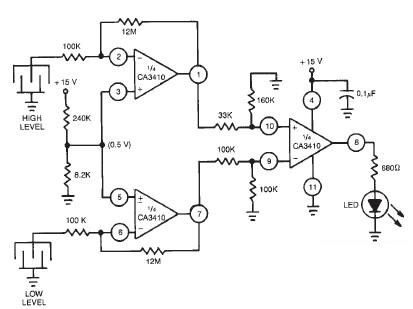
Acoustic Sensor

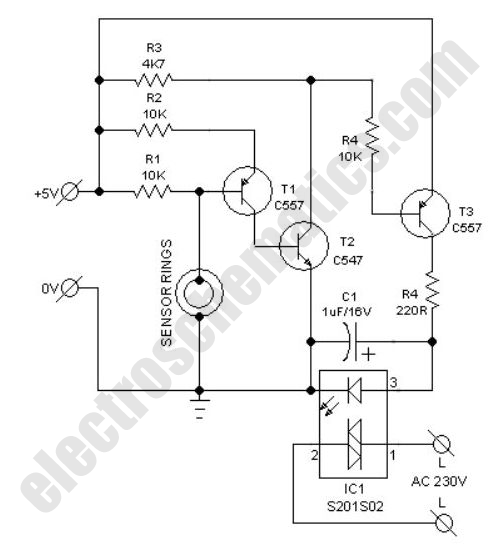
The sensitivity of the circuit can be adjusted using potentiometer P1 to avoid responding to ambient noise levels. Diodes D1 and D2 rectify the signal, while capacitor C4 provides smoothing. When the voltage across C4 exceeds 0.5 V, transistor T2 activates, lighting the LED connected to its collector. Transistor T3 inverts this signal. If the microphone does not detect sound, T3 remains on, and the output is at ground potential. Conversely, if a signal is detected, T3 turns off, and the output is pulled to +24 V by resistors R4 and R5. To accommodate an output current of 10 mA, the collector resistor of T3 must be 2.4 kΩ. For safety when using 0.25 W resistors, this should be achieved by connecting two 4.7 kΩ resistors in parallel. Diode D4 protects the circuit from reverse polarity connections, and D3 safeguards the output from damage in case of accidental connection to the power supply.
The described circuit functions as a microphone signal processing unit, where the sensitivity adjustment via potentiometer P1 allows the user to tailor the circuit's response to varying ambient noise conditions. The rectification of the audio signal by diodes D1 and D2 ensures that only positive voltage levels are processed, which is essential for the subsequent smoothing action of capacitor C4. This smoothing capacitor filters out high-frequency noise, stabilizing the voltage level that triggers the activation of transistor T2.
When the voltage across C4 exceeds the threshold of 0.5 V, T2 turns on, illuminating the connected LED, which serves as a visual indicator of the circuit's active state. The inverting behavior of transistor T3 ensures that the output signal reflects the presence or absence of sound detected by the microphone. In a state of silence, T3 is in a conducting state, maintaining the output at ground potential. Upon detection of an audio signal, T3 switches off, allowing the output to rise to +24 V, facilitated by resistors R4 and R5, which are appropriately sized to handle the required output current.
The design incorporates a safety feature with diode D4, which prevents damage from reverse polarity connections, a common issue in circuit assembly. Additionally, diode D3 serves to protect the output stage from potential over-voltage conditions that could arise from incorrect power supply connections. The choice of using two 4.7 kΩ resistors in parallel to achieve the necessary collector resistance for T3 ensures that the circuit can handle the required power dissipation safely while maintaining the desired performance characteristics. Overall, this circuit design demonstrates effective signal processing and protection mechanisms suitable for various audio applications.The sensitivity of the circuit can be adjusted using potentiometer P1 so that it does not respond to ambient noise levels. Diodes D1 and D2 recitfy the signal and C4 provides smoothing. As soon as the voltage across C4 rises above 0. 5 V, T2 turns on and the LED connected to the collector of the transistor lights. T3 inverts this signal. If the mic rophone receives no sound, T3 turns on and the output will be at ground. If a signal is detected, T3 turns off and the output is pulled to +24 V by R4 and R5. In order to allow for an output current of 10 mA, T3`s collector resistor needs to be 2. 4 k. If 0. 25 W resistors are to be used, then to be on the safe side this should be made up of two 4. 7 k resistors wired in parallel. Diode D4 protects the circuit from reverse polarity connection, and D3 protects the output from damage if it is inadvertently connected to the supply. Be the first of your friends to get free diy electronics projects, circuits diagrams, hacks, mods, gadgets & gizmo automatically each time we publish.
Your email address & privacy are safe with us ! 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a microphone signal processing unit, where the sensitivity adjustment via potentiometer P1 allows the user to tailor the circuit's response to varying ambient noise conditions. The rectification of the audio signal by diodes D1 and D2 ensures that only positive voltage levels are processed, which is essential for the subsequent smoothing action of capacitor C4. This smoothing capacitor filters out high-frequency noise, stabilizing the voltage level that triggers the activation of transistor T2.
When the voltage across C4 exceeds the threshold of 0.5 V, T2 turns on, illuminating the connected LED, which serves as a visual indicator of the circuit's active state. The inverting behavior of transistor T3 ensures that the output signal reflects the presence or absence of sound detected by the microphone. In a state of silence, T3 is in a conducting state, maintaining the output at ground potential. Upon detection of an audio signal, T3 switches off, allowing the output to rise to +24 V, facilitated by resistors R4 and R5, which are appropriately sized to handle the required output current.
The design incorporates a safety feature with diode D4, which prevents damage from reverse polarity connections, a common issue in circuit assembly. Additionally, diode D3 serves to protect the output stage from potential over-voltage conditions that could arise from incorrect power supply connections. The choice of using two 4.7 kΩ resistors in parallel to achieve the necessary collector resistance for T3 ensures that the circuit can handle the required power dissipation safely while maintaining the desired performance characteristics. Overall, this circuit design demonstrates effective signal processing and protection mechanisms suitable for various audio applications.The sensitivity of the circuit can be adjusted using potentiometer P1 so that it does not respond to ambient noise levels. Diodes D1 and D2 recitfy the signal and C4 provides smoothing. As soon as the voltage across C4 rises above 0. 5 V, T2 turns on and the LED connected to the collector of the transistor lights. T3 inverts this signal. If the mic rophone receives no sound, T3 turns on and the output will be at ground. If a signal is detected, T3 turns off and the output is pulled to +24 V by R4 and R5. In order to allow for an output current of 10 mA, T3`s collector resistor needs to be 2. 4 k. If 0. 25 W resistors are to be used, then to be on the safe side this should be made up of two 4. 7 k resistors wired in parallel. Diode D4 protects the circuit from reverse polarity connection, and D3 protects the output from damage if it is inadvertently connected to the supply. Be the first of your friends to get free diy electronics projects, circuits diagrams, hacks, mods, gadgets & gizmo automatically each time we publish.
Your email address & privacy are safe with us ! 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713