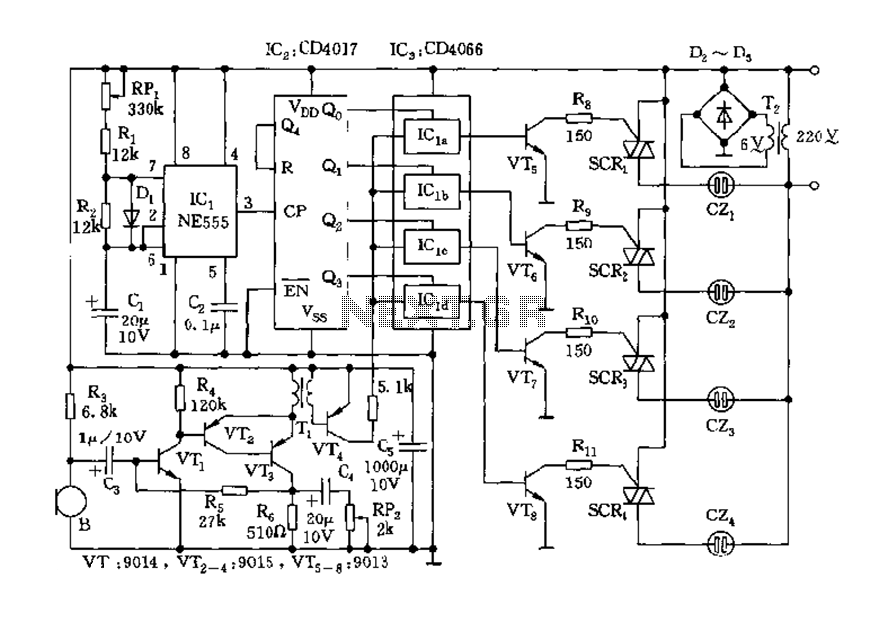
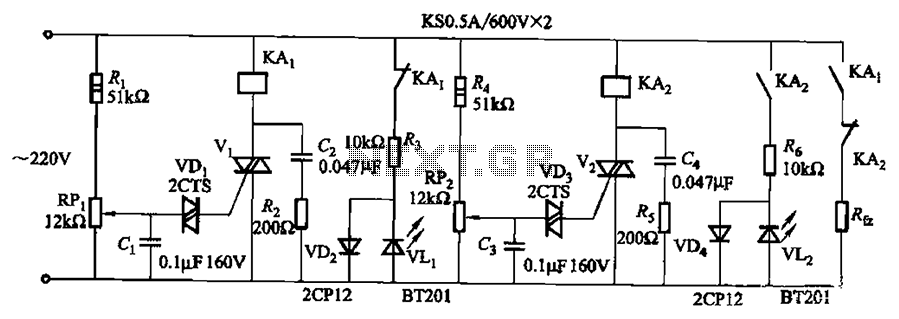
Access room people number counter circuit
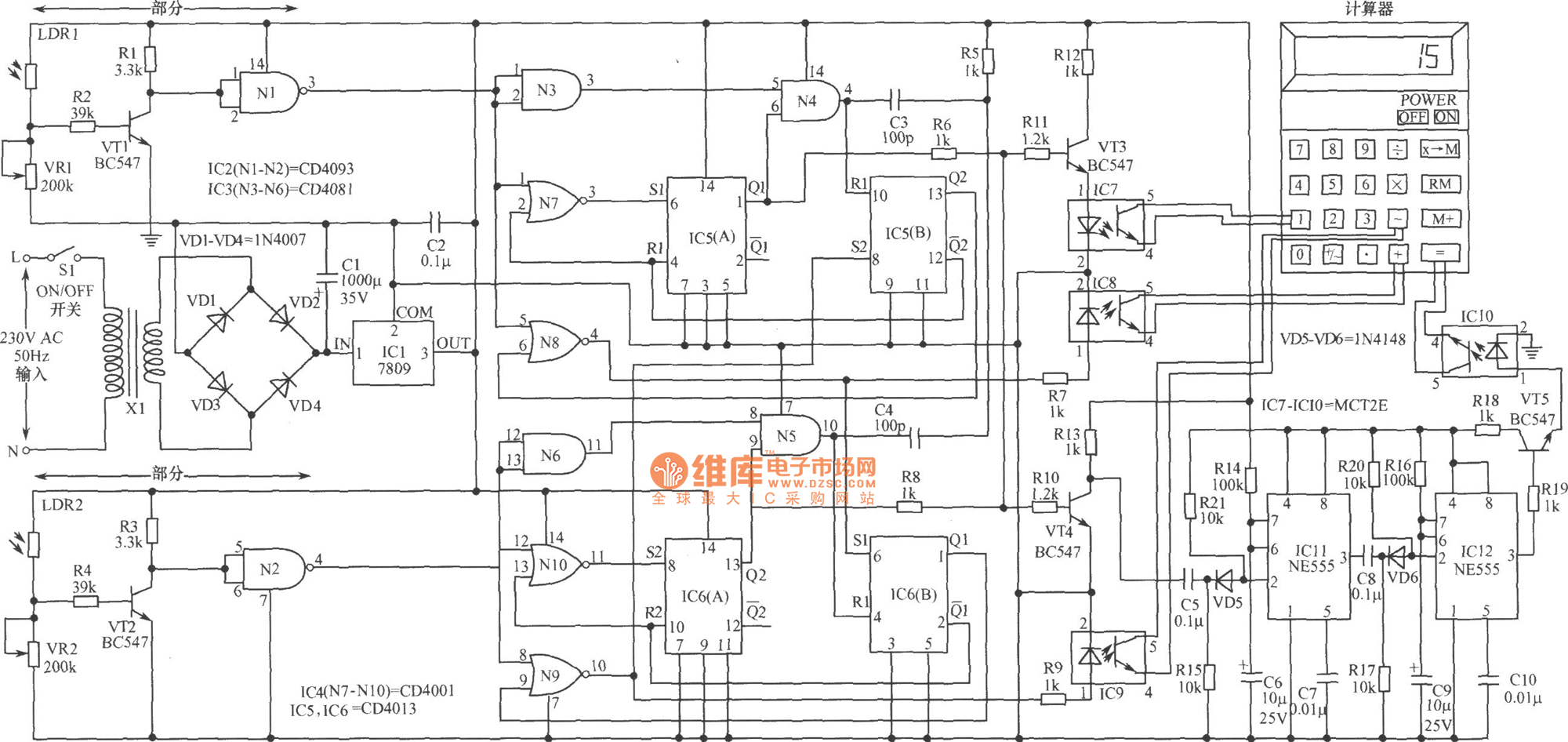
The working principle involves two pairs of photoelectric detection devices installed in the access channel. One side features light source A (transmitter) and photoresistor LDR1 (receiver) at the entrance of the channel, while the other side contains light source B (transmitter) and photoresistor LDR2 (receiver) at the outlet of the channel.
The circuit operates based on the interruption of light beams emitted by the transmitters A and B, which are aimed at their respective photoresistors LDR1 and LDR2. When an object passes through the access channel, it obstructs the light path between the transmitter and receiver pair, resulting in a change in resistance of the photoresistor.
In practical terms, when light from source A strikes LDR1, it causes a decrease in its resistance, allowing current to flow through the circuit. This change can be detected by a microcontroller or a comparator circuit, which can trigger an output action, such as sounding an alarm or activating a gate mechanism. Similarly, when light from source B is interrupted, LDR2 experiences a change in resistance that can also be monitored.
The circuit can be designed to include additional components such as amplifiers to enhance the signal from the photoresistors, and logic gates to process the output signals more effectively. Power supply considerations should also be addressed to ensure that the light sources and the detection devices operate efficiently. Overall, this photoelectric detection system provides a reliable method for monitoring access channels in various applications, such as security systems or automated entry controls.Working principle: Two pairs of photoelectric detection devices are installed in the access channel. On one side the light source A (transmitter) and the photoresistor LDR1 (receiver) are installed in the entrance of the channel; on the other side, the light source B (transmitter) and the photoresistor LDR2 (receiver) are installed in the outlet of the chann.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates based on the interruption of light beams emitted by the transmitters A and B, which are aimed at their respective photoresistors LDR1 and LDR2. When an object passes through the access channel, it obstructs the light path between the transmitter and receiver pair, resulting in a change in resistance of the photoresistor.
In practical terms, when light from source A strikes LDR1, it causes a decrease in its resistance, allowing current to flow through the circuit. This change can be detected by a microcontroller or a comparator circuit, which can trigger an output action, such as sounding an alarm or activating a gate mechanism. Similarly, when light from source B is interrupted, LDR2 experiences a change in resistance that can also be monitored.
The circuit can be designed to include additional components such as amplifiers to enhance the signal from the photoresistors, and logic gates to process the output signals more effectively. Power supply considerations should also be addressed to ensure that the light sources and the detection devices operate efficiently. Overall, this photoelectric detection system provides a reliable method for monitoring access channels in various applications, such as security systems or automated entry controls.Working principle: Two pairs of photoelectric detection devices are installed in the access channel. On one side the light source A (transmitter) and the photoresistor LDR1 (receiver) are installed in the entrance of the channel; on the other side, the light source B (transmitter) and the photoresistor LDR2 (receiver) are installed in the outlet of the chann.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713