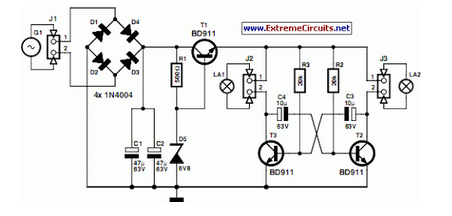
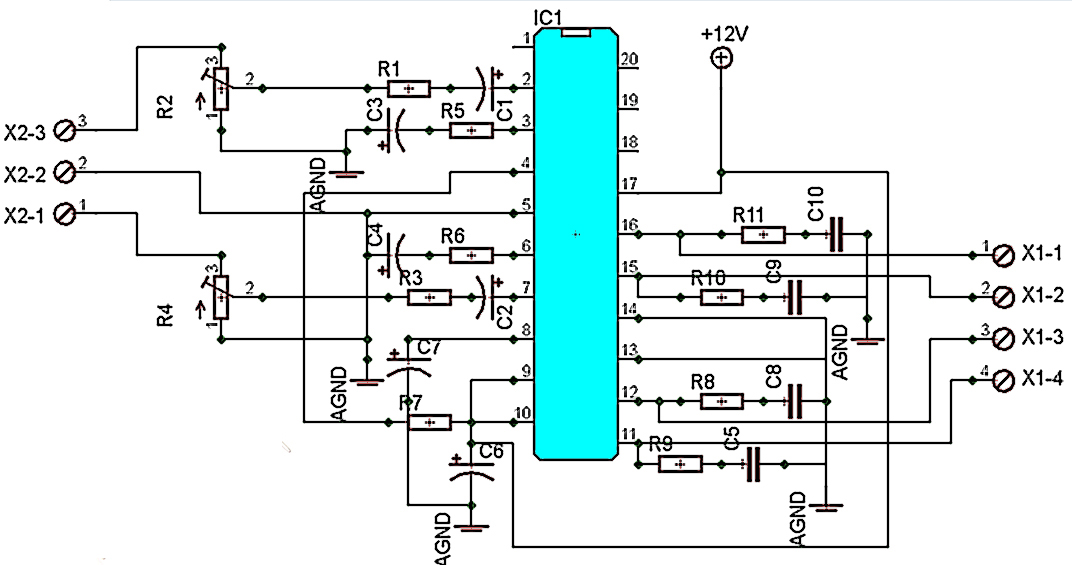
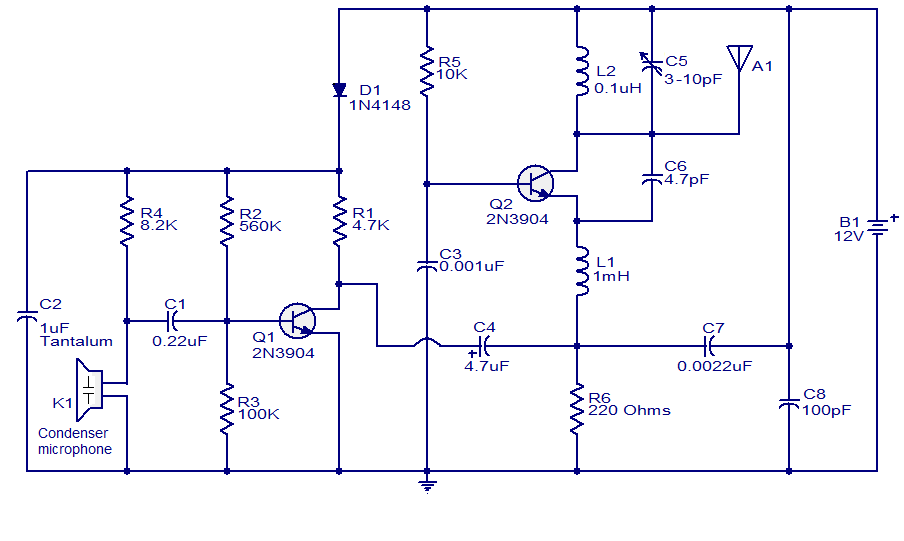
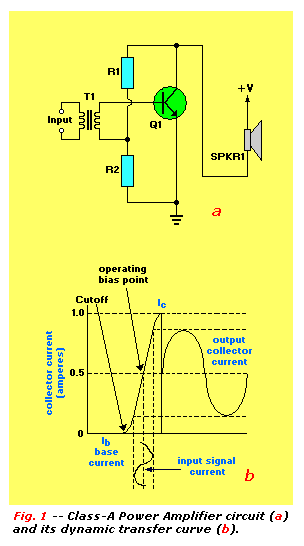
A variable frequency oscillating circuit transistor
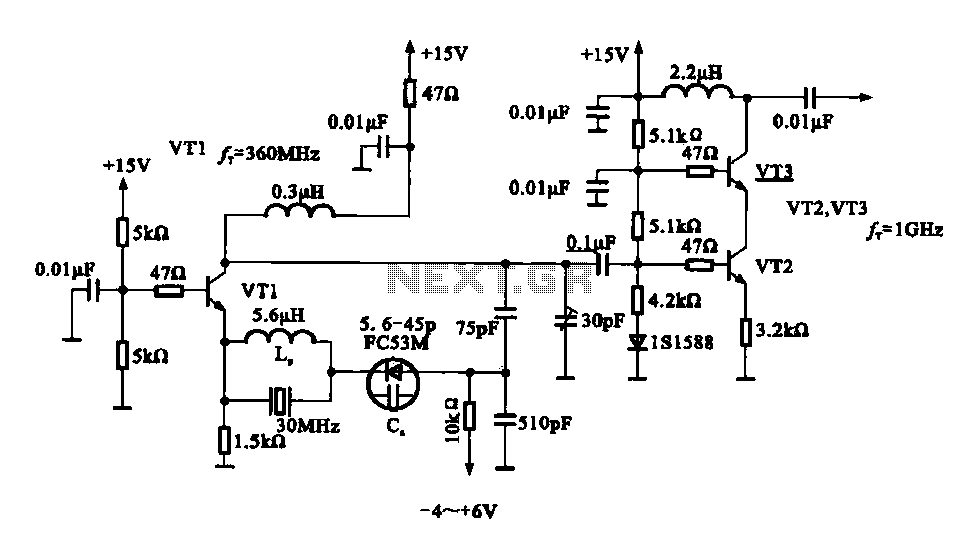
A variable frequency oscillator transistor circuit, primarily functioning as an oscillator, incorporates a crystal resonator and a varactor diode. The output is amplified, typically used for generating high-frequency signals. This 30 MHz transistor circuit features an inductor (LP) connected to the emitter of transistor VT1, which is arranged in parallel and then in series with varactor diodes. Additionally, a 75 pF capacitor is connected in series between the emitter and collector of VT1. Transistors VT2 and VT3 serve as amplifiers, with the oscillation signal being amplified at the collector output of VT3. The control voltage for the varactor diode varies between -4V and +4V.
The variable frequency oscillator (VFO) circuit described operates at a frequency of 30 MHz, utilizing a combination of transistors and passive components to achieve its functionality. The core of the oscillator is transistor VT1, which is configured to form the primary oscillation circuit. The inductor (LP) connected to the emitter of VT1 plays a crucial role in determining the oscillation frequency in conjunction with the crystal resonator.
The use of varactor diodes in this configuration allows for frequency tuning. By varying the control voltage applied to the varactor diodes, the capacitance changes, which in turn alters the resonant frequency of the oscillator circuit. This tuning capability is essential for applications requiring precise frequency adjustments.
The circuit also includes a 75 pF capacitor, strategically placed in series between the emitter and collector of VT1. This capacitor helps to stabilize the oscillation and enhance the overall performance of the oscillator. The amplified output is taken from the collector of transistor VT3, which is part of a cascading amplifier stage that includes VT2. This multi-stage amplification ensures that the oscillation signal is sufficiently strong for further processing or transmission.
The overall design of the variable frequency oscillator circuit reflects a balance between stability, tunability, and amplification, making it suitable for high-frequency applications in various electronic systems. The careful selection of components and their arrangement is critical for achieving the desired performance characteristics, particularly in maintaining a stable oscillation while allowing for frequency adjustments through the control voltage applied to the varactor diodes.Fig variable frequency oscillator transistor circuit, which is mainly an oscillator, the crystal resonator and varactor circuit by the transistor diode, the output of the ampli fier, typically used to make high-frequency transistor oscillator. 30 MHz transistor circuit inductor LP is connected VT1 emitter circuit, it is connected in parallel and then in series with varactor diodes, and then with 75 p capacitor connected in series between the emitter and collector VT1. VT2, VT3 amplifier constituted after the oscillation signal is amplified by the VT3 collector electrode output.
