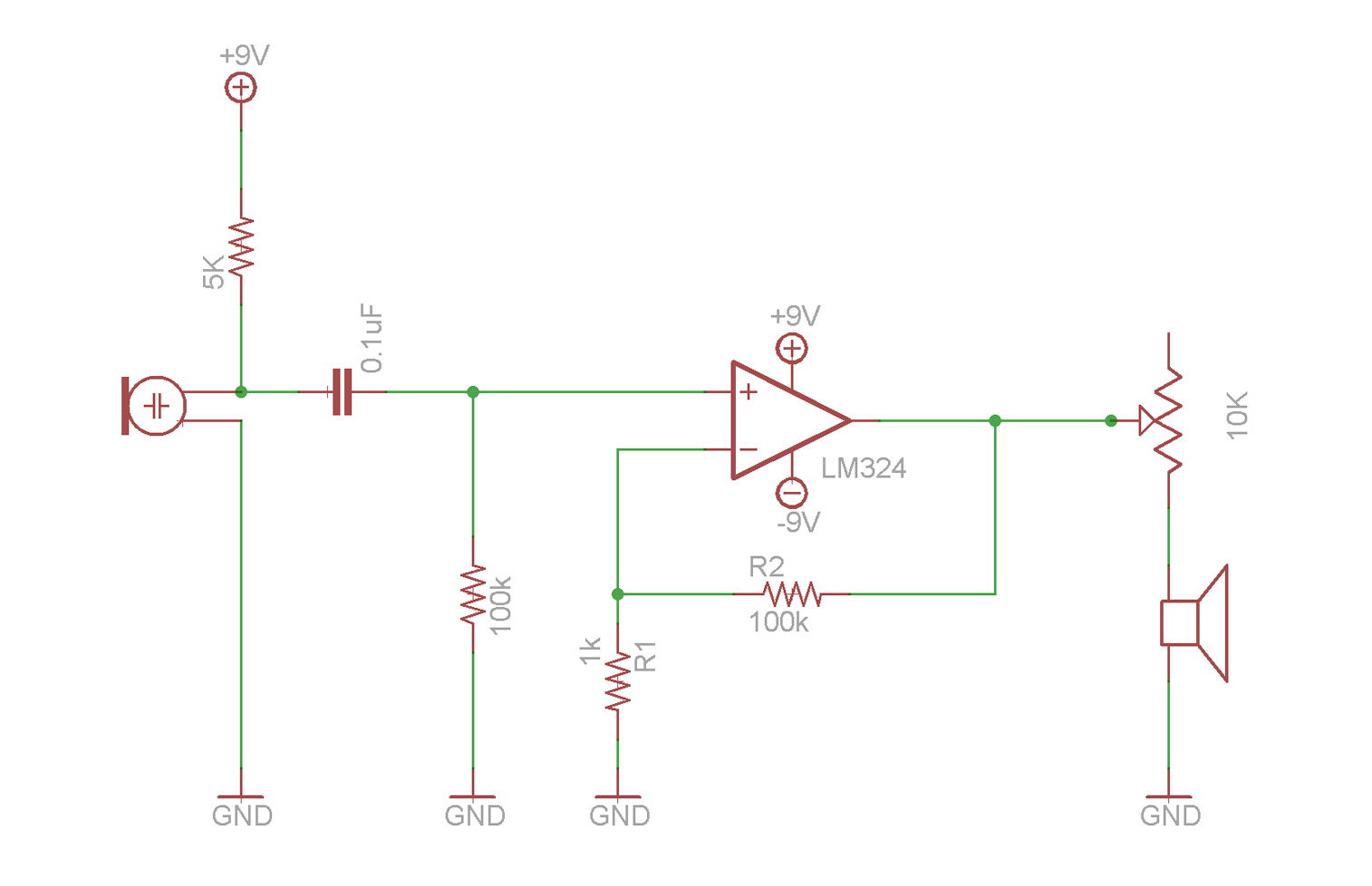
9 volt headphone amplifier
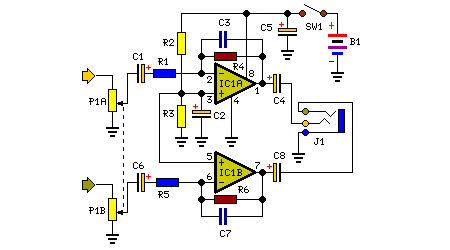
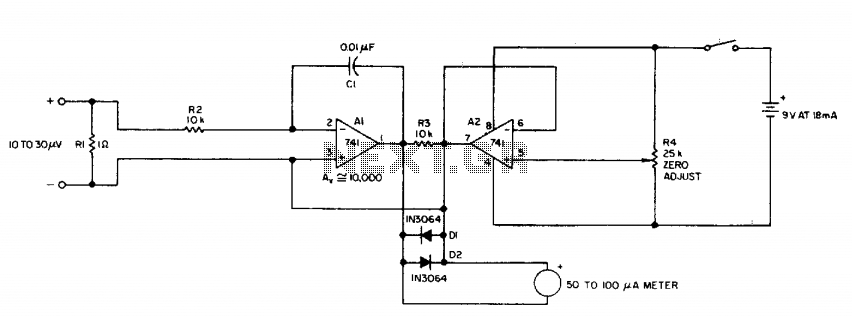
The decision to design a 9V powered headphone amplifier has been finalized. The primary requirement was to power the circuit using a common PP3 (transistor radio) alkaline battery. The introduction of the 5534 low-noise op-amp at a reasonable price has been well received by audio designers. Designing a discrete stage that matches the performance of the 5534 without excessive complexity has become increasingly difficult, if not impossible. The 5534 op-amps are available from various suppliers in a conventional 8-pin dual in-line package (DIP) format. This version is internally compensated for gains of three or more but requires a small external capacitor (5-15pF) for stability at unity gain. The 5532 is a convenient package containing two 5534s in a single 8-pin device with internal unity-gain compensation, as it does not have spare pins. The 5534/2 is a low-distortion, low-noise device capable of driving low-impedance loads to full voltage swing while maintaining low distortion. Additionally, it is fully protected against output short circuits. Consequently, this circuit utilizes a single 5532 chip to form a pair of stereo inverting amplifiers, providing an AC gain of approximately 3.5 and capable of delivering up to 3.6V peak-to-peak into a 32-ohm load (equivalent to 50mW RMS) with less than 0.025% total harmonic distortion at both 1kHz and 10kHz. Considering that the average current draw at a power output of 15mW per channel is around 12-13mA (when both channels are driven), this headphone amplifier is poised to be an essential component for many DIY enthusiasts seeking a high-quality, high-performance portable device.
