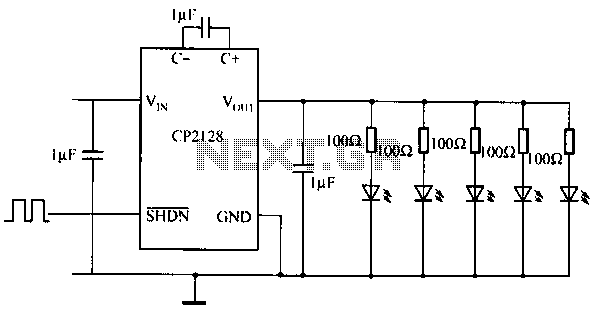
9V LED light organ
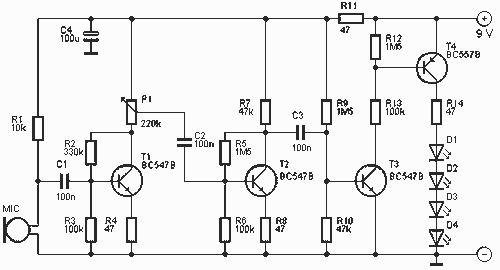
This is a nice example circuit that can be used at parties. The four LEDs blink to the beat of the music. The light organ using a microphone responds to sound. T1 amplifies the signal from MIC. The sensitivity can be adjusted with P1. T4 controls the LEDs. These are preferably high intensity LEDs. MIC is a condenser microphone. The circuit can be powered by a 9 V block battery.
The described circuit functions as a sound-activated light organ, ideal for creating dynamic visual effects in response to audio input, particularly at social gatherings. The primary components include a condenser microphone (MIC), a transistor amplifier (T1), a variable resistor (P1) for sensitivity adjustment, and a control transistor (T4) to manage the operation of four high-intensity LEDs.
The condenser microphone captures ambient sound, converting acoustic energy into an electrical signal. This signal is relatively weak and requires amplification for further processing. The transistor T1 serves this purpose by amplifying the microphone's output. The gain of T1 can be adjusted through the variable resistor P1, allowing users to set the sensitivity of the circuit based on the ambient noise level or the desired responsiveness to sound.
Once the signal is amplified, it is fed into the control transistor T4, which is responsible for driving the LEDs. The output from T1 triggers T4 to switch the LEDs on and off in synchrony with the detected sound pulses, creating a visual representation of the audio input. The choice of high-intensity LEDs ensures that the light output is sufficient to be noticed in a party environment, enhancing the overall effect.
Powering the circuit is straightforward, as it operates on a standard 9 V block battery, making it portable and easy to set up in various locations. The simplicity of the design, combined with the ability to adjust sensitivity, makes this circuit a versatile solution for entertainment applications, providing an engaging experience through synchronized light and sound.This is a nice example circuit that can be used at parties. The four LEDs blink to the beat of the music. The light organ using a microphone responds to sound. T1 amplifies the signal from MIC. The sensitivity can be adjusted with P1. T4 controls the LEDs. These are preferably high intensity LEDs. MIC is a condenser microphone. The circuit can be powered by a 9 V block battery. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a sound-activated light organ, ideal for creating dynamic visual effects in response to audio input, particularly at social gatherings. The primary components include a condenser microphone (MIC), a transistor amplifier (T1), a variable resistor (P1) for sensitivity adjustment, and a control transistor (T4) to manage the operation of four high-intensity LEDs.
The condenser microphone captures ambient sound, converting acoustic energy into an electrical signal. This signal is relatively weak and requires amplification for further processing. The transistor T1 serves this purpose by amplifying the microphone's output. The gain of T1 can be adjusted through the variable resistor P1, allowing users to set the sensitivity of the circuit based on the ambient noise level or the desired responsiveness to sound.
Once the signal is amplified, it is fed into the control transistor T4, which is responsible for driving the LEDs. The output from T1 triggers T4 to switch the LEDs on and off in synchrony with the detected sound pulses, creating a visual representation of the audio input. The choice of high-intensity LEDs ensures that the light output is sufficient to be noticed in a party environment, enhancing the overall effect.
Powering the circuit is straightforward, as it operates on a standard 9 V block battery, making it portable and easy to set up in various locations. The simplicity of the design, combined with the ability to adjust sensitivity, makes this circuit a versatile solution for entertainment applications, providing an engaging experience through synchronized light and sound.This is a nice example circuit that can be used at parties. The four LEDs blink to the beat of the music. The light organ using a microphone responds to sound. T1 amplifies the signal from MIC. The sensitivity can be adjusted with P1. T4 controls the LEDs. These are preferably high intensity LEDs. MIC is a condenser microphone. The circuit can be powered by a 9 V block battery. 🔗 External reference