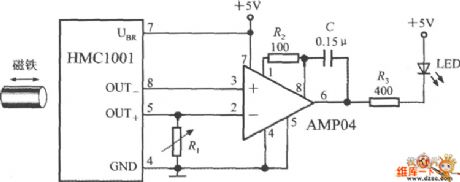
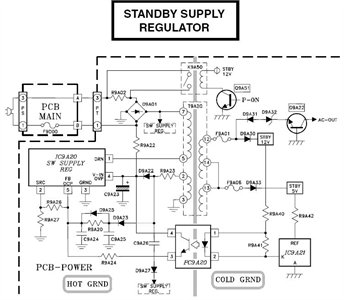
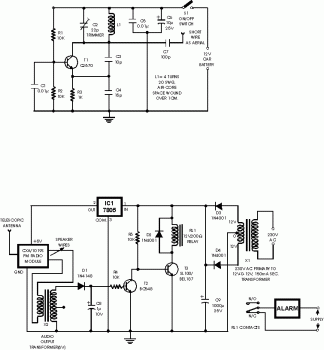
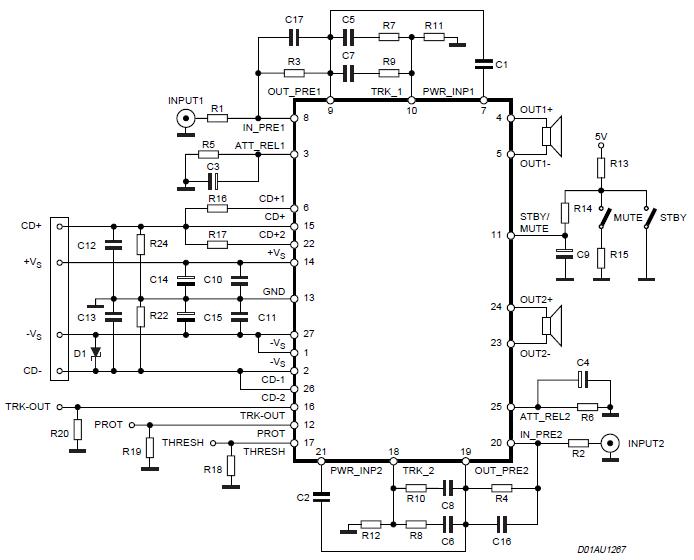
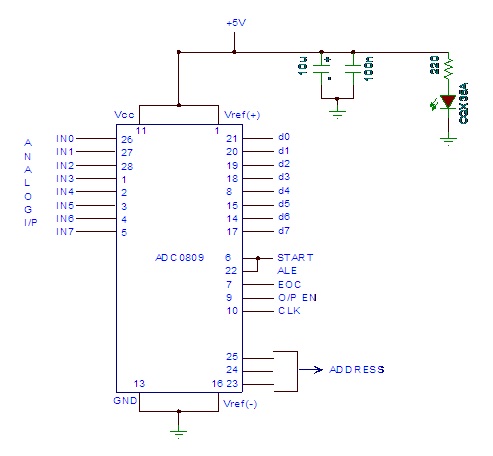
Switching Regulator Converter Circuit
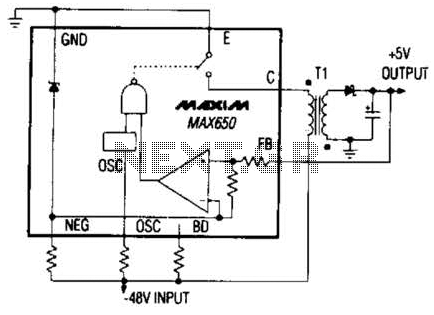
The Max650 switching regulator generates a regulated 5 V output from large negative voltages, such as the -48 V commonly found on telephone lines. This power supply requires several external components, including a transformer, and is capable of delivering 250 mA. The device features a 140-V, 250-mA PNP transistor, short-circuit protection, and all necessary control circuitry.
The Max650 is designed to efficiently convert high negative voltage levels into a stable 5 V output, making it suitable for applications in telecommunications and other systems that require reliable power from unconventional voltage sources. The regulator operates by utilizing a switching mechanism, which allows it to maintain high efficiency and minimize heat generation compared to linear regulators.
The inclusion of a transformer is critical in this design, as it facilitates the necessary voltage conversion and isolation. The transformer steps down the -48 V input to a level that can be further processed by the regulator circuitry. The PNP transistor serves as the main switching element, controlling the flow of current through the transformer and regulating the output voltage.
In addition to the primary components, the circuit includes various passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors that help filter and stabilize the output voltage. These components work together to ensure that the output remains consistent under varying load conditions.
Furthermore, the short-circuit protection feature is essential for safeguarding both the regulator and the connected load. In the event of a short circuit, the regulator can detect the fault and automatically limit the output current, preventing damage to the system.
Overall, the Max650 switching regulator is a robust solution for generating a regulated 5 V output from high negative voltages, with built-in protection and control features that enhance its reliability and performance in demanding applications. The Max650 switching regulator produces a regulated 5 V from large negative voltages, such as the -48 V found on telephone lines. The resulting power supply operates with several external components, including a transformer, and it delivers 250 mA.
The device includes a 140-V 250-mA pnp transistor, short-circuit protection, and all necessary control circuitry.
The Max650 is designed to efficiently convert high negative voltage levels into a stable 5 V output, making it suitable for applications in telecommunications and other systems that require reliable power from unconventional voltage sources. The regulator operates by utilizing a switching mechanism, which allows it to maintain high efficiency and minimize heat generation compared to linear regulators.
The inclusion of a transformer is critical in this design, as it facilitates the necessary voltage conversion and isolation. The transformer steps down the -48 V input to a level that can be further processed by the regulator circuitry. The PNP transistor serves as the main switching element, controlling the flow of current through the transformer and regulating the output voltage.
In addition to the primary components, the circuit includes various passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors that help filter and stabilize the output voltage. These components work together to ensure that the output remains consistent under varying load conditions.
Furthermore, the short-circuit protection feature is essential for safeguarding both the regulator and the connected load. In the event of a short circuit, the regulator can detect the fault and automatically limit the output current, preventing damage to the system.
Overall, the Max650 switching regulator is a robust solution for generating a regulated 5 V output from high negative voltages, with built-in protection and control features that enhance its reliability and performance in demanding applications. The Max650 switching regulator produces a regulated 5 V from large negative voltages, such as the -48 V found on telephone lines. The resulting power supply operates with several external components, including a transformer, and it delivers 250 mA.
The device includes a 140-V 250-mA pnp transistor, short-circuit protection, and all necessary control circuitry.