The proposed headphone amplifier circuit is designed to operate efficiently with a 9V power supply, utilizing a PP3 alkaline battery, which is widely available and convenient for portable applications. The choice of the 5532 op-amp is strategic, given its dual-channel capability, low noise, and low distortion characteristics, making it an ideal choice for audio applications.
The circuit configuration employs the 5532 in a standard inverting amplifier configuration, allowing for precise control over gain and signal integrity. The gain of approximately 3.5 is achieved through feedback resistors that set the gain ratio. The input stage is designed to accommodate various audio sources, ensuring compatibility with standard headphone outputs from devices such as smartphones, computers, and audio players.
Output coupling capacitors may be included to block any DC offset that could affect headphone performance. The design should also incorporate bypass capacitors close to the power pins of the op-amp to minimize power supply noise and enhance stability.
Thermal management is considered in the design, ensuring that the op-amp operates within its specified temperature range, especially under continuous load conditions. The output stage is capable of driving 32-ohm headphones, delivering adequate power while maintaining low distortion levels, making it suitable for high-fidelity audio reproduction.
Overall, this headphone amplifier circuit represents a practical solution for audio enthusiasts and DIY builders, offering a compact, efficient, and high-quality audio amplification solution for portable use.the decision of designing a 9V powered Headphone Amplifier was finally taken. The main requirement was to power the circuit by means of a common, PP3 (transistor radio) alkaline battery. The appearance of the 5534 low-noise op-amp at a reasonable price was much appreciated by audio designers.
