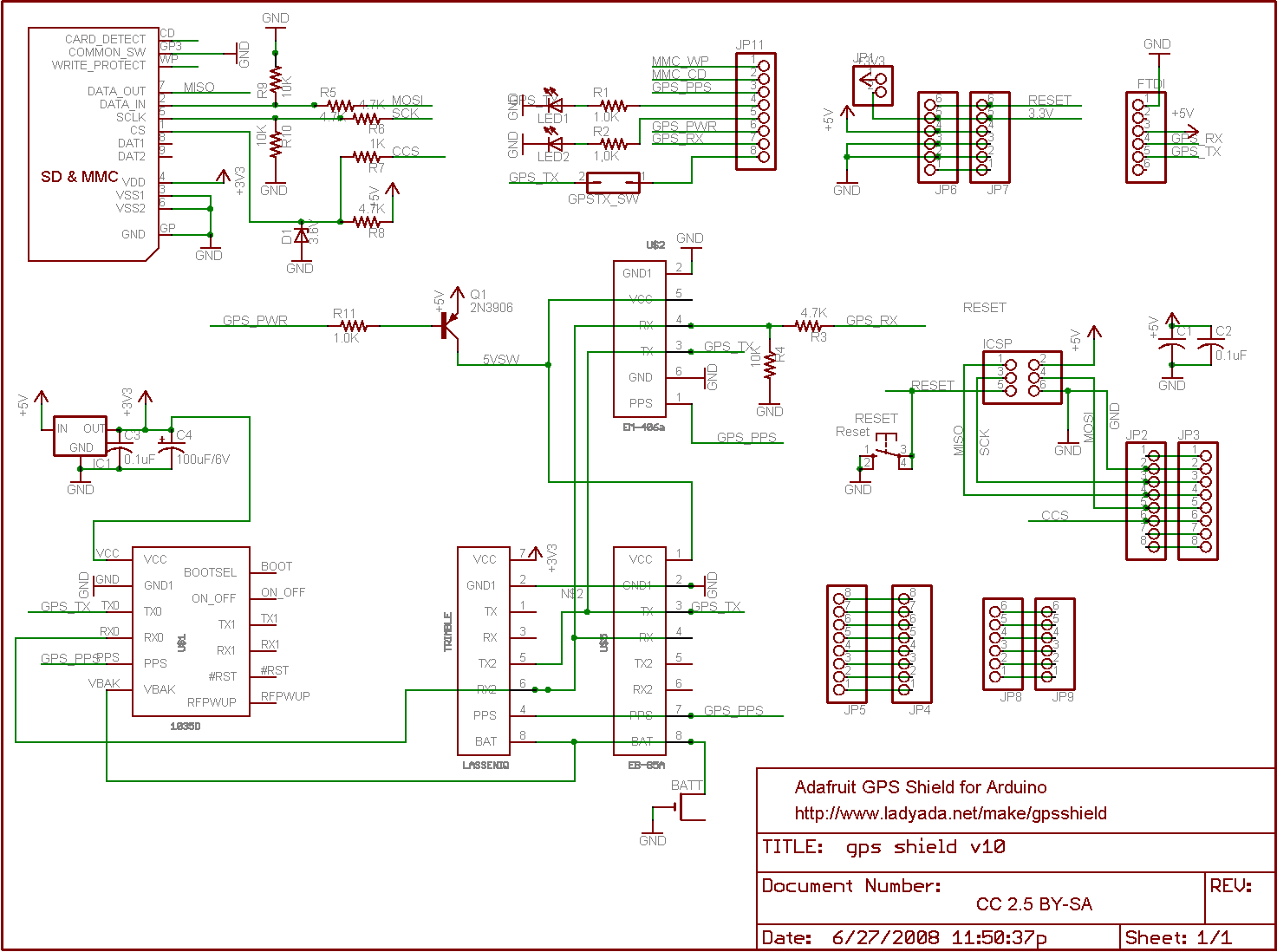
arduino buzzer
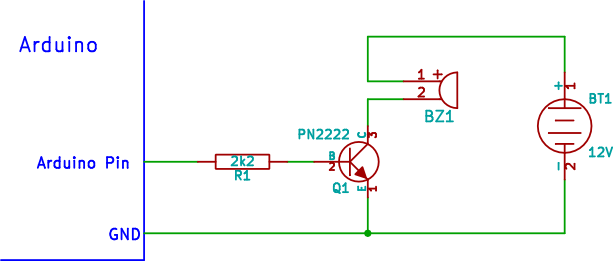
Connecting a buzzer to an Arduino when the buzzer operates at a different voltage than the Arduino involves using an NPN transistor to interface between the two.
To implement this circuit, the following components are required: an Arduino board, a buzzer rated for a specific voltage (e.g., 5V or 12V), an NPN transistor (such as the 2N3904 or BC547), a resistor (typically 1kΩ for the base of the transistor), and a power supply suitable for the buzzer's operating voltage.
The connection process begins by identifying the pin configuration of the NPN transistor. The emitter of the transistor should be connected to the ground (GND) of both the Arduino and the buzzer's power supply. The collector of the transistor is connected to one terminal of the buzzer, while the other terminal of the buzzer connects to the positive terminal of the power supply.
Next, a resistor is connected to the base of the NPN transistor. The other end of this resistor is connected to one of the digital output pins on the Arduino. This configuration allows the Arduino to control the transistor, which in turn switches the buzzer on and off. When the Arduino outputs a high signal (5V), current flows through the resistor into the base of the transistor, turning it on and allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter, thus activating the buzzer.
It is crucial to ensure that the voltage ratings of the components are compatible. The Arduino typically operates at 5V, while the buzzer may require a different voltage. The NPN transistor acts as a switch, isolating the Arduino from the higher voltage of the buzzer circuit, thereby protecting the Arduino from potential damage.
In summary, this circuit design effectively allows the control of a buzzer operating at a different voltage using an Arduino, utilizing an NPN transistor to facilitate safe and efficient operation.How to connect a buzzer to an Arduino when the buzzer operates at a different voltage to the Arduino. The circuit uses a NPN transistor for connecting the buzzer.. 🔗 External reference
To implement this circuit, the following components are required: an Arduino board, a buzzer rated for a specific voltage (e.g., 5V or 12V), an NPN transistor (such as the 2N3904 or BC547), a resistor (typically 1kΩ for the base of the transistor), and a power supply suitable for the buzzer's operating voltage.
The connection process begins by identifying the pin configuration of the NPN transistor. The emitter of the transistor should be connected to the ground (GND) of both the Arduino and the buzzer's power supply. The collector of the transistor is connected to one terminal of the buzzer, while the other terminal of the buzzer connects to the positive terminal of the power supply.
Next, a resistor is connected to the base of the NPN transistor. The other end of this resistor is connected to one of the digital output pins on the Arduino. This configuration allows the Arduino to control the transistor, which in turn switches the buzzer on and off. When the Arduino outputs a high signal (5V), current flows through the resistor into the base of the transistor, turning it on and allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter, thus activating the buzzer.
It is crucial to ensure that the voltage ratings of the components are compatible. The Arduino typically operates at 5V, while the buzzer may require a different voltage. The NPN transistor acts as a switch, isolating the Arduino from the higher voltage of the buzzer circuit, thereby protecting the Arduino from potential damage.
In summary, this circuit design effectively allows the control of a buzzer operating at a different voltage using an Arduino, utilizing an NPN transistor to facilitate safe and efficient operation.How to connect a buzzer to an Arduino when the buzzer operates at a different voltage to the Arduino. The circuit uses a NPN transistor for connecting the buzzer.. 🔗 External reference