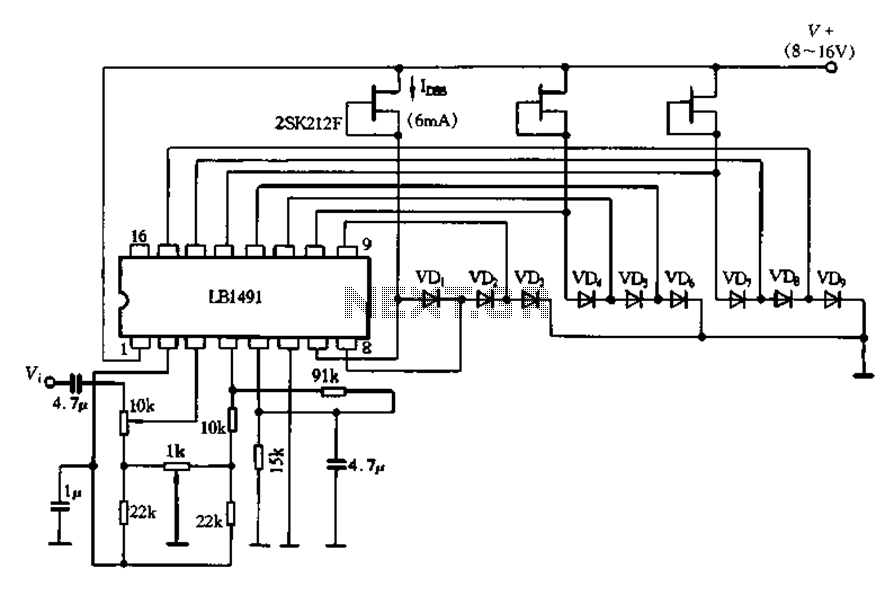
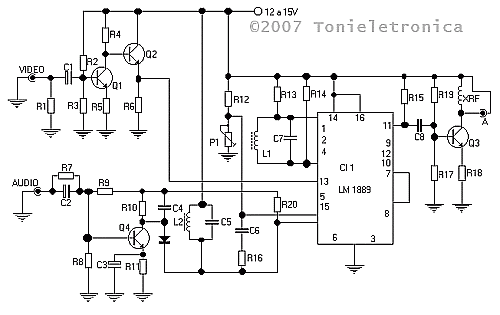
AM Radio Receiver Circuit
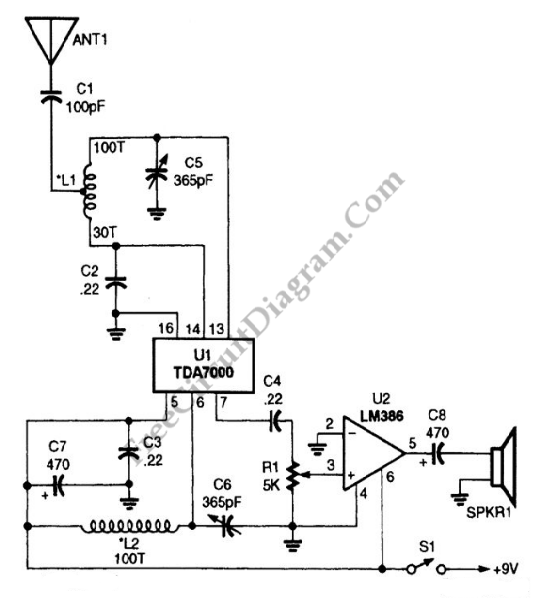
An AM radio receiver circuit utilizing an FM IC chip as the primary component. This AM radio receiver circuit incorporates hand-wound coils to adjust the frequency within the AM bandwidth.
The AM radio receiver circuit is designed to capture amplitude-modulated (AM) signals and convert them into audible sound. The core of this circuit is an FM IC chip, which is typically optimized for frequency modulation but can be adapted to receive AM signals through specific configurations.
The circuit begins with the antenna, which collects the incoming radio waves. The signals are then fed into a front-end amplifier, which enhances the weak signal strength for better processing. Following amplification, the signal enters the FM IC chip, which has been configured to demodulate AM signals. This involves detecting the amplitude variations in the signal, which correspond to the audio information being transmitted.
Hand-wound coils play a crucial role in tuning the circuit to the desired AM frequency. These coils are inductors that, together with capacitors, form a resonant LC circuit. By adjusting the number of turns in the coil and the value of the capacitor, the circuit can be tuned to specific frequencies within the AM bandwidth, typically ranging from 530 kHz to 1700 kHz.
The output from the FM IC chip is an audio signal that is still relatively weak, requiring further amplification. This is achieved through a power amplifier stage, which drives a speaker or an earphone, allowing the audible sound to be heard.
In summary, this AM radio receiver circuit combines an FM IC chip with hand-wound coils to effectively receive and demodulate AM signals, providing a functional and efficient design for AM radio applications.AM radio receiver circuit employing FM IC chip as the main component. This AM radio receiver circuit uses hand-wounded coils to tune the frequency at AM bandwidth 🔗 External reference
The AM radio receiver circuit is designed to capture amplitude-modulated (AM) signals and convert them into audible sound. The core of this circuit is an FM IC chip, which is typically optimized for frequency modulation but can be adapted to receive AM signals through specific configurations.
The circuit begins with the antenna, which collects the incoming radio waves. The signals are then fed into a front-end amplifier, which enhances the weak signal strength for better processing. Following amplification, the signal enters the FM IC chip, which has been configured to demodulate AM signals. This involves detecting the amplitude variations in the signal, which correspond to the audio information being transmitted.
Hand-wound coils play a crucial role in tuning the circuit to the desired AM frequency. These coils are inductors that, together with capacitors, form a resonant LC circuit. By adjusting the number of turns in the coil and the value of the capacitor, the circuit can be tuned to specific frequencies within the AM bandwidth, typically ranging from 530 kHz to 1700 kHz.
The output from the FM IC chip is an audio signal that is still relatively weak, requiring further amplification. This is achieved through a power amplifier stage, which drives a speaker or an earphone, allowing the audible sound to be heard.
In summary, this AM radio receiver circuit combines an FM IC chip with hand-wound coils to effectively receive and demodulate AM signals, providing a functional and efficient design for AM radio applications.AM radio receiver circuit employing FM IC chip as the main component. This AM radio receiver circuit uses hand-wounded coils to tune the frequency at AM bandwidth 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713