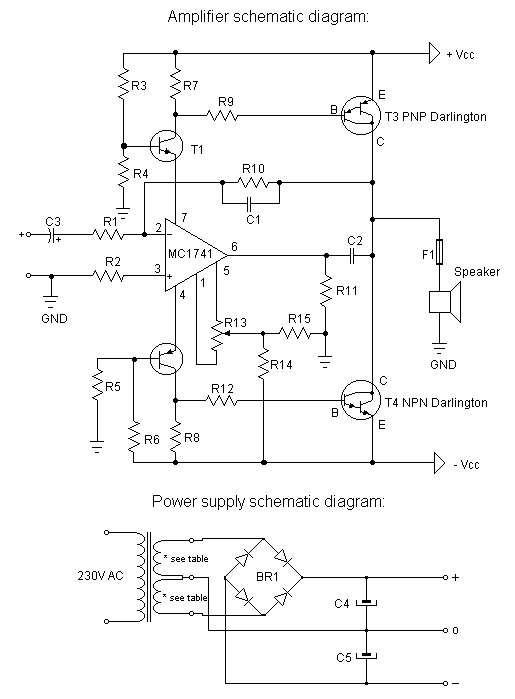
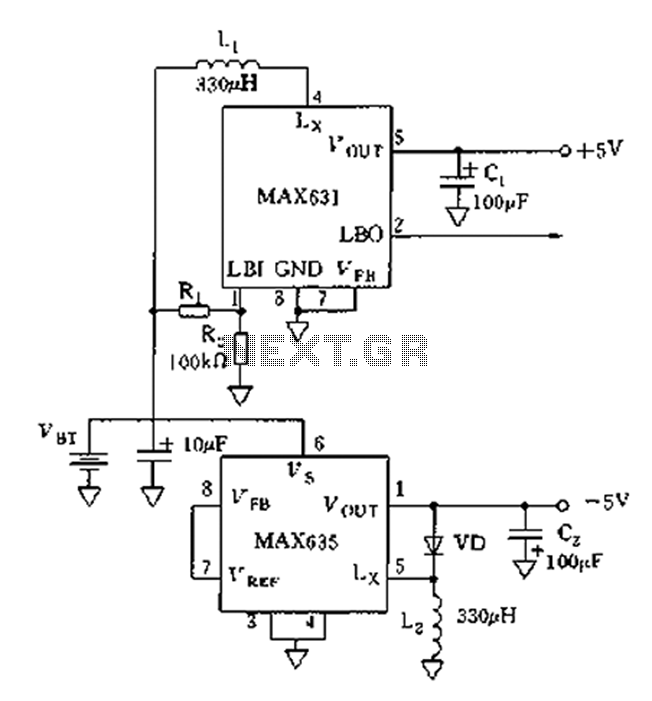
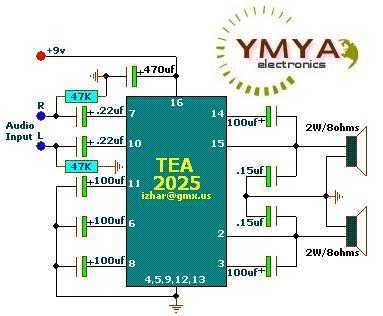
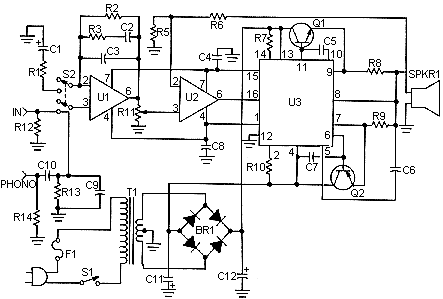
AM-FM-TV RF AMPLIFIER
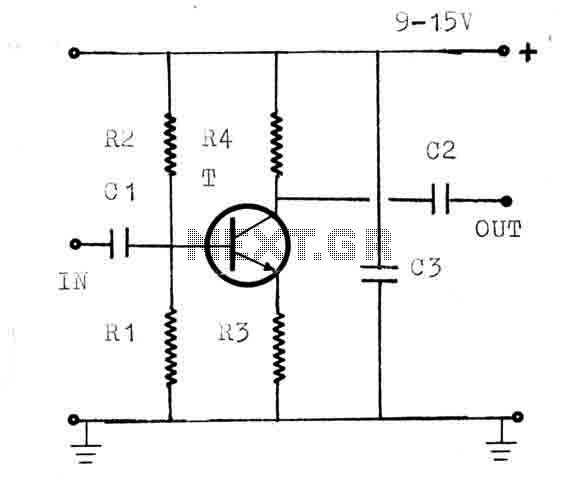
The circuit is a universal amplifier capable of amplifying any RF signal. The BF194 or BF198 transistors can be utilized. Coaxial cable should be used for connections. Additional components include: R1=22K, R2=100K, R3=18, R4=1.2K, C1=470PF, C2=470PF, C3=1NF, and T=BF194 or BF198.
