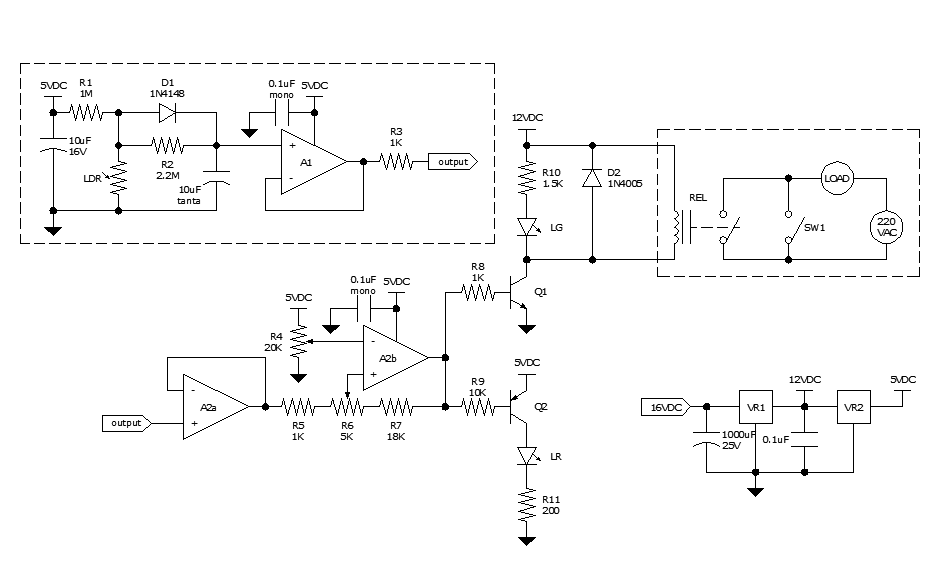
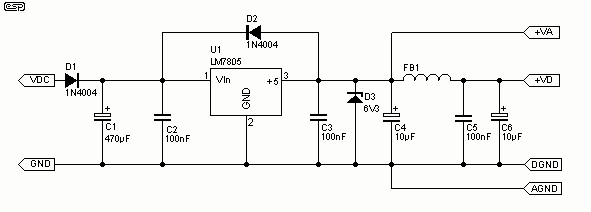
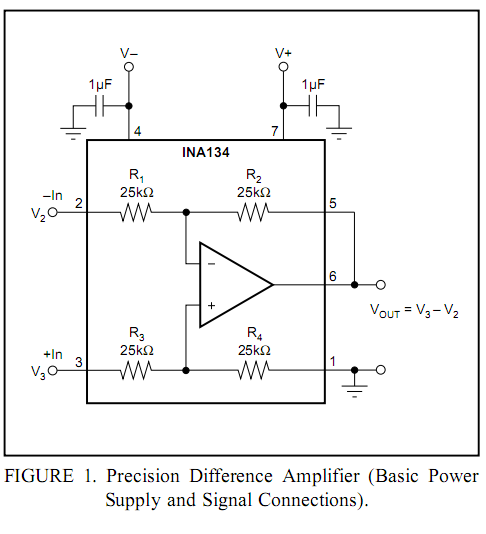
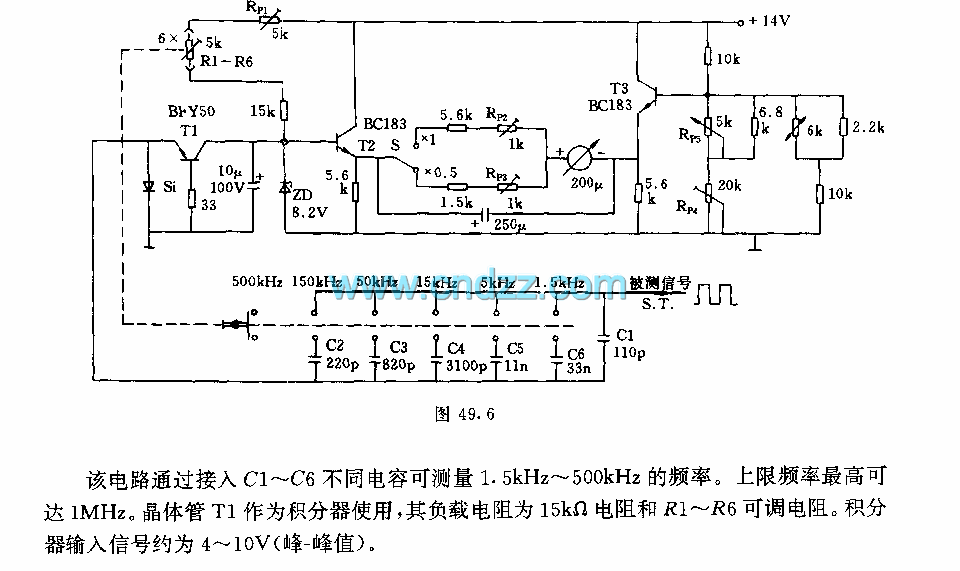
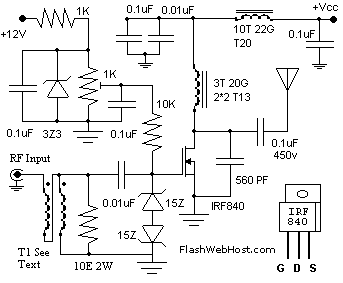
analog delay line (echo and reverb)
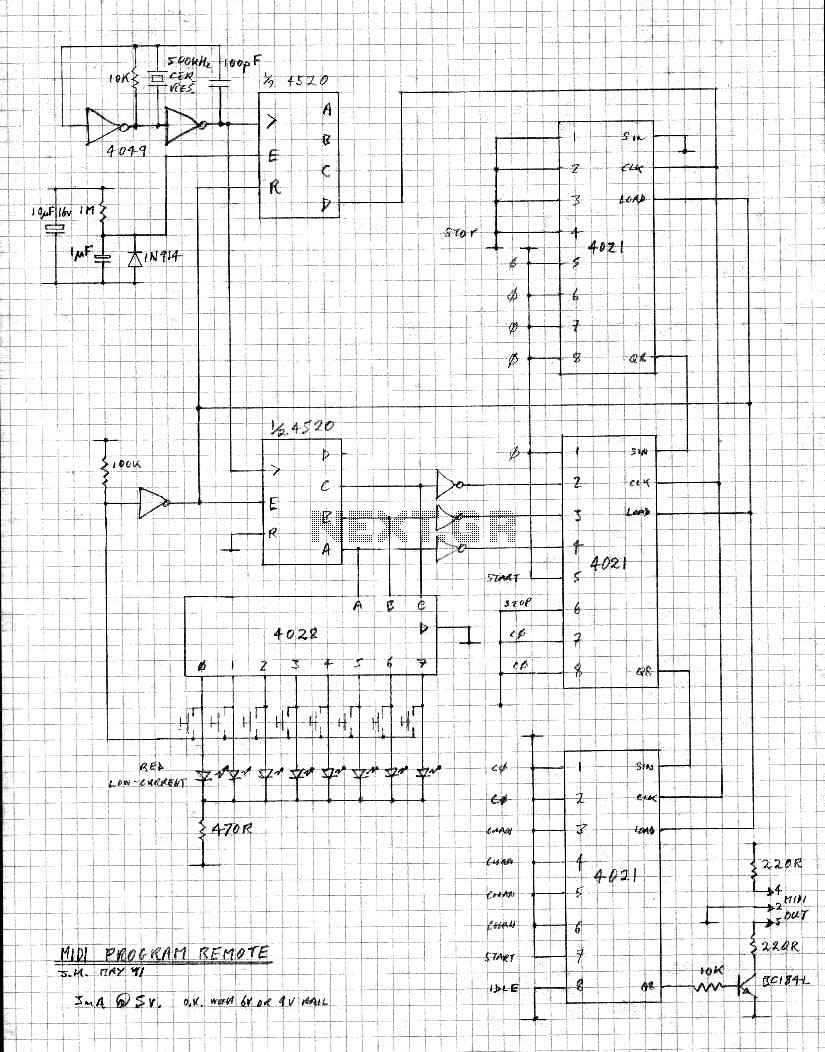
The clock frequency ranges from 5 kHz to 50 kHz, with a delay time adjustable between 51.2 ms and 5.12 ms. The clock frequency must be at least double the highest audio frequency.
The described circuit operates within a clock frequency range of 5 kHz to 50 kHz. This frequency range is critical for ensuring that the circuit can adequately process audio signals, as it must be at least twice the maximum audio frequency to satisfy the Nyquist theorem. Typically, audio signals can reach frequencies up to 20 kHz; therefore, the minimum clock frequency of 40 kHz is necessary to avoid aliasing and ensure accurate signal representation.
The delay time, adjustable from 51.2 ms to 5.12 ms, indicates the circuit's capacity to introduce a time lag in the processing of signals. This feature can be utilized for various audio effects such as echo or reverb, where the delayed signal is mixed with the original to create a fuller sound.
In practical terms, the clock signal can be generated using a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode or by employing a microcontroller with a PWM output that can be fine-tuned to achieve the desired frequency. The delay can be implemented using a digital delay line, which can be constructed using shift registers or dedicated delay line ICs.
The circuit should also include appropriate filtering components to manage the frequency response and minimize noise. Capacitors and resistors may be utilized in conjunction with operational amplifiers to shape the signal and ensure that it remains within the desired frequency range.
Overall, careful consideration must be given to the selection of components to maintain signal integrity and achieve the desired performance within the specified frequency and delay parameters.E clock frequency between 5 and 50 kHz, delay time can be set between 51. 2 and 5. 12 ms. The clock frequency must be at least twice the highest audio frequency. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates within a clock frequency range of 5 kHz to 50 kHz. This frequency range is critical for ensuring that the circuit can adequately process audio signals, as it must be at least twice the maximum audio frequency to satisfy the Nyquist theorem. Typically, audio signals can reach frequencies up to 20 kHz; therefore, the minimum clock frequency of 40 kHz is necessary to avoid aliasing and ensure accurate signal representation.
The delay time, adjustable from 51.2 ms to 5.12 ms, indicates the circuit's capacity to introduce a time lag in the processing of signals. This feature can be utilized for various audio effects such as echo or reverb, where the delayed signal is mixed with the original to create a fuller sound.
In practical terms, the clock signal can be generated using a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode or by employing a microcontroller with a PWM output that can be fine-tuned to achieve the desired frequency. The delay can be implemented using a digital delay line, which can be constructed using shift registers or dedicated delay line ICs.
The circuit should also include appropriate filtering components to manage the frequency response and minimize noise. Capacitors and resistors may be utilized in conjunction with operational amplifiers to shape the signal and ensure that it remains within the desired frequency range.
Overall, careful consideration must be given to the selection of components to maintain signal integrity and achieve the desired performance within the specified frequency and delay parameters.E clock frequency between 5 and 50 kHz, delay time can be set between 51. 2 and 5. 12 ms. The clock frequency must be at least twice the highest audio frequency. 🔗 External reference