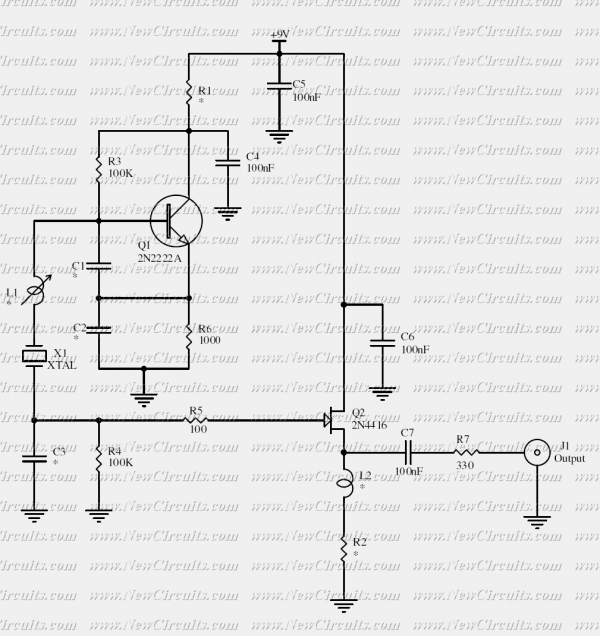
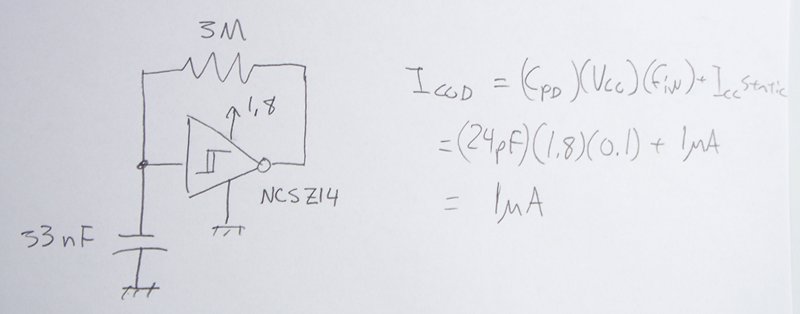96Mhz crystal oscillator
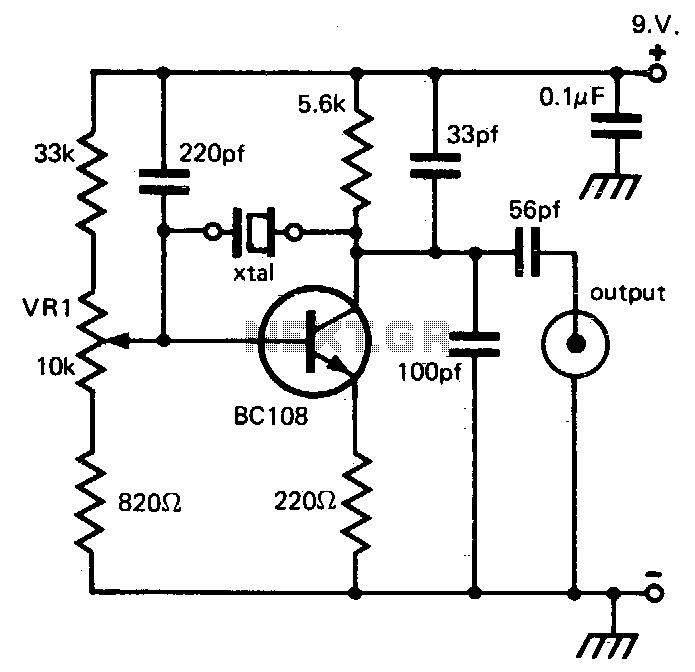
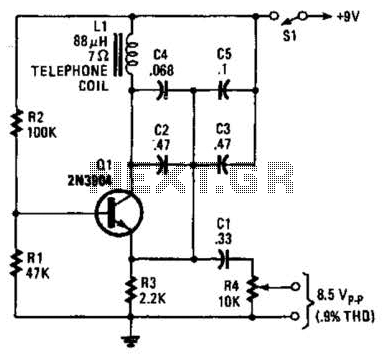
This circuit provides reliable oscillation and an output close to one volt peak-to-peak. Power consumption is around 1 mA from a nine-volt supply.
The described circuit is likely a simple oscillator designed to generate a periodic waveform with a peak-to-peak voltage of approximately one volt. The oscillation can be achieved through various methods such as using a relaxation oscillator, a Colpitts oscillator, or a simple RC oscillator configuration.
The power supply requirement is specified as nine volts, which suggests that the circuit may be powered by a standard battery or a regulated power supply. The low power consumption of around 1 mA indicates that the circuit is efficient, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or applications where power conservation is critical.
The output waveform can be utilized in various applications, including signal generation for testing purposes, clock signals for digital circuits, or as a modulation source in communication systems. The circuit's design should ensure stability and reliability in its oscillation performance, possibly incorporating feedback mechanisms to maintain consistent output characteristics.
In practical implementations, components such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors (or operational amplifiers) are typically used to define the oscillation frequency and shape of the output waveform. The choice of components and their values will significantly influence the performance of the circuit, including factors like frequency stability, output amplitude, and waveform distortion.
Overall, this circuit represents a fundamental building block in electronics, demonstrating the principles of oscillation and signal generation with a focus on low power consumption and manageable output levels.This circuit provides reliable oscillation and an output dose to one volt peak-to-peak Power consumption is around 1 mA from a nine volt supply. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is likely a simple oscillator designed to generate a periodic waveform with a peak-to-peak voltage of approximately one volt. The oscillation can be achieved through various methods such as using a relaxation oscillator, a Colpitts oscillator, or a simple RC oscillator configuration.
The power supply requirement is specified as nine volts, which suggests that the circuit may be powered by a standard battery or a regulated power supply. The low power consumption of around 1 mA indicates that the circuit is efficient, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or applications where power conservation is critical.
The output waveform can be utilized in various applications, including signal generation for testing purposes, clock signals for digital circuits, or as a modulation source in communication systems. The circuit's design should ensure stability and reliability in its oscillation performance, possibly incorporating feedback mechanisms to maintain consistent output characteristics.
In practical implementations, components such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors (or operational amplifiers) are typically used to define the oscillation frequency and shape of the output waveform. The choice of components and their values will significantly influence the performance of the circuit, including factors like frequency stability, output amplitude, and waveform distortion.
Overall, this circuit represents a fundamental building block in electronics, demonstrating the principles of oscillation and signal generation with a focus on low power consumption and manageable output levels.This circuit provides reliable oscillation and an output dose to one volt peak-to-peak Power consumption is around 1 mA from a nine volt supply. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713