Changes between V - + - 4 varactor control voltage.
The variable frequency oscillator (VFO) circuit described operates at a frequency of 30 MHz, utilizing a combination of transistors and passive components to achieve its functionality. The core of the oscillator is transistor VT1, which is configured to form the primary oscillation circuit. The inductor (LP) connected to the emitter of VT1 plays a crucial role in determining the oscillation frequency in conjunction with the crystal resonator.
The use of varactor diodes in this configuration allows for frequency tuning. By varying the control voltage applied to the varactor diodes, the capacitance changes, which in turn alters the resonant frequency of the oscillator circuit. This tuning capability is essential for applications requiring precise frequency adjustments.
The circuit also includes a 75 pF capacitor, strategically placed in series between the emitter and collector of VT1. This capacitor helps to stabilize the oscillation and enhance the overall performance of the oscillator. The amplified output is taken from the collector of transistor VT3, which is part of a cascading amplifier stage that includes VT2. This multi-stage amplification ensures that the oscillation signal is sufficiently strong for further processing or transmission.
The overall design of the variable frequency oscillator circuit reflects a balance between stability, tunability, and amplification, making it suitable for high-frequency applications in various electronic systems. The careful selection of components and their arrangement is critical for achieving the desired performance characteristics, particularly in maintaining a stable oscillation while allowing for frequency adjustments through the control voltage applied to the varactor diodes.Fig variable frequency oscillator transistor circuit, which is mainly an oscillator, the crystal resonator and varactor circuit by the transistor diode, the output of the ampli fier, typically used to make high-frequency transistor oscillator. 30 MHz transistor circuit inductor LP is connected VT1 emitter circuit, it is connected in parallel and then in series with varactor diodes, and then with 75 p capacitor connected in series between the emitter and collector VT1. VT2, VT3 amplifier constituted after the oscillation signal is amplified by the VT3 collector electrode output.
Changes between V - + - 4 varactor control voltage.