The universal RF amplifier circuit employs either the BF194 or BF198 transistors, both of which are suitable for high-frequency applications. The circuit is designed to enhance RF signals, making it ideal for various communication tasks, including radio frequency transmission and reception.
The resistors in the circuit include R1 (22KΩ), R2 (100KΩ), R3 (18Ω), and R4 (1.2KΩ). R1 and R2 form a voltage divider that sets the biasing conditions for the transistor, ensuring it operates within its active region for optimal amplification. R3 serves as a load resistor, helping to convert the amplified current from the transistor into a voltage signal. R4 is used for emitter biasing, stabilizing the transistor's operating point against variations in temperature and transistor parameters.
Capacitors C1 (470pF), C2 (470pF), and C3 (1nF) are crucial for coupling and bypassing in the circuit. C1 and C2 are used for AC coupling, allowing the RF signals to pass while blocking any DC components, thus preventing distortion in the amplified signal. C3 serves as a bypass capacitor, helping to maintain a stable voltage across the transistor by filtering out high-frequency noise.
The use of coaxial cable for connections is essential in RF applications to minimize signal loss and interference. Coaxial cable provides a shielded environment for the signal, reducing the impact of external electromagnetic interference, which is critical for maintaining the integrity of the RF signals being amplified.
Overall, this universal amplifier circuit is versatile and can be adapted for various RF applications, making it a valuable tool in the field of electronics and communication systems. Proper assembly and layout are crucial to ensure the circuit functions as intended, with attention paid to component placement and the use of appropriate shielding techniques.The circuit is a universal amplifier that can amplify any rf signal. You can use the BF194 or the BF198. Make sure you use coaxial cable. Parts: R1=22K R2=100K R3=18 R4=1.2K C1=470PF C2=470PF C3=1NF T= BF194 OR BF198 🔗 External reference
The universal RF amplifier circuit employs either the BF194 or BF198 transistors, both of which are suitable for high-frequency applications. The circuit is designed to enhance RF signals, making it ideal for various communication tasks, including radio frequency transmission and reception.
The resistors in the circuit include R1 (22KΩ), R2 (100KΩ), R3 (18Ω), and R4 (1.2KΩ). R1 and R2 form a voltage divider that sets the biasing conditions for the transistor, ensuring it operates within its active region for optimal amplification. R3 serves as a load resistor, helping to convert the amplified current from the transistor into a voltage signal. R4 is used for emitter biasing, stabilizing the transistor's operating point against variations in temperature and transistor parameters.
Capacitors C1 (470pF), C2 (470pF), and C3 (1nF) are crucial for coupling and bypassing in the circuit. C1 and C2 are used for AC coupling, allowing the RF signals to pass while blocking any DC components, thus preventing distortion in the amplified signal. C3 serves as a bypass capacitor, helping to maintain a stable voltage across the transistor by filtering out high-frequency noise.
The use of coaxial cable for connections is essential in RF applications to minimize signal loss and interference. Coaxial cable provides a shielded environment for the signal, reducing the impact of external electromagnetic interference, which is critical for maintaining the integrity of the RF signals being amplified.
Overall, this universal amplifier circuit is versatile and can be adapted for various RF applications, making it a valuable tool in the field of electronics and communication systems. Proper assembly and layout are crucial to ensure the circuit functions as intended, with attention paid to component placement and the use of appropriate shielding techniques.The circuit is a universal amplifier that can amplify any rf signal. You can use the BF194 or the BF198. Make sure you use coaxial cable. Parts: R1=22K R2=100K R3=18 R4=1.2K C1=470PF C2=470PF C3=1NF T= BF194 OR BF198 🔗 External reference