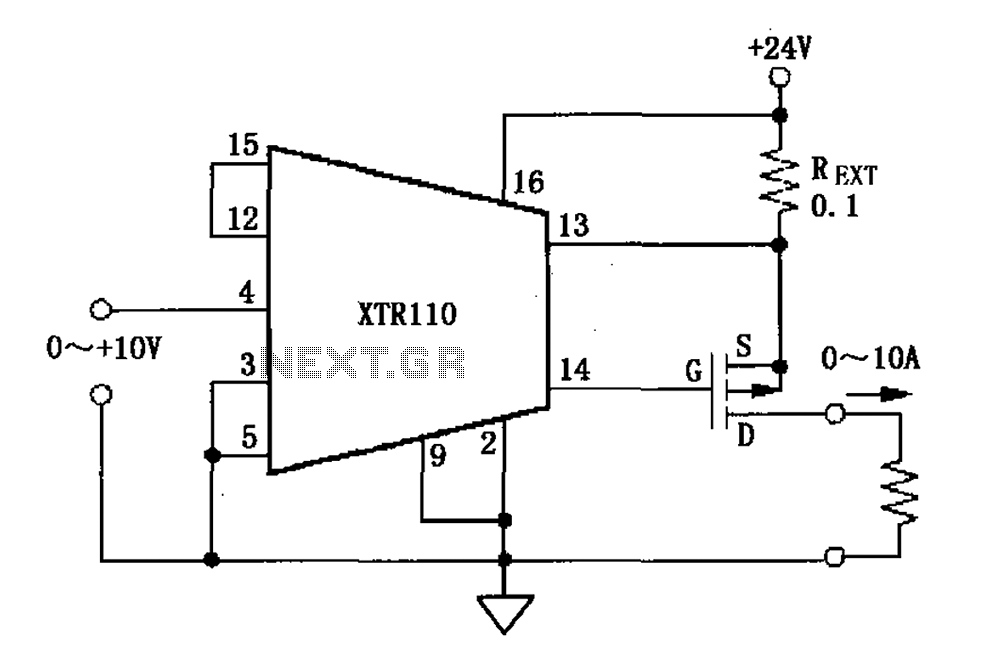
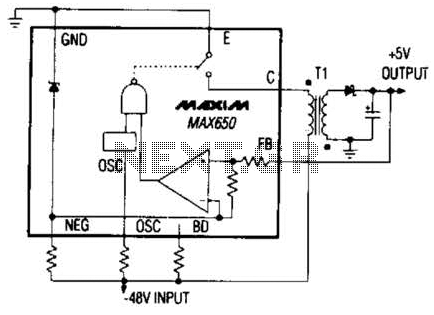
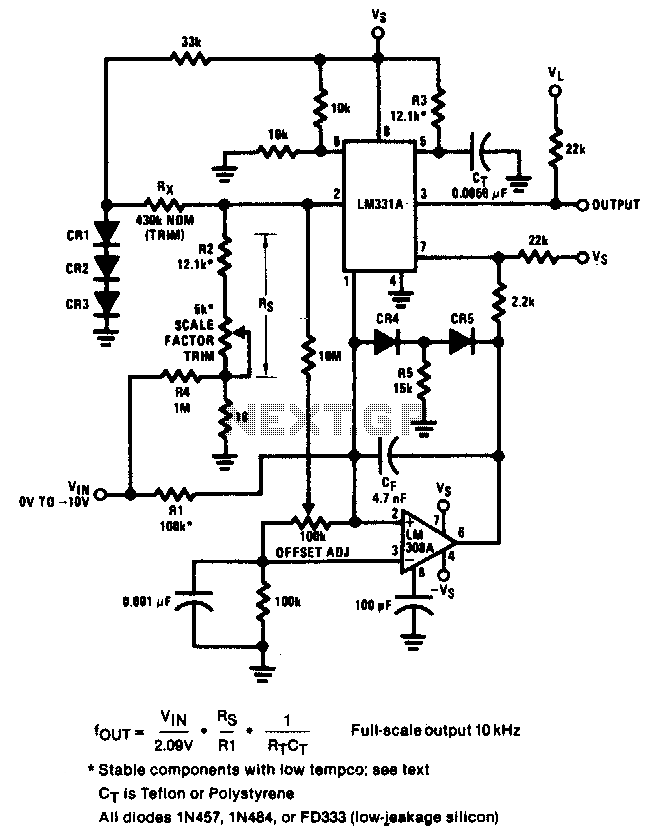
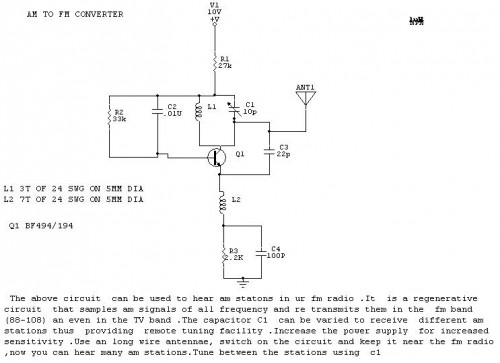
Accurate Low-Cost Square-Root Converter
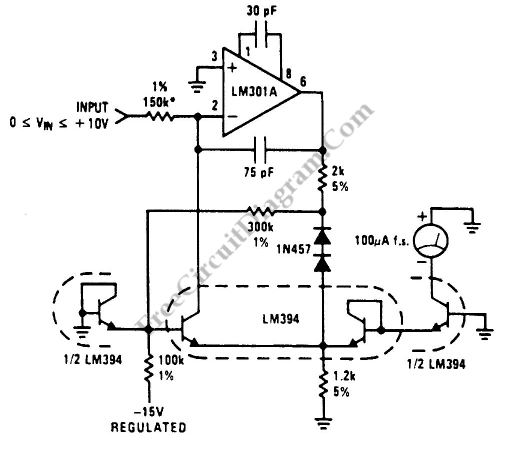
This is a low-cost accurate square-root circuit. This circuit is used to provide a square-root function with good accuracy. The benefit of this circuit is its affordability and precision.
The low-cost accurate square-root circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, and diodes to achieve its functionality. The primary objective of this circuit is to convert an input voltage, representing a squared value, into its square root equivalent, thereby facilitating various applications in analog computing and signal processing.
The circuit design may start with a basic op-amp configuration, where the input voltage is applied to the non-inverting terminal. A feedback network composed of resistors can be utilized to establish the gain required for accurate square-rooting. Diodes may be incorporated to ensure that the output remains within the desired voltage range and to provide temperature stability, enhancing the overall accuracy of the circuit.
The output voltage, which represents the square root of the input voltage, can be further refined using additional filtering stages to minimize noise and improve signal integrity. The performance of the circuit can be evaluated by measuring the output against known square values, ensuring that the deviation from expected results remains within acceptable limits.
Applications for this square-root circuit include analog signal processing in instrumentation systems, control systems, and any scenario where a square-root function is required, such as in calculating distances in sensor applications. The low-cost nature of this circuit makes it particularly attractive for educational purposes and prototype development, allowing users to explore mathematical functions without significant financial investment.This is a Low-Cost Accurate Square-Root Circuit. This circuit is used to provide a square-root function with a good accuracy. The benefit of This circuit is. 🔗 External reference
The low-cost accurate square-root circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, and diodes to achieve its functionality. The primary objective of this circuit is to convert an input voltage, representing a squared value, into its square root equivalent, thereby facilitating various applications in analog computing and signal processing.
The circuit design may start with a basic op-amp configuration, where the input voltage is applied to the non-inverting terminal. A feedback network composed of resistors can be utilized to establish the gain required for accurate square-rooting. Diodes may be incorporated to ensure that the output remains within the desired voltage range and to provide temperature stability, enhancing the overall accuracy of the circuit.
The output voltage, which represents the square root of the input voltage, can be further refined using additional filtering stages to minimize noise and improve signal integrity. The performance of the circuit can be evaluated by measuring the output against known square values, ensuring that the deviation from expected results remains within acceptable limits.
Applications for this square-root circuit include analog signal processing in instrumentation systems, control systems, and any scenario where a square-root function is required, such as in calculating distances in sensor applications. The low-cost nature of this circuit makes it particularly attractive for educational purposes and prototype development, allowing users to explore mathematical functions without significant financial investment.This is a Low-Cost Accurate Square-Root Circuit. This circuit is used to provide a square-root function with a good accuracy. The benefit of This circuit is. 🔗 External reference