It is now difficult or impossible to design a discrete stage that has the performance of the 5534 without quite unacceptable complexity. 5534 op-amps are now available from several sources, in a conventional 8-pin d. i. l. format. This version is internally compensated for gains of three or more, but requires a small external capacitor (5-15pF) for unity-gain stability.
The 5532 is a very convenient package of two 5534s in one 8-pin device with internal unity-gain compensation, as there are no spare pins. The 5534/2 is a low-distortion, low-noise device, having also the ability to drive low-impedance loads to a full voltage swing while maintaining low distortion.
Furthermore, it is fully output short-circuit proof. Therefore, this circuit was implemented with a single 5532 chip forming a pair of stereo, inverting amplifiers, having an ac gain of about 3. 5 and capable of delivering up to 3. 6V peak-to-peak into a 32 Ohm load (corresponding to 50mW RMS) at less than 0. 025% total harmonic distortion (1kHz & 10kHz). If we consider that the mean current drawing at a power output of 15mW per channel is around 12-13mA (both channels driven), this Headphone Amplifier will become a `must` for many DIY enthusiasts needing a High Quality, High Performance portable device.
🔗 External reference
The proposed headphone amplifier circuit is designed to operate efficiently with a 9V power supply, utilizing a PP3 alkaline battery, which is widely available and convenient for portable applications. The choice of the 5532 op-amp is strategic, given its dual-channel capability, low noise, and low distortion characteristics, making it an ideal choice for audio applications.
The circuit configuration employs the 5532 in a standard inverting amplifier configuration, allowing for precise control over gain and signal integrity. The gain of approximately 3.5 is achieved through feedback resistors that set the gain ratio. The input stage is designed to accommodate various audio sources, ensuring compatibility with standard headphone outputs from devices such as smartphones, computers, and audio players.
Output coupling capacitors may be included to block any DC offset that could affect headphone performance. The design should also incorporate bypass capacitors close to the power pins of the op-amp to minimize power supply noise and enhance stability.
Thermal management is considered in the design, ensuring that the op-amp operates within its specified temperature range, especially under continuous load conditions. The output stage is capable of driving 32-ohm headphones, delivering adequate power while maintaining low distortion levels, making it suitable for high-fidelity audio reproduction.
Overall, this headphone amplifier circuit represents a practical solution for audio enthusiasts and DIY builders, offering a compact, efficient, and high-quality audio amplification solution for portable use.the decision of designing a 9V powered Headphone Amplifier was finally taken. The main requirement was to power the circuit by means of a common, PP3 (transistor radio) alkaline battery. The appearance of the 5534 low-noise op-amp at a reasonable price was much appreciated by audio designers.
It is now difficult or impossible to design a discrete stage that has the performance of the 5534 without quite unacceptable complexity. 5534 op-amps are now available from several sources, in a conventional 8-pin d. i. l. format. This version is internally compensated for gains of three or more, but requires a small external capacitor (5-15pF) for unity-gain stability.
The 5532 is a very convenient package of two 5534s in one 8-pin device with internal unity-gain compensation, as there are no spare pins. The 5534/2 is a low-distortion, low-noise device, having also the ability to drive low-impedance loads to a full voltage swing while maintaining low distortion.
Furthermore, it is fully output short-circuit proof. Therefore, this circuit was implemented with a single 5532 chip forming a pair of stereo, inverting amplifiers, having an ac gain of about 3. 5 and capable of delivering up to 3. 6V peak-to-peak into a 32 Ohm load (corresponding to 50mW RMS) at less than 0. 025% total harmonic distortion (1kHz & 10kHz). If we consider that the mean current drawing at a power output of 15mW per channel is around 12-13mA (both channels driven), this Headphone Amplifier will become a `must` for many DIY enthusiasts needing a High Quality, High Performance portable device.
🔗 External reference