A Friendly Charger Schematic for Mobile Phones
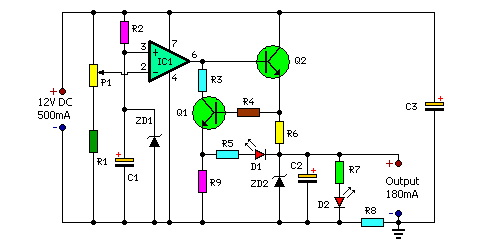
Charges and protects your mobile phone from voltage spikes and short circuits. Most mobile chargers do not have current or voltage regulation, nor do they provide short-circuit protection.
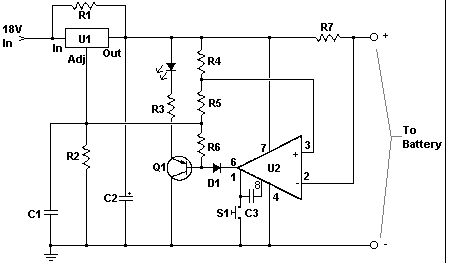
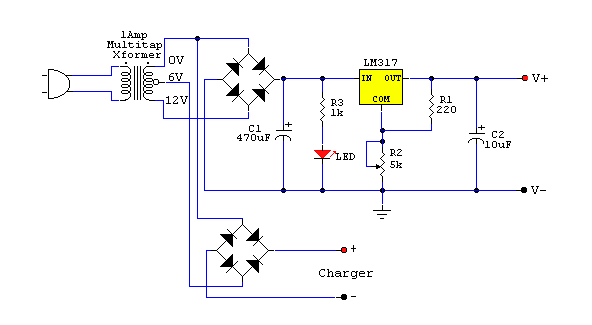
The described circuit functions as a mobile phone charger designed to safeguard the device from voltage spikes and short circuits. In typical scenarios, many standard mobile chargers lack adequate current and voltage regulation, which can lead to potential damage to the mobile phone's internal components.
This charger incorporates essential protective features. The voltage spike protection is typically achieved through the integration of transient voltage suppression (TVS) diodes or varistors, which divert excess voltage away from the device. This mechanism ensures that any sudden surges in voltage do not reach the mobile phone, thereby preserving its functionality and longevity.
Additionally, short-circuit protection is a critical feature that prevents excessive current flow that could otherwise lead to overheating or damage. This is often implemented using a current sensing circuit that detects abnormal current levels and automatically disconnects the charger from the power source. This disconnection can be accomplished through a relay or a MOSFET switch, which acts to open the circuit in the event of a detected fault.
Current and voltage regulation can be achieved using linear regulators or switching regulators, depending on the desired efficiency and thermal performance. Linear regulators provide a simple solution with low noise, while switching regulators can offer higher efficiency, especially in battery-powered applications.
In summary, the charger is equipped with protective measures against voltage spikes and short circuits, while also ensuring stable current and voltage regulation. This design not only enhances the safety of the mobile phone during charging but also contributes to the overall reliability and performance of the device.Charges and protects your mobile phone from voltage spikes and short-circuit Most mobile chargers do not have current/voltage regulation or short-circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a mobile phone charger designed to safeguard the device from voltage spikes and short circuits. In typical scenarios, many standard mobile chargers lack adequate current and voltage regulation, which can lead to potential damage to the mobile phone's internal components.
This charger incorporates essential protective features. The voltage spike protection is typically achieved through the integration of transient voltage suppression (TVS) diodes or varistors, which divert excess voltage away from the device. This mechanism ensures that any sudden surges in voltage do not reach the mobile phone, thereby preserving its functionality and longevity.
Additionally, short-circuit protection is a critical feature that prevents excessive current flow that could otherwise lead to overheating or damage. This is often implemented using a current sensing circuit that detects abnormal current levels and automatically disconnects the charger from the power source. This disconnection can be accomplished through a relay or a MOSFET switch, which acts to open the circuit in the event of a detected fault.
Current and voltage regulation can be achieved using linear regulators or switching regulators, depending on the desired efficiency and thermal performance. Linear regulators provide a simple solution with low noise, while switching regulators can offer higher efficiency, especially in battery-powered applications.
In summary, the charger is equipped with protective measures against voltage spikes and short circuits, while also ensuring stable current and voltage regulation. This design not only enhances the safety of the mobile phone during charging but also contributes to the overall reliability and performance of the device.Charges and protects your mobile phone from voltage spikes and short-circuit Most mobile chargers do not have current/voltage regulation or short-circuit.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713