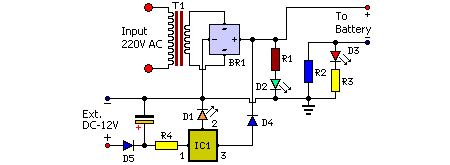
transistors Low power low voltage slow (0.1Hz) oscillator
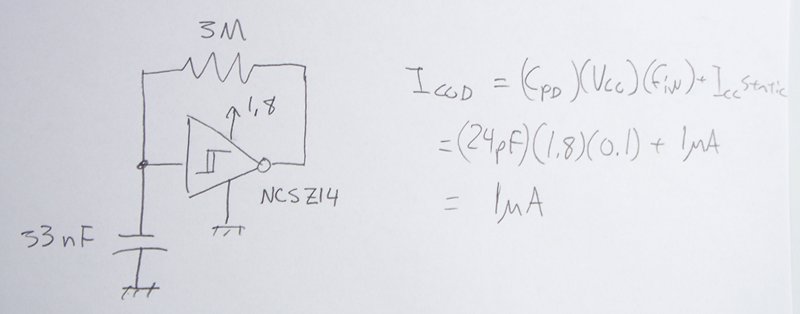
The power supply varies, and the circuit must operate at under 10 µA of current (excluding the capacitor charging). It triggers a Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) every 10 to 30 seconds as long as the power supply is above 1.8 VDC and must function across a voltage range of 1.8 to 7.0 VDC. The timing is not critical; intervals of around 10 to 30 seconds for triggering the SCR are acceptable (a short positive pulse). The lower the voltage, the longer the time interval can be. The key requirements are low current consumption (10 µA or less), low voltage operation (1.8 V), and low cost (for instance, replacing a 10-cent Programmable Unijunction Transistor (PUT) with a 30-cent microcontroller would not be ideal).
The circuit described is a low-power SCR triggering system designed to operate efficiently within a specified voltage range. The primary function of this circuit is to periodically trigger an SCR, which allows for controlled switching in various applications, such as in lighting or motor control systems.
The circuit operates by utilizing a timing mechanism that generates a pulse every 10 to 30 seconds, depending on the power supply voltage. A resistor-capacitor (RC) timing network can be employed to achieve the desired timing intervals. The capacitor is charged through a resistor, and once it reaches a threshold voltage, it can trigger the SCR. The design must ensure that the capacitor charging current does not exceed 10 µA, which necessitates careful selection of resistor values to extend the timing intervals at lower voltages.
In terms of voltage operation, the circuit is designed to function effectively at a minimum of 1.8 VDC and up to 7.0 VDC. This range allows for flexibility in power supply choices, accommodating both battery-operated and mains-powered applications. The design should incorporate components that can reliably operate within this voltage range without significant power loss.
Cost-effectiveness is a critical factor in the design process. The use of low-cost components such as resistors, capacitors, and the SCR itself is preferred over more expensive alternatives like microcontrollers. This approach not only reduces the overall cost of the circuit but also simplifies the design, making it easier to implement in various applications.
Overall, the circuit must be optimized for low power consumption, reliable operation across a specified voltage range, and cost efficiency, ensuring that it meets the requirements while remaining practical for real-world applications.The power supply varies, and the circuit must operate on under 10uA of current (not counting charging the cap). It triggers an SCR every 10-30 seconds as long as the power supply is above 1. 8VDC, and must operate across a range of 1. 8 and 7. 0 VDC. The timing isn`t critical - around 10-30 second intervals to trigger the SCR is fine (a short positiv
e pulse). The lower the voltage, the longer the time interval is fine. The kicker is the low current requirement (10uA or less), low voltage requirement (1. 8V) and, as always, low cost (ie, replacing a 10 cent PUT with a 30 cent microcontroller would not be ideal). 🔗 External reference
The circuit described is a low-power SCR triggering system designed to operate efficiently within a specified voltage range. The primary function of this circuit is to periodically trigger an SCR, which allows for controlled switching in various applications, such as in lighting or motor control systems.
The circuit operates by utilizing a timing mechanism that generates a pulse every 10 to 30 seconds, depending on the power supply voltage. A resistor-capacitor (RC) timing network can be employed to achieve the desired timing intervals. The capacitor is charged through a resistor, and once it reaches a threshold voltage, it can trigger the SCR. The design must ensure that the capacitor charging current does not exceed 10 µA, which necessitates careful selection of resistor values to extend the timing intervals at lower voltages.
In terms of voltage operation, the circuit is designed to function effectively at a minimum of 1.8 VDC and up to 7.0 VDC. This range allows for flexibility in power supply choices, accommodating both battery-operated and mains-powered applications. The design should incorporate components that can reliably operate within this voltage range without significant power loss.
Cost-effectiveness is a critical factor in the design process. The use of low-cost components such as resistors, capacitors, and the SCR itself is preferred over more expensive alternatives like microcontrollers. This approach not only reduces the overall cost of the circuit but also simplifies the design, making it easier to implement in various applications.
Overall, the circuit must be optimized for low power consumption, reliable operation across a specified voltage range, and cost efficiency, ensuring that it meets the requirements while remaining practical for real-world applications.The power supply varies, and the circuit must operate on under 10uA of current (not counting charging the cap). It triggers an SCR every 10-30 seconds as long as the power supply is above 1. 8VDC, and must operate across a range of 1. 8 and 7. 0 VDC. The timing isn`t critical - around 10-30 second intervals to trigger the SCR is fine (a short positiv
e pulse). The lower the voltage, the longer the time interval is fine. The kicker is the low current requirement (10uA or less), low voltage requirement (1. 8V) and, as always, low cost (ie, replacing a 10 cent PUT with a 30 cent microcontroller would not be ideal). 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713