. The output from the HT9200B is designed to be compatible with standard telecommunications equipment, providing a clean signal at a manageable voltage level.
The overall design of the DTMF encoder circuit is robust, making it suitable for integration into various applications, including security systems that require remote activation via telephone, home automation systems that utilize DTMF signals for control, and communication systems that rely on reliable tone generation for user input. The combination of the HT9200B with other components like the 74HC148 and the crystal oscillator creates a comprehensive solution for generating and decoding DTMF signals effectively.The signal is encoded as a pair of sine waves, ensuring that no frequency is a multiple of the other and the sum and difference between two frequencies does not match any single tone and that`s why DTMF sounds so ugly!T he DTMF encoder circuit show n here is based on the HT9200B tone generator device produced by Holtek and distributed by Futurlec (. com) among others. The encoder is complemented by a decoder elsew her e in this publication. The HT2900B is supplied as a nice old fashioned 14-pin device. It can be instructed by a microcontroller to generate 16 dual tones and (in serial mode only) 8 single tones from the DTMF pin output. It s 8 - pin younger brother` the HT9200A provides a serial mode only whereas the HT9200B contains a select-able serial/parallel mode interface for various applications such as security systems, home automation, remote control through telephone lines, communication systems, etc.
A 74HC148 8-to-3 priority encoder is used to convert the keypad` information from S1 S8 into 3-bit tone selection words the HT9200B wants to see at its input. The ninth switch, S9, is connected to input D3 on the encoder chip. Pressing one of the switches S1 S8 generates a complementary 3-bit binary word at outputs A0, A1, A2 of IC1.
IC2 then generates the dual tones accordingly to these binary codes. Pressing S1 S8 generates the dual tones for DTMF digits C, B, A, #, *, 0, 9 and 8. By pressing and holding down S9 the DTMF digits 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and D are generated. To generate the eight single frequencies accurately a 3. 58 MHz crystal quartz is connected to pin 2 and 3 of IC2. Pin 13 of the HT9200B supplies a DTMF signal of about 150 mV at a 5 KO load. 🔗 External reference