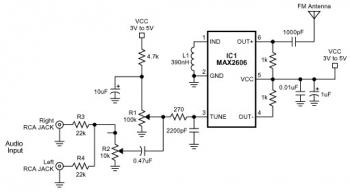
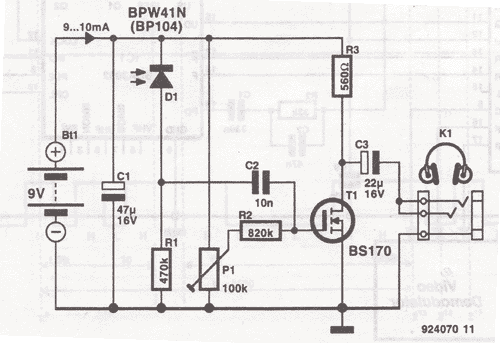
88-108Mhz FM Radio Transmitter
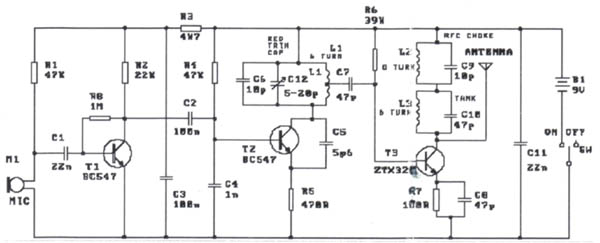
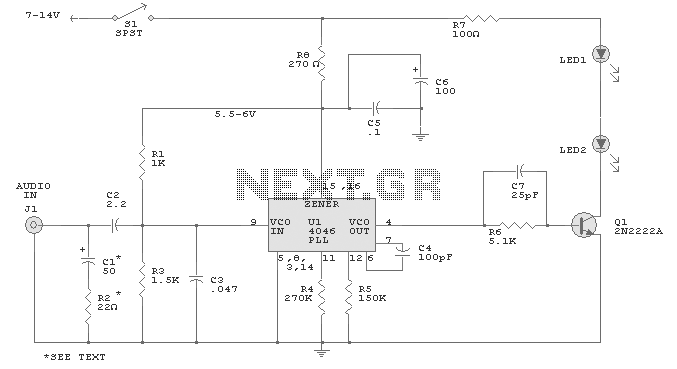
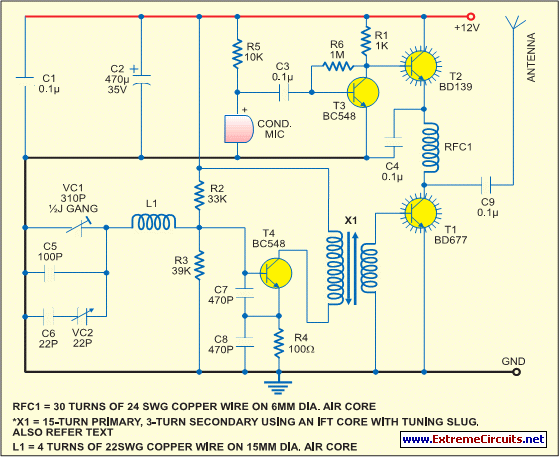
The modification presented involves using a 2N2219 NPN transistor to replace T2 and a 2N3553 NPN transistor to replace T3. Both transistors are categorized as VHF transistors. It is necessary to attach a heatsink to the last transistor. No additional modifications to the circuit are required for it to function effectively. The wavelength refers to the physical height of the wave in meters. By dividing it to an acceptable length, a smaller antenna can resonate at the same frequency, such as one of the multiple harmonics of the wavelength. For a dipole antenna (180 degrees out of phase), this length should be halved, resulting in 75 cm on the antenna output and 75 cm on the positive rail, with the two segments oriented in opposite directions.
The circuit modification involves substituting two specific transistors, enhancing the performance characteristics of the circuit while maintaining its original functionality. The 2N2219 NPN transistor is well-suited for low to medium power applications, providing reliable switching capabilities, while the 2N3553 NPN transistor is designed for higher power applications, making it ideal for VHF operations. The requirement for a heatsink on the 2N3553 is critical due to its higher power dissipation, which helps to prevent overheating and ensures stable operation.
The concept of wavelength is essential in antenna design, as it directly influences the antenna's dimensions and performance. The wavelength, defined as the distance between successive peaks of a wave, can be adjusted to optimize antenna size for specific frequency ranges. By scaling the antenna down to a fraction of the wavelength, such as using harmonics, the antenna can still effectively transmit and receive signals at the desired frequency.
In the case of a dipole antenna, which consists of two conductive elements oriented in opposite directions, the length of each element should be precisely calculated to achieve resonance. By cutting the wavelength in half, each segment of the dipole antenna is configured to 75 cm, allowing for efficient radiation of electromagnetic waves. This configuration enhances the antenna's ability to operate effectively at the desired frequency while ensuring that the two elements remain out of phase, which is crucial for dipole functionality.
Proper implementation of this modification requires careful attention to the transistor specifications, thermal management, and antenna design principles to ensure optimal performance in VHF applications.The mod I present here is to use a 2n2219 NPN transistor in place of T2 and a 2n3553 NPN transistor in place of T3. Both are VHF transistors. The last transistor will need to be put on a heatsink. I haven`t found the need to make any other modifications to the circuit to make this work. Wave Length is the physical height of the wave in meters. By diving it to an acceptable length, you are making a smaller antenna resonate at the same frequency, eg one of the multiple harmonics of the wave length. If you want a dipole (180 degree out of phase antenna), cut this length in 2, so you have 75cm on the antenna output and 75cm on the positive rail and point them in oppose directions.
🔗 External reference
The circuit modification involves substituting two specific transistors, enhancing the performance characteristics of the circuit while maintaining its original functionality. The 2N2219 NPN transistor is well-suited for low to medium power applications, providing reliable switching capabilities, while the 2N3553 NPN transistor is designed for higher power applications, making it ideal for VHF operations. The requirement for a heatsink on the 2N3553 is critical due to its higher power dissipation, which helps to prevent overheating and ensures stable operation.
The concept of wavelength is essential in antenna design, as it directly influences the antenna's dimensions and performance. The wavelength, defined as the distance between successive peaks of a wave, can be adjusted to optimize antenna size for specific frequency ranges. By scaling the antenna down to a fraction of the wavelength, such as using harmonics, the antenna can still effectively transmit and receive signals at the desired frequency.
In the case of a dipole antenna, which consists of two conductive elements oriented in opposite directions, the length of each element should be precisely calculated to achieve resonance. By cutting the wavelength in half, each segment of the dipole antenna is configured to 75 cm, allowing for efficient radiation of electromagnetic waves. This configuration enhances the antenna's ability to operate effectively at the desired frequency while ensuring that the two elements remain out of phase, which is crucial for dipole functionality.
Proper implementation of this modification requires careful attention to the transistor specifications, thermal management, and antenna design principles to ensure optimal performance in VHF applications.The mod I present here is to use a 2n2219 NPN transistor in place of T2 and a 2n3553 NPN transistor in place of T3. Both are VHF transistors. The last transistor will need to be put on a heatsink. I haven`t found the need to make any other modifications to the circuit to make this work. Wave Length is the physical height of the wave in meters. By diving it to an acceptable length, you are making a smaller antenna resonate at the same frequency, eg one of the multiple harmonics of the wave length. If you want a dipole (180 degree out of phase antenna), cut this length in 2, so you have 75cm on the antenna output and 75cm on the positive rail and point them in oppose directions.
🔗 External reference