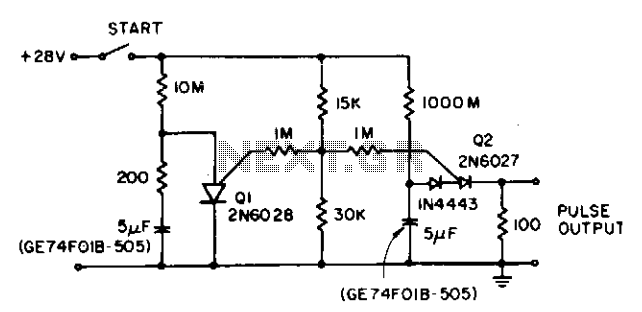
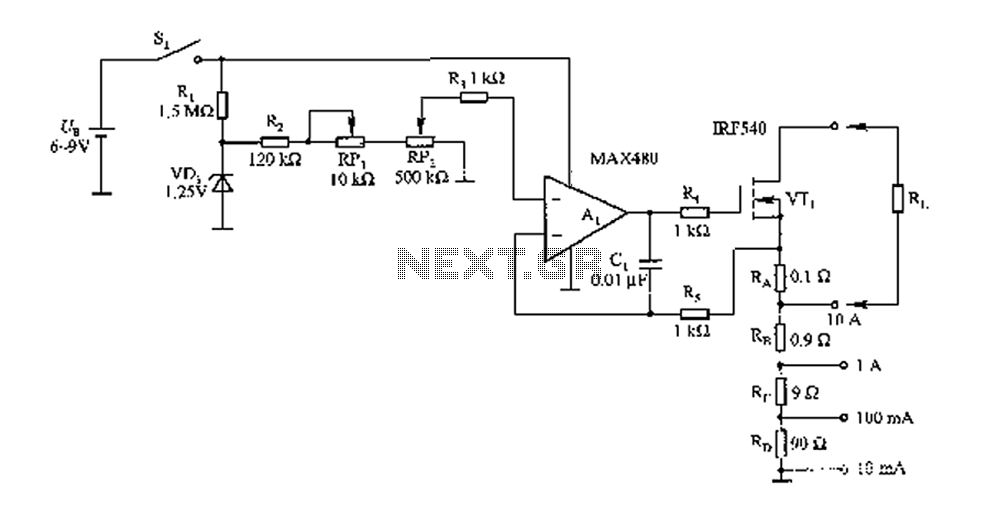
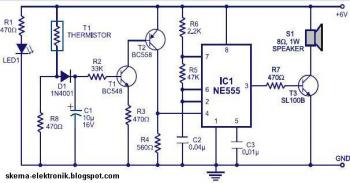
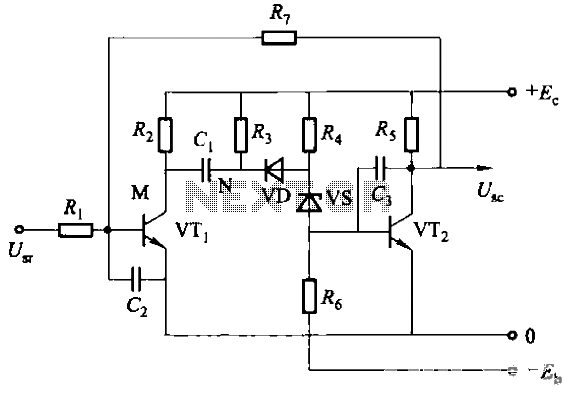
Analog Compensation Circuit for PT100 RTD Temperature Sensor
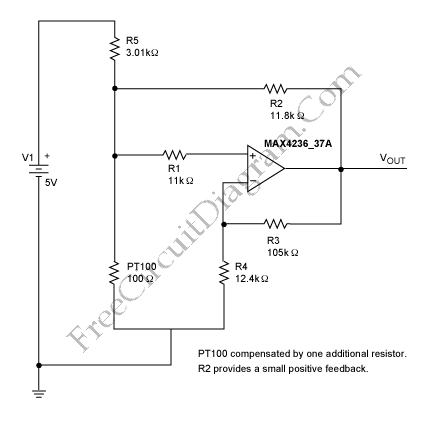
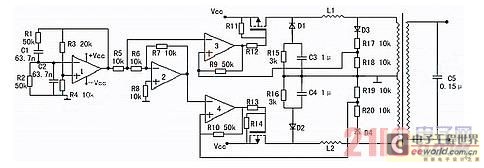
There are digital and analog methods that can be used to compensate for the nonlinearity of a PT100 RTD. Digital linearization can be implemented through various techniques.
Compensation for the nonlinearity of a PT100 RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) is essential for achieving accurate temperature measurements. The PT100 RTD exhibits a nonlinear response to temperature changes, which can lead to measurement errors if not properly addressed.
Digital methods for linearization often involve the use of microcontrollers or digital signal processors (DSPs) that apply algorithms to correct the nonlinear response. These algorithms can include polynomial fitting, lookup tables, or spline interpolation to map the nonlinear characteristics of the PT100 to a linear output. The implementation typically requires an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to sample the RTD output, followed by processing the data using the chosen algorithm, and finally outputting the corrected digital signal.
Analog methods may involve the use of operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in specific arrangements to create a linear output based on the RTD resistance. This can include using resistor networks or feedback loops to shape the response curve. The choice between digital and analog methods depends on the specific application requirements, including factors such as cost, complexity, and desired accuracy.
In summary, both digital and analog techniques are viable for compensating the nonlinearity of PT100 RTDs, with each method offering distinct advantages and considerations for implementation.There are some digital and analog that can be used for compensating a PT100 RTD nonlinearity. We can implemented the digital linearization by implementing the. 🔗 External reference
Compensation for the nonlinearity of a PT100 RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) is essential for achieving accurate temperature measurements. The PT100 RTD exhibits a nonlinear response to temperature changes, which can lead to measurement errors if not properly addressed.
Digital methods for linearization often involve the use of microcontrollers or digital signal processors (DSPs) that apply algorithms to correct the nonlinear response. These algorithms can include polynomial fitting, lookup tables, or spline interpolation to map the nonlinear characteristics of the PT100 to a linear output. The implementation typically requires an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to sample the RTD output, followed by processing the data using the chosen algorithm, and finally outputting the corrected digital signal.
Analog methods may involve the use of operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in specific arrangements to create a linear output based on the RTD resistance. This can include using resistor networks or feedback loops to shape the response curve. The choice between digital and analog methods depends on the specific application requirements, including factors such as cost, complexity, and desired accuracy.
In summary, both digital and analog techniques are viable for compensating the nonlinearity of PT100 RTDs, with each method offering distinct advantages and considerations for implementation.There are some digital and analog that can be used for compensating a PT100 RTD nonlinearity. We can implemented the digital linearization by implementing the. 🔗 External reference