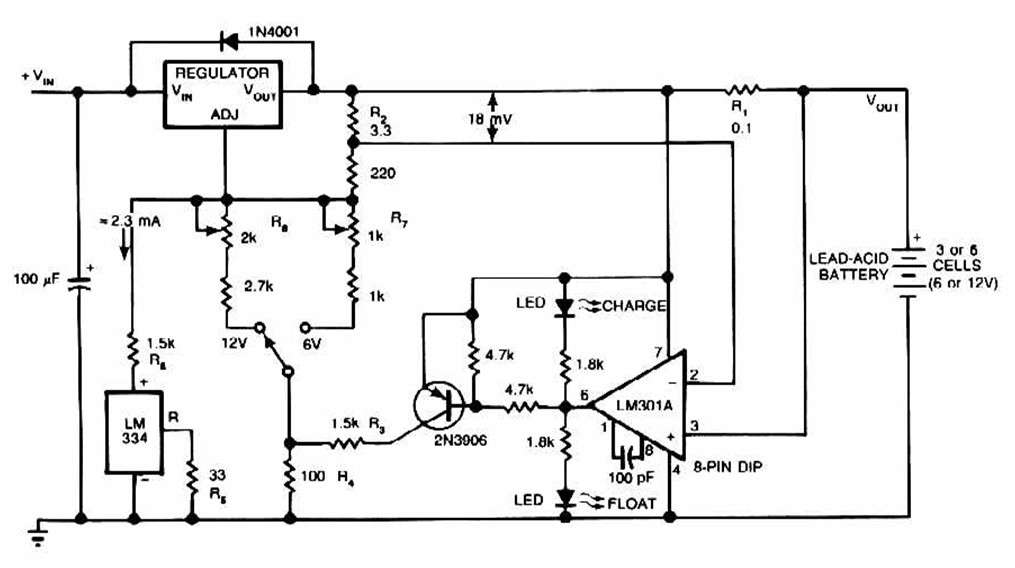
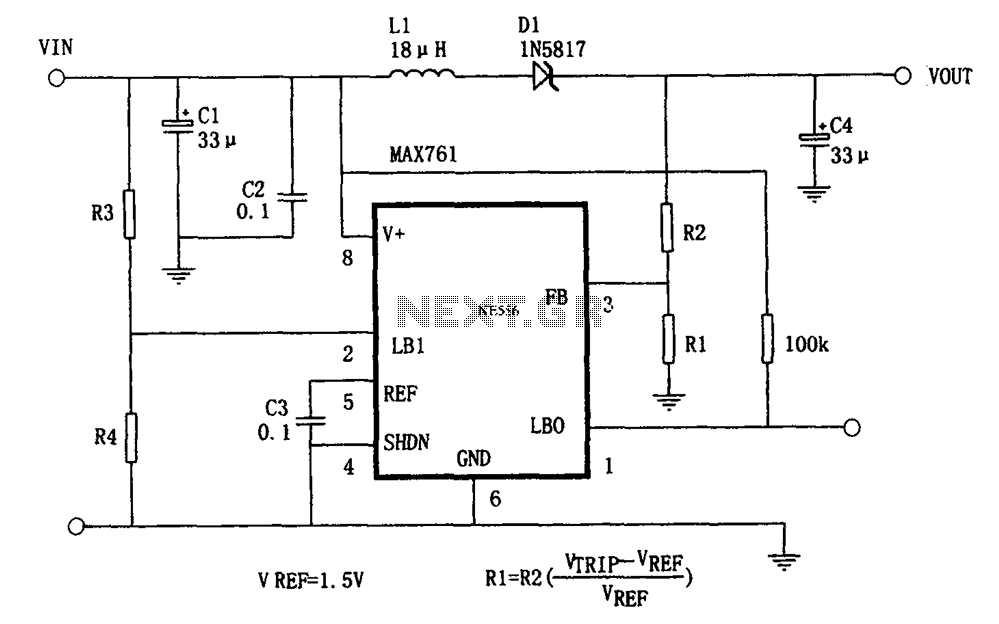
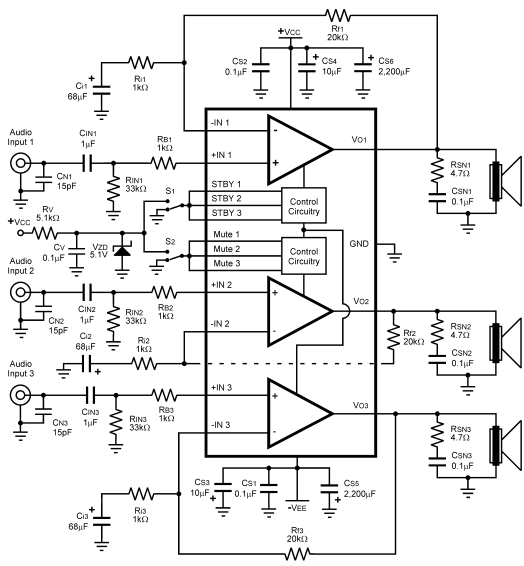
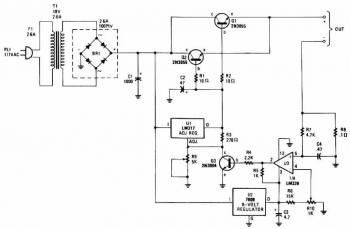
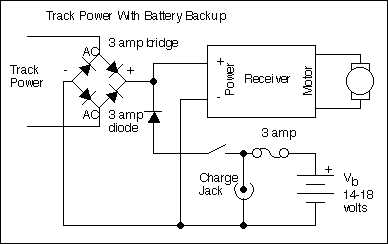
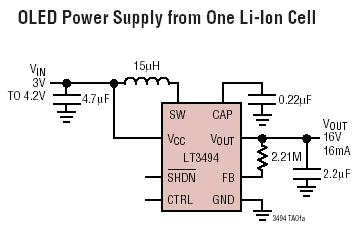
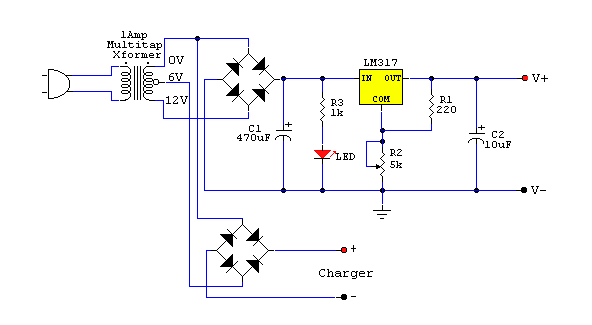
Adjustable Power Supply with Charger Output
The purpose of a DC power supply is to deliver the necessary level of DC power to a load by utilizing an AC supply at the input. Various applications demand different specifications; however, contemporary DC power supplies often ensure an accurate output voltage. This voltage is regulated through electronic circuitry to maintain a constant output voltage across a broad range of output loads. Linear power supplies are commonly employed in scenarios where low noise and ripple are essential. As indicated by their name, they utilize linear technology, typically incorporating a series linear regulator element to reduce voltage. Consequently, they dissipate power but, in the absence of any switching mode, can provide high performance levels.
DC power supplies convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) and are critical in various electronic applications, from powering consumer electronics to industrial equipment. The basic operation involves rectifying the AC input, filtering it to smooth out fluctuations, and regulating the output voltage to ensure consistency under varying load conditions.
Linear power supplies, a specific type of DC power supply, are characterized by their simplicity and reliability. They consist of a transformer to step down the voltage, followed by a rectifier to convert AC to DC, and a linear voltage regulator to provide a stable output. The linear regulator operates by dropping excess voltage across a pass element (typically a transistor), allowing for precise voltage control. This method results in minimal electrical noise and ripple, making linear power supplies ideal for sensitive applications such as audio equipment, laboratory instruments, and precision measurement devices.
Despite their advantages, linear power supplies have some limitations. They tend to be less efficient than switching power supplies, especially when there is a significant difference between the input and output voltage. The power dissipated as heat in the linear regulator can lead to thermal management challenges, necessitating the use of heat sinks or cooling systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Overall, the design and implementation of DC power supplies, particularly linear types, require careful consideration of the specific application requirements, including load characteristics, efficiency, noise tolerance, and thermal management.The aim of a DC power supply is to provide the required level of DC power to the load using an AC supply at the input. Different applications require different attributes, but more often than not these days DC power supplies provide an accurate output voltage - this is regulated using electronic circuitry so that it provides a constant output voltage over a wide range of output loads.
Linear power supplies are widely used for applications where low noise and ripple are required. As the name suggests, they use linear technology - typically a series linear regulator element to drop voltage. As such they dissipate power, but without any switching mode, they are able to offer high levels of eprformance
🔗 External reference
DC power supplies convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) and are critical in various electronic applications, from powering consumer electronics to industrial equipment. The basic operation involves rectifying the AC input, filtering it to smooth out fluctuations, and regulating the output voltage to ensure consistency under varying load conditions.
Linear power supplies, a specific type of DC power supply, are characterized by their simplicity and reliability. They consist of a transformer to step down the voltage, followed by a rectifier to convert AC to DC, and a linear voltage regulator to provide a stable output. The linear regulator operates by dropping excess voltage across a pass element (typically a transistor), allowing for precise voltage control. This method results in minimal electrical noise and ripple, making linear power supplies ideal for sensitive applications such as audio equipment, laboratory instruments, and precision measurement devices.
Despite their advantages, linear power supplies have some limitations. They tend to be less efficient than switching power supplies, especially when there is a significant difference between the input and output voltage. The power dissipated as heat in the linear regulator can lead to thermal management challenges, necessitating the use of heat sinks or cooling systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Overall, the design and implementation of DC power supplies, particularly linear types, require careful consideration of the specific application requirements, including load characteristics, efficiency, noise tolerance, and thermal management.The aim of a DC power supply is to provide the required level of DC power to the load using an AC supply at the input. Different applications require different attributes, but more often than not these days DC power supplies provide an accurate output voltage - this is regulated using electronic circuitry so that it provides a constant output voltage over a wide range of output loads.
Linear power supplies are widely used for applications where low noise and ripple are required. As the name suggests, they use linear technology - typically a series linear regulator element to drop voltage. As such they dissipate power, but without any switching mode, they are able to offer high levels of eprformance
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713