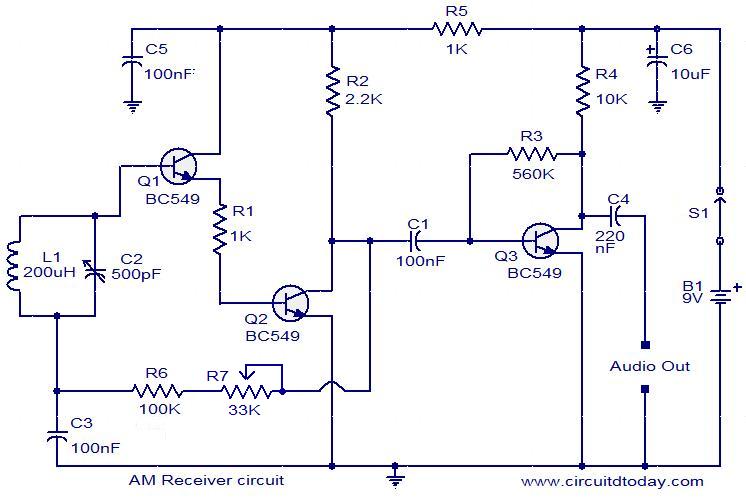
Amplitude Modulator with OTA
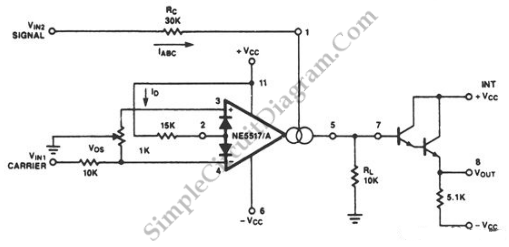
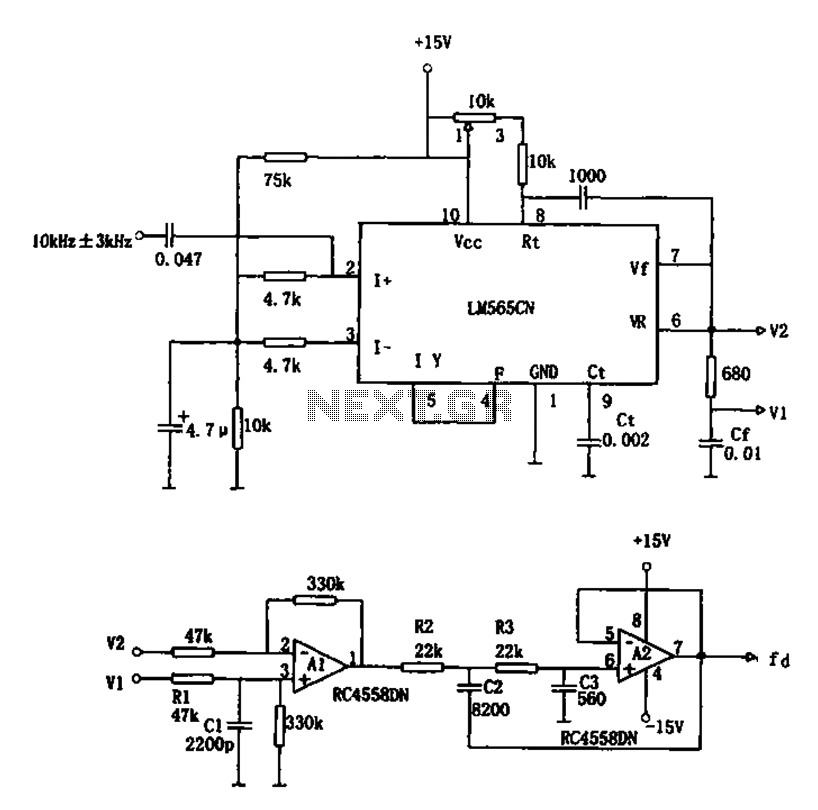
The circuit depicted in the schematic diagram below can achieve 99% modulation with a maximum frequency of 200 kHz. The amplification of this circuit can be...
This circuit is designed for high-efficiency amplitude modulation, capable of achieving a modulation depth of 99%. The operational frequency range extends up to 200 kHz, making it suitable for various applications in communication systems. The circuit typically comprises several key components, including transistors for amplification, resistors for biasing, and capacitors for filtering and coupling signals.
The modulation process begins with an input signal, which is fed into the circuit. The transistors used in the design function as amplifiers, boosting the input signal's amplitude while maintaining the fidelity of the modulation. The circuit configuration may include feedback mechanisms to stabilize the gain and improve linearity, ensuring that the output signal closely follows the input signal's variations.
Furthermore, the circuit may incorporate a low-pass filter to eliminate unwanted high-frequency components that could affect the quality of the modulation. This filter is essential in maintaining the integrity of the modulated signal and preventing distortion in the output.
To achieve the desired modulation depth, careful selection of component values is crucial. Resistors and capacitors must be chosen to match the specific frequency response required for optimal performance. Additionally, the power supply must provide sufficient voltage and current to support the amplification stages without introducing noise or fluctuations in the output.
Overall, this circuit represents a robust solution for achieving high levels of modulation at significant frequencies, making it applicable in various electronic communication devices and systems.Circuit described in the schematic diagram below can achieve 99% modulation easily with maximum frequency of 200kHz. The amplification of this circuit can be.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed for high-efficiency amplitude modulation, capable of achieving a modulation depth of 99%. The operational frequency range extends up to 200 kHz, making it suitable for various applications in communication systems. The circuit typically comprises several key components, including transistors for amplification, resistors for biasing, and capacitors for filtering and coupling signals.
The modulation process begins with an input signal, which is fed into the circuit. The transistors used in the design function as amplifiers, boosting the input signal's amplitude while maintaining the fidelity of the modulation. The circuit configuration may include feedback mechanisms to stabilize the gain and improve linearity, ensuring that the output signal closely follows the input signal's variations.
Furthermore, the circuit may incorporate a low-pass filter to eliminate unwanted high-frequency components that could affect the quality of the modulation. This filter is essential in maintaining the integrity of the modulated signal and preventing distortion in the output.
To achieve the desired modulation depth, careful selection of component values is crucial. Resistors and capacitors must be chosen to match the specific frequency response required for optimal performance. Additionally, the power supply must provide sufficient voltage and current to support the amplification stages without introducing noise or fluctuations in the output.
Overall, this circuit represents a robust solution for achieving high levels of modulation at significant frequencies, making it applicable in various electronic communication devices and systems.Circuit described in the schematic diagram below can achieve 99% modulation easily with maximum frequency of 200kHz. The amplification of this circuit can be.. 🔗 External reference