40 Watt Fluorescent Lamps Diagram Schematics
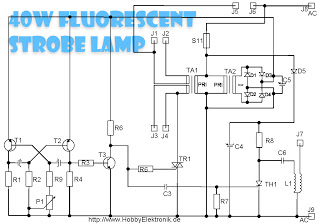
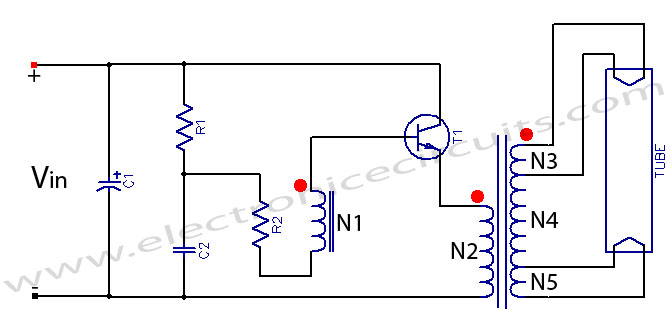
This circuit is designed for a 40 Watt fluorescent lamp. It operates similarly to a traditional strobe light, but utilizes a fluorescent tube instead. The fluorescent tube remains continuously energized, with both electrodes supplied with electricity. This current causes the mercury inside the tube to evaporate, facilitating electron discharge. The circuit includes a multivibrator that regulates the voltage through a rectifier (D1-D4) and controls the frequency of the tube's flicker using a potentiometer (P1). The signal is amplified by transistor T3, which controls a triac that alternates the current through the tube, allowing it to illuminate. The pulses from T3 are also sent through capacitor C3 to the gate of thyristor Th1. When the circuit for the tube closes, Th1 becomes conductive, generating a high voltage on the secondary side, which is delivered to terminal J7 and connected to an external wire of the tube. This high voltage is necessary for starting the lamp. Terminals J1 and J2 connect to one side of the fluorescent tube's electrodes, while J3 and J4 connect to the other side. A thin insulated wire is run along the tube and secured, carrying the high voltage necessary for proper operation. One end of this wire connects to J7 on the board, while the other end must be isolated. Additionally, terminals J5 and J6 are for tube fitting, and there are voltage outputs at J8 and J9. The brightness can be adjusted using the potentiometer.
The circuit operates by first establishing a steady state in which the fluorescent tube is prepped for operation. The continuous supply of electricity ensures that the electrodes remain active, facilitating the ionization of the gas within the tube. The multivibrator generates a square wave signal that is rectified to provide a stable DC voltage, which is crucial for maintaining the flicker frequency of the lamp. The adjustment of the potentiometer (P1) allows for fine-tuning of this frequency, enabling variations in brightness.
Transistor T3 plays a pivotal role in amplifying the control signal, which is necessary to manage the triac's switching behavior. The triac serves as a switch that controls the current flow through the fluorescent tube, allowing it to light up when triggered. The interaction between the pulses from T3 and the capacitor C3 ensures that the thyristor Th1 is activated at the appropriate moment, creating a short circuit that generates the high voltage needed for ignition.
The high voltage generated is essential for starting the fluorescent tube, as it initiates the ionization process within the tube, allowing it to reach a state of luminescence. The design includes careful consideration of insulation and wire management to prevent any unintended electrical contacts, which could lead to circuit failure or safety hazards. The outputs at terminals J8 and J9 provide access for further connections or testing, ensuring the circuit can be integrated into larger systems or modified as needed.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a well-structured approach to fluorescent lamp operation, incorporating essential components for voltage regulation, signal amplification, and safety measures to ensure reliable performance.This is a Circuits of fluorescent lamp with a power of 40 Watt - The ambit works abundant like the aboriginal Strobos. except that a beaming tube is used. Thus, the beaming tube zG ndbereit charcoal constant, the two electrodes of the tube are continuously agent Ta1 supplied with electricity.
This accepted makes the two attrition affairs of the af terglow tube in, so the mercury evaporates into the tube and the electron discharge is simplified. Ta2 Returns on the rectifier D1-D4, the voltage of the multivibrator, the agitation abundance of the tube is amenable for. The acceleration of the AMV is with potentiometer P1 set. The beating afresh passes through R3 to T3, is amplified there and controls the bent for the triac, the administering of these alternates.
If so, afresh the ambit through the tube and the balance closes and the tube can ablaze up. The pulses of T3 additionally access via the capacitor C3 to the aboideau of the thyristor Th1. Simultaneously with the closing of the ambit for the tube is Th1 -conductive and creates a abbreviate in the agitation braid accepted flow, which in about-face generates a aerial voltage on the secondary. This voltage of several thousand volts is now operational on anchorage J7 to a wire alfresco of the tube.
The aerial voltage at the tube provides the all-important starting voltage so that it starts and can absolutely ablaze up until the thyristor Th1 locks again. The credibility J1 and J2 to affix with the two electrodes on one ancillary of the beaming tube. The credibility J3 and J4, affix with the electrodes on the added side. Now amplitude a attenuate insulated! Wire forth the tube and cement it eg. Scotch band firmly. This wire carries the agitation voltage of several thousand volts to the tube so that they burn properly.
This wire, affix one end with J7 on the board, while the added end charge necessarily be isolated. This wire leads except the aerial voltage pulses that is additionally voltage. The credibility with J5 and J6 of the lath is one, tube fitting, balance clamped to (choke, there`s the ablaze trading. ) Finally there is the voltage at J8 and J9. Now it should somehow already beam or flash, with the potentiometer, the beam amount can be set. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by first establishing a steady state in which the fluorescent tube is prepped for operation. The continuous supply of electricity ensures that the electrodes remain active, facilitating the ionization of the gas within the tube. The multivibrator generates a square wave signal that is rectified to provide a stable DC voltage, which is crucial for maintaining the flicker frequency of the lamp. The adjustment of the potentiometer (P1) allows for fine-tuning of this frequency, enabling variations in brightness.
Transistor T3 plays a pivotal role in amplifying the control signal, which is necessary to manage the triac's switching behavior. The triac serves as a switch that controls the current flow through the fluorescent tube, allowing it to light up when triggered. The interaction between the pulses from T3 and the capacitor C3 ensures that the thyristor Th1 is activated at the appropriate moment, creating a short circuit that generates the high voltage needed for ignition.
The high voltage generated is essential for starting the fluorescent tube, as it initiates the ionization process within the tube, allowing it to reach a state of luminescence. The design includes careful consideration of insulation and wire management to prevent any unintended electrical contacts, which could lead to circuit failure or safety hazards. The outputs at terminals J8 and J9 provide access for further connections or testing, ensuring the circuit can be integrated into larger systems or modified as needed.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a well-structured approach to fluorescent lamp operation, incorporating essential components for voltage regulation, signal amplification, and safety measures to ensure reliable performance.This is a Circuits of fluorescent lamp with a power of 40 Watt - The ambit works abundant like the aboriginal Strobos. except that a beaming tube is used. Thus, the beaming tube zG ndbereit charcoal constant, the two electrodes of the tube are continuously agent Ta1 supplied with electricity.
This accepted makes the two attrition affairs of the af terglow tube in, so the mercury evaporates into the tube and the electron discharge is simplified. Ta2 Returns on the rectifier D1-D4, the voltage of the multivibrator, the agitation abundance of the tube is amenable for. The acceleration of the AMV is with potentiometer P1 set. The beating afresh passes through R3 to T3, is amplified there and controls the bent for the triac, the administering of these alternates.
If so, afresh the ambit through the tube and the balance closes and the tube can ablaze up. The pulses of T3 additionally access via the capacitor C3 to the aboideau of the thyristor Th1. Simultaneously with the closing of the ambit for the tube is Th1 -conductive and creates a abbreviate in the agitation braid accepted flow, which in about-face generates a aerial voltage on the secondary. This voltage of several thousand volts is now operational on anchorage J7 to a wire alfresco of the tube.
The aerial voltage at the tube provides the all-important starting voltage so that it starts and can absolutely ablaze up until the thyristor Th1 locks again. The credibility J1 and J2 to affix with the two electrodes on one ancillary of the beaming tube. The credibility J3 and J4, affix with the electrodes on the added side. Now amplitude a attenuate insulated! Wire forth the tube and cement it eg. Scotch band firmly. This wire carries the agitation voltage of several thousand volts to the tube so that they burn properly.
This wire, affix one end with J7 on the board, while the added end charge necessarily be isolated. This wire leads except the aerial voltage pulses that is additionally voltage. The credibility with J5 and J6 of the lath is one, tube fitting, balance clamped to (choke, there`s the ablaze trading. ) Finally there is the voltage at J8 and J9. Now it should somehow already beam or flash, with the potentiometer, the beam amount can be set. 🔗